Innovations That Will Transform Road Construction (2026)

Table of Contents
Critical Issues Faced by the Road Construction Industry
Before diving into innovations that have the potential to transform the road construction industry, let's look at some of the challenges that the industry faces. These include:-
Design-related problems: These include a lack of detailed specifications by the architects, poor design reflection and continuous changes in the design by the client.
-
Cost overruns: Too many undocumented design changes can incur a cost overrun beyond the allocated budget. It also makes the process tedious to trace back and locate the exact points that triggered these additional costs.
-
Environmental impacts: Some negative environmental impacts of road construction include waste disposal dumping, nuisance noise, dust pollution, soil erosion, natural vegetation removal, disturbance to wildlife, and population displacement.
-
Project delays: Construction delay is considered to be one of the most recurring problems in the road construction industry and it damages project success in terms of time, cost, quality, and safety.
-
Maintenance and repairs: Road repair is a costly job. For example, in fiscal 2026, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, India, allocated Rs 3,150 crore for the maintenance of roads and highways, which is 17% higher than the revised estimates for fiscal 2019.
The innovations in the sector can be divided into three phases of the project lifecycle, namely, road construction materials and machines, design and implementation, and highway operations and management. In the road construction materials and machines sector, the use of innovative materials, automation, and machine control technologies has been encouraged to improve efficiency and lower the environmental impact. In the design and implementation phases, the technological advancements have increased the construction speed and lowered the project lifecycle cost. Furthermore, technology-based initiatives are increasingly being adopted in the highway operations and management phase to improve the operation and management of highways.
Promising Innovations in Road Construction Industry
1. Self-healing concrete

-
Minimal repair costs: This is because the self-healing asphalt only requires minimal repairs and replacement.
-
Fewer cracks: The asphalt reinforces the road surfaces causing fewer cracks to appear.
-
Faster repairs: This speeds up the operation and maintenance phase.
2. Recycled Plastic Roads

Recycled plastic roads were developed by Rajagopalan Vasudevan, a professor of chemistry at the Thiagarajar College of Engineering in India. The material replaces 10% of a road's bitumen with repurposed plastic waste. Many different types of plastics can be added to the mix, including carrier bags, disposable cups, hard-to-recycle multi-layer films, and polyethylene and polypropylene foams. So far, 2,500 km (1,560 miles) of plastic-tar roads have been laid in India. Chennai was among the first cities globally to adopt this technology when the municipality commissioned 1000 km of plastic roads in 2004. The advantages of using recycled plastic roads include:
-
Lower carbon emissions: By 2040, there are set to be 1.3 billion tonnes of plastic in the environment globally. Recycling this plastic can help lower carbon emissions.
-
Enhanced Maintenance: Adding plastic to roads appears to slow their deterioration and minimise potholes.
-
Economic benefits: The incorporation of plastic results in savings of roughly $670 (£480) per kilometre of road.
-
Durability: Plastic roads can withstand both heavy loads and traffic.
3. Prefabricated Plastic Roads.webp?width=900&height=506&name=Prefabricated%20Plastic%20Roads%20(1).webp)
This innovation addresses the problem of environmental impacts caused by road construction. With a rapidly growing supply of plastic waste, reuse options that turn waste into resources are the need of the hour. These are prefabricated, modular, and hollow road structures built from recycled plastics. In Zwolle and Giethoorn, Netherlands, there are two bicycle paths made purely from waste plastics. This is the result of an invention by Simon Jorritsma and Anne Koudstaal, who launched their first product in 2018. The advantages of using Prefabricated Plastic Roads include:-
Faster project completion: PlasticRoads lead to the reduction of the project completion time from months to a few days. This is due to the lightweight and modular design of the roads.
-
Water Storage: The hollow space in PlasticRoads can be used to temporarily store water. This helps prevent flooding during extreme precipitation.
-
Storage: The hollow space can also be used for the transit of cables, pipes, sensors, or the electric charging of vehicles.
-
Smaller carbon footprint: The PlasticRoad is a completely circular product and, thus, has a significantly smaller carbon footprint than traditional road designs.
4. Solar Roads

-
Production of renewable energy: Solar roadways are employed to generate electricity, thus contributing to sustainable development.
-
Greater life span: The lifespan of solar roads is around 20 years which is much greater than that of Asphalt roads which is 7-12 years.
-
Enhanced safety: Solar roads come with the possibility to affix solar lamps, charged by these solar panels.
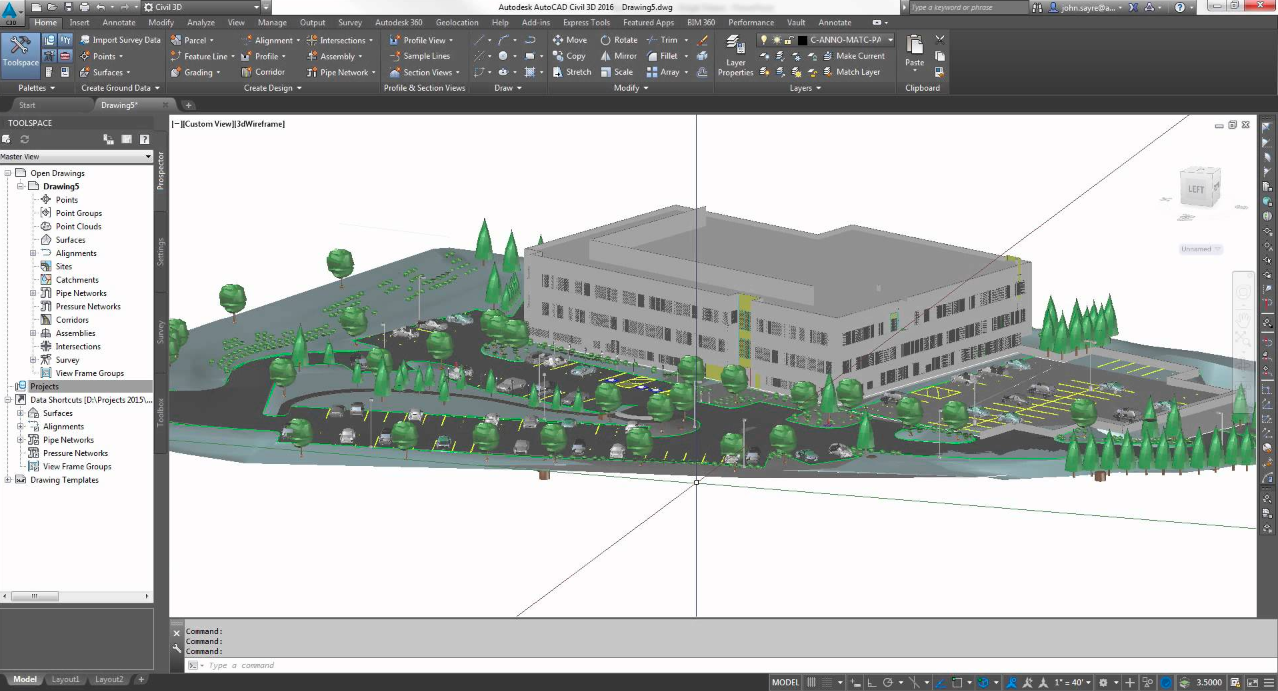
5. Building Information Modelling
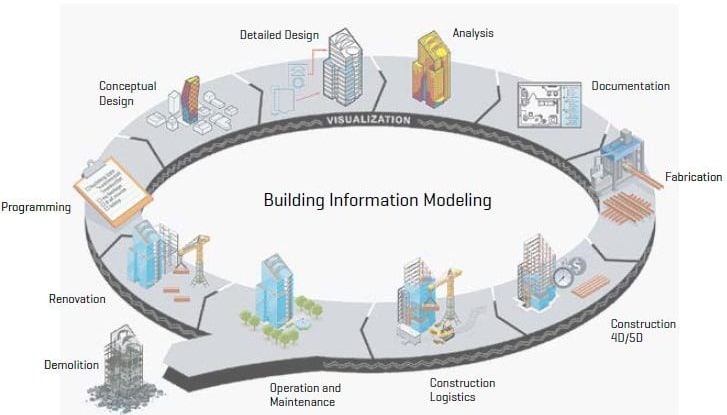
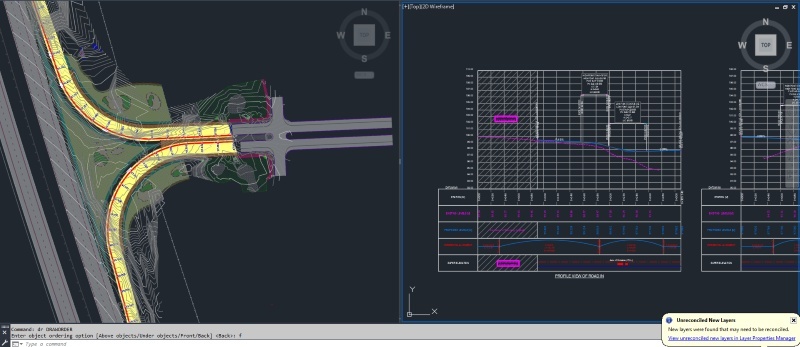
The construction and maintenance of road infrastructure are one of the most important sectors for a company's national economy and also one of the least digitized ones. This leads to an insufficient level of cooperation and inadequate information management. BIM technology helps aid the digitalization of the construction process. It allows all stakeholders involved in a project to collaborate on a single 3D model. Norconsult, Norway's leading multidisciplinary consulting firm, completed the construction on a 15-mile stretch of the 680-mile Coastal Highway project using BIM technology. The result included reduced environmental impact. The advantages of using the BIM design process include:
-
Enhanced Collaboration: BIM helps teams collaborate on a single 3D model. This helps with design-related problems such as poor design reflection in the project.
-
Reduced Errors: BIM allows construction teams to resolve constructability issues early in the design process to prevent conflicts on-site. Navisworks is a powerful software that can help teams achieve this.
-
Time and cost benefits: 4D and 5D BIM services help with proper time and cost management.
-
Renovation: New design processes like “Scan to BIM” are advantageous when it comes to renovating or reconstructing existing infrastructure.
A recent report from Dodge Data & Analytics found that BIM is rapidly becoming a standard practice throughout the industry. While architecture firms are the fastest to adopt BIM practices, civil engineering and road construction firms are also embracing BIM at record levels.
Interested in getting started with BIM?
Interested in getting started with BIM?
Build a future-ready career in construction with Novatr’s BIM Professional Course for Civil Engineers, a hands-on, industry-aligned program designed to help you master Building Information Modeling (BIM) from design to execution. Learn how top global firms use BIM to plan, coordinate, and deliver smarter, more efficient projects, while gaining the technical confidence to work on large-scale infrastructure and building developments.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
- 5+ industry softwares, including Autodesk Revit, Navisworks, Autodesk Construction Cloud: Docs, Coordination & Collaboration.
- Master essential plugins such as EF-Tools, DiRoots.One, pyRevit, ProSheets, Issue and Model Checker for Revit to automate documentation and improve precision.
- Learn complete BIM workflows, from digital design development, estimation & BOQ, and information modeling to clash detection, sequencing, and multidisciplinary coordination.
- Get hands-on experience working on real commercial and residential projects following ISO 19650 standards, guided by mentors from the global AEC industry.
- Develop professional construction documentation, audits, and deliverables aligned with international BIM practices.
Earn globally recognized certifications:
- Novatr Course Certificate, signed by the Academic Director.
- Autodesk User Certification, validating your command over Autodesk tools.
- NSDC Certificate, officially recognizing your BIM expertise.
- Optional Specialization Certificates, for learners who wish to deepen their skills in niche BIM applications.
Go Further with Optional Post-Program Specializations
After completing the core BIM program, learners can choose to add any two specializations to refine their expertise in advanced BIM workflows and tools. These add-on modules let you tailor your learning path based on your career goals and project interests.
Available specializations include:
- Visual Programming with Dynamo – Automate repetitive modeling tasks and customize Revit workflows through parametric scripting.
- 4D, 5D & 6D with BIM – Integrate time, cost, and sustainability data into your BIM models for end-to-end project management.
- Design Development with Autodesk Forma – Explore conceptual design and site analysis with cloud-based environmental data.
- Project Strategy & Optimization with Plannerly – Plan, structure, and audit BIM execution plans with real-world project strategies.
- BIM for Infrastructure with Civil 3D – Model, simulate, and analyze roads, bridges, and other civil infrastructure projects.
- Prefabrication & RCC Modeling with Tekla – Design and coordinate reinforced concrete and steel structures for constructability.
- Visualising Landscape with Enscape – Create immersive real-time visualizations for landscape and site design presentations.
- Interior Detailing & Visual Storytelling with Twinmotion – Transform architectural and interior BIM models into photorealistic, story-driven visuals.
These optional specializations provide an in-depth understanding of how different software and workflows enhance project performance, sustainability, and design visualization, making you a more versatile BIM professional.
6. Digital Twin Technology
Digital Twin Technology creates a virtual replica of a road or highway system using IoT sensors, BIM data, and real-time analytics. This mirror model helps engineers monitor how a road performs under different weather conditions, vehicle loads, and environmental pressures. It enables authorities to predict failures before they happen, reducing both maintenance delays and long-term repair costs.
Advantages of Digital Twin Technology:
- Predictive maintenance reduces costly emergency repairs
- Real-time monitoring improves road safety and asset planning
- Digital simulations accelerate approvals and regulatory reviews
- Lower lifecycle expenditure due to proactive interventions
7. 3D Printing in Road Construction
3D printing is transforming road infrastructure by manufacturing road components directly on-site. From drainage modules and barriers to repair slabs, the technology uses specialized mixtures and recycled aggregates to produce durable road elements. This reduces transportation needs, accelerates construction timelines, and enables customized geometries for complex terrains.
Advantages of 3D Printing:
- Faster production and deployment of road elements
- Reduced material waste and lower carbon footprint
- Eliminates logistical dependencies on off-site fabrication
- Enables repair modules that are easy to install and replace
8. Smart Roads and Embedded Sensor Networks
Smart roads incorporate sensors, fiber optics, and communication chips beneath the pavement. These embedded systems track temperature, stress levels, traffic density, and vehicle behavior. When integrated with BIM and cloud computing, this data helps governments detect structural issues early, manage congestion, and enhance infrastructure safety, creating roads that communicate, adapt, and evolve with usage patterns.
Advantages of Smart Roads:
- Real-time alerts reduce accidents and response time
- Advanced data analytics improves traffic flow
- Life-cycle-based maintenance extends pavement lifespan
- Supports the future of autonomous and electric vehicles
9. Geopolymer and Bio-Based Road Materials
Geopolymer and bio-based materials are emerging as sustainable alternatives to bitumen and concrete. Developed from industrial by-products like slag or fly ash, and organic binders from agricultural waste, these materials offer greater resistance to heat and chemical wear. Their environmental benefits and durability make them ideal for Asia’s expanding roadway networks.
Advantages of Geopolymer and Bio-Based Materials:
- Up to 80% reduction in carbon emissions
- Higher resilience in humid and high-temperature regions
- Supports circular economy through waste reuse
- Increased lifespan reduces maintenance demands
Conclusion
The future of road construction in 2026 will be shaped by sustainability, digital engineering, and intelligent infrastructure systems. Innovations such as self-healing concrete, BIM-powered workflows, smart road surfaces, and geopolymer materials are helping governments and engineers deliver roads that are safer, more durable, and far more efficient to maintain. As technology continues to evolve, professionals who adopt digital tools like BIM will be at the forefront of infrastructure transformation.
To understand how BIM shapes modern infrastructure roles, explore Novatr’s BIM Professional Course for Civil Engineers and build the skills needed for tomorrow’s road construction industry.
Visit our resource page to learn more about AEC careers, tools, and trends.
FAQs
1. What is the future of road construction?
With promising innovations, road construction is going to be smarter. With the increasing inclination towards a sustainable approach, the usage of recycled materials and biomaterials will increase with green roads and modular roadways coming into the picture. With technology driving this progress, 3D modeling, AI and sensors are going to be a major part of it.
2. What are some examples of road innovation in India?
The concept of plastic roads, developed by Rajagopalan Vasudevan is one of the shiniest examples of road innovation made in India. Solar and electrical roads are another addition to the list.
3. How BIM is driving innovation in road construction across India?
With BIM leading the construction of main highways in India, it is driving the innovation in road construction in India. The application of BIM in road construction projects is increasing as it facilitates clash detection, 3D visualisation, and more.
4. What is the latest technology used in road construction?
From BIM to 3D printing, automation to solar roads, are some of the technologies that are revolutionising road construction. With the approach to making more smart roads, AI, robotics and cloud computing is also being embedded in road construction.

 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!



.png)
.png)



.jpg)