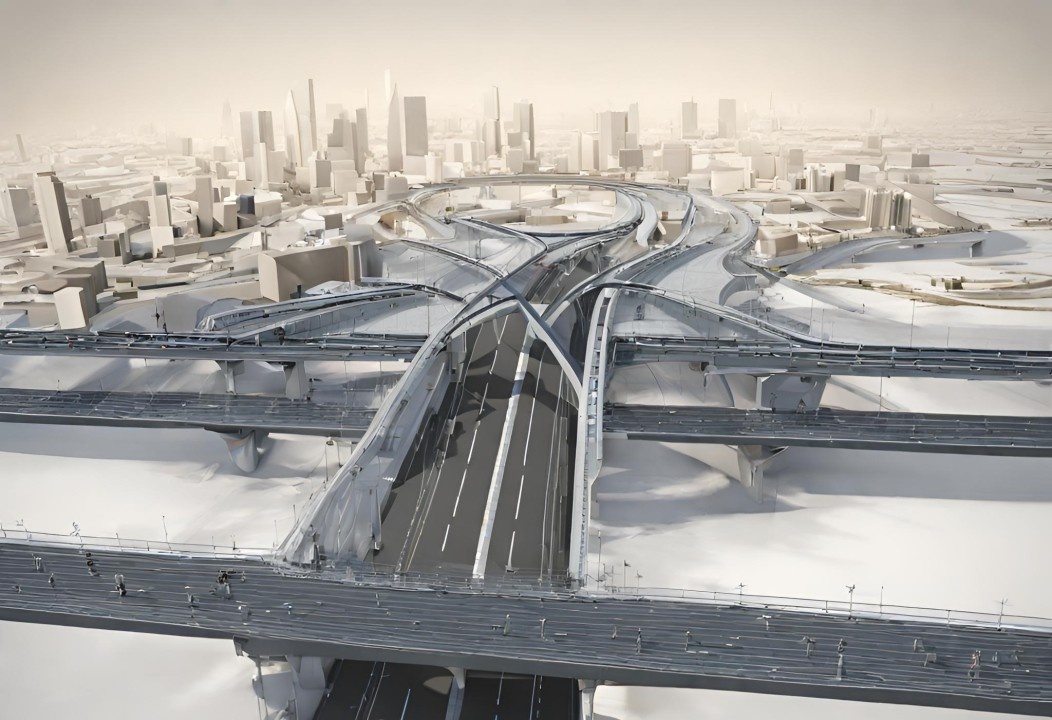
Transit infrastructure is among the most sought-after essential infrastructure in a rapidly urbanizing world. It aids cities in achieving better connectivity, reducing travel time, and establishing convenient journeys for its people. An extensive network of roads and bridges ensures effective mobility, enhanced tourism opportunities, and neighbourhood developments thereby enabling urban areas to expand with economic benefits.
Challenges in Developing Road and Bridge Infrastructure
Roads and bridges are mega-infrastructure projects. They involve a significant investment of time, money, labor, technology, and other resources. Therefore, it is important for countries to evaluate the feasibility and long-term success of every infrastructure project before venturing into it. Below are the key challenges countries face while developing road and bridge infrastructure.
1. Geotechnical Complexities
Understanding the soil and other geological conditions of a site is crucial for constructing roads and bridges. Variations in soil composition and groundwater content can significantly impact the structural integrity of any infrastructure project. Therefore it is vital for professionals to conduct appropriate geotechnical investigations to implement appropriate design and build solutions. A good geological study can help in developing soil stabilisation techniques and foundation work to mitigate risks.
2. Environmental Impact
Road and bridge construction are large-scale infrastructure projects and have an equally large impact, especially on the environment. Given their massive scale, building roads and bridges need extensive land clearance thereby reducing green cover and increasing carbon footprint. Additionally, roads increase the amount of impervious surfaces, increasing the probability of flooding and impacting the groundwater table. So, designers must conduct Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs), optimise energy efficiency, and integrate landscaping into the project.
3. Traffic Management and Safety
During the construction phase, managing traffic flow and ensuring the safety of both workers and road users can be a significant challenge. Construction zones often disrupt the regular flow of traffic, causing congestion and increasing the risk of accidents. Implementing effective traffic management plans, including proper signage, lane diversions, and speed restrictions, is essential. Ensuring the safety of workers through adequate training and enforcing strict safety protocols is paramount to minimise risks and maintain a smooth construction process.
Read more: What's New in Architecture - Automation, Coding, and BIM!
4. Budget Constraints and Cost Overruns
With multiple stakeholders involved in an infrastructure project, adhering to a budget is one of the significant challenges faced by engineers and contractors. Since road and bridge construction span over longer periods of time, unforeseen issues such as inflation, labor shortage, and site conditions are not accounted for. Poor initial cost estimation, inadequate risk assessment, and changes in project scope can further contribute to budgetary challenges. So, the project team must rely on effective project management software, comprehensive feasibility studies, and rigorous cost control measures.
5. Ongoing Maintenance and Upkeep
The maintenance and repair of roads and bridges post-construction are crucial to preserving their functionality and safety. Neglected maintenance can result in deteriorating infrastructure, increased accidents, and higher repair costs in the long run. Limited budgets, inadequate maintenance planning, and a lack of timely repairs can lead to a backlog of maintenance work. Prioritising regular maintenance, implementing effective asset management strategies, and allocating sufficient funds for upkeep are key challenges faced by infrastructure authorities.
6. Technological Advancements and Adaptation
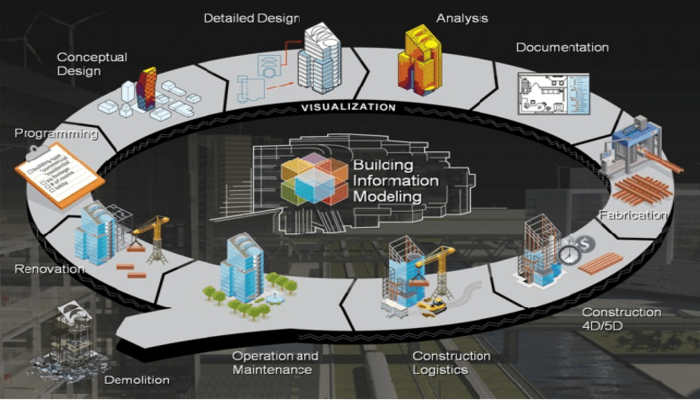
The construction industry has witnessed technological advancements that have the potential to improve the efficiency and quality of road and bridge infrastructure projects. However, adopting and integrating new technologies can be challenging due to factors like resistance to change, lack of expertise, or insufficient investment. Embracing digital tools, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), computational design tools and processes, advanced surveying techniques, digital fabrication, robotics, and construction automation, requires upskilling the workforce and creating an environment conducive to innovation.
Benefits Of BIM In Road and Bridge Infrastructure
BIM uses for construction offer immense potential to reinvent traditional construction processes. Recognizing this opportunity, countries such as the United Kingdom (UK), the United States of America (USA), Norway, Singapore, and Finland are leading the way forward for BIM adoption in infrastructure projects. Following their trail, many countries have now started to embrace BIM in large-scale infrastructure and public projects.
Let’s have a look at BIM applications and how it is helping the seamless design, construction, and management of roads and bridges.
1. Design and Planning
-
Enhanced Visualization and Collaboration
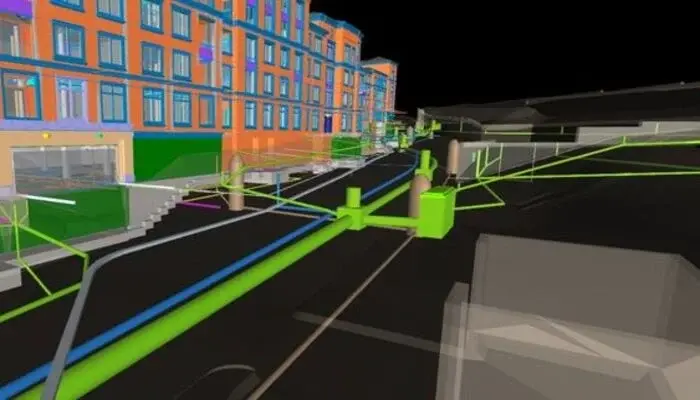
BIM software application for construction such as Tekla 3d provides a visual model of road and bridge designs, allowing the design team to better understand and experiment with ideas. Through software generated 3D models, designers can visualize and analyze various design alternatives, identifying potential clashes or conflicts early in the process. BIM also facilitates co-ordination among multidisciplinary teams, enabling real-time collaboration thereby improving communication throughout the design phase.
-
Improved Clash Detection and Conflict Resolution
By creating a virtual model that incorporates all design disciplines, BIM enables potential clash detection that aids in reducing and resolving conflict. For instance, design clashes such as utilities interfering with bridge foundations or road alignments conflicting with existing structures can be identified and resolved before the construction begins. This reduces expensive reworks, saves time, and ensures an accurate execution of design.
-
Simulated Analysis and Performance Evaluation
Using BIM for road and highway design enables designers to conduct advanced simulations and analysis, thereby enabling them to assess the performance of road and bridge designs. Factors such as traffic flow, bottlenecks, structural integrity, and environmental impacts can be evaluated through simulations, aiding design optimization and informed decision-making. This leads to more efficient designs that meet functional requirements and improve long-term performance.
-
Sustainable Infrastructure Development
BIM technology supports the integration of sustainable design practices into building construction and infrastructure development activities. By using BIM for construction, designers can analyze and optimize energy consumption, select and evaluate the impact of materials, and incorporate sustainable design features such as green infrastructure, renewable energy systems, or low-impact development techniques.
-
Geotechnical Studies and Analysis
Using BIM for road and highway design facilitates the integration of geotechnical studies into the design process. With the help of the BIM model, designers can assess soil properties, stability considerations, and potential risks. This enables more accurate and efficient design solutions that account for geotechnical factors, ensuring the stability and safety of road and bridge infrastructure in the long run.
2. Construction and Execution
-
Accurate BOQs and Cost Estimation
Using BIM for construction enables automated quantity takeoff and cost estimation based on the data provided by the 3D model. By linking design and structural elements with associated material quantities and costs, BIM streamlines the estimation process. This reduces scope for errors and provides more accurate cost projections. It facilitates better budget control for the project manager and helps contractors make informed decisions during the procurement and construction phases.
-
Enhanced Construction Planning and Sequencing
BIM supports construction planning and sequencing by simulating the construction process virtually. By using BIM, contractors can develop detailed construction schedules, identify potential logistical issues, and optimize resource allocation. Additionally, visualizing the construction sequence helps identify and address potential conflicts, optimize schedules, improve construction efficiency and minimize delays.
-
Improved Collaboration and Coordination
BIM serves as a centralized platform for collaboration among project stakeholders during construction. Project managers, contractors, subcontractors, and suppliers can access the BIM model to coordinate activities, resolve conflicts, and share real-time information. Such a collaborative environment promotes efficient communication, reducing errors, rework, and delays on-site.
Read More:Innovations That Will Transform Road Construction
3. Management and Maintenance
-
Asset Information and Data Management
BIM serves as a comprehensive repository of asset information throughout the lifecycle of road and bridge infrastructure. By integrating asset data into the BIM model, facility managers can access vital information such as maintenance schedules, component specifications, and historical data. This streamlines asset management, facilitates efficient maintenance planning, and enables better decision-making regarding repairs, replacements, upgrades and future expansion.
-
Predictive Maintenance and Lifecycle Analysis
BIM supports predictive maintenance strategies for road and bridge infrastructure. By linking the BIM model with asset management systems, maintenance teams can monitor the condition of various building components and predict maintenance requirements. Such a proactive approach helps identify potential issues before they escalate, improves asset longevity, and reduces maintenance costs over a road's or bridge’s lifecycle.
-
Streamlined Facility Operations and Sustainability
Using BIM for construction management streamlines facility operations by providing access to critical information about the infrastructure. Facility managers can visualize the asset in the BIM model, locate components, and retrieve important documentation. This facilitates efficient maintenance activities, enhances safety planning, and promotes sustainability by allowing managers to monitor energy consumption, track performance, and implement energy-saving measures.
4 Exemplary BIM- Integrated Road and Bridge Infrastructure Projects
BIM is now being widely adopted across the globe for public infrastructure projects due to its ability to enhance project outcomes. Let’s have a look at four most promising BIM- integrated road and bridge infrastructure projects.
1. Bharatmala Pariyojana, India
The Bharatmala Pariyojana Project led by the Government of India’s Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) aims to enhance connectivity, promote economic growth, and improve infrastructure across India. This extensive project, spanning approximately 83,677 kilometers, began in October 2017 and is expected to be complete by 2026.
The use of BIM for construction of highways has played a crucial role in streamlining the design and construction of the Bharatmala Pariyojana project. It facilitated 3D visualization, clash detection, and design optimization, enabling stakeholders to collaborate effectively and make informed decisions. BIM also aided in accurate quantity estimation and cost optimization of the project thereby avoiding cost overruns.
2. Queensferry Crossing, United Kingdom
The Queensferry Crossing in Scotland, United Kingdom is a road bridge infrastructure project connecting Edinburgh and Fife. The construction of this cable - stayed bridge began in 2011 and was completed in 2017. Constructed by Forth Crossing Bridge Constructors (FCBC), this road bridge has a length of 2.7 kilometres.
BIM was used for structural reinforcement and project execution purposes. Its integration allowed for seamless collaboration among different project teams, including architects, engineers, and contractors. By visualizing the 3D digital model, stakeholders could identify and resolve clashes, optimize design elements, and enhance construction sequencing.
3. North-South Corridor Project, Singapore
The construction of North-South Corridor Project (NSC) in Singapore originally conceptualized as the North-South Expressway commenced in 2018 and is expected to be completed by 2027. Developed by the Singapore Land Transport Authority, this 21.5 kilometre expressway aims to improve connectivity and ease traffic congestion along Singapore's north-south corridor.
The use of BIM for construction played a vital role in optimizing construction processes in the NSC project. It enables effective clash detection, design visualization, and accurate quantity estimation. BIM enhances collaboration among project teams, streamlining the identification of clashes and constructability issues.
4. New Champlain Bridge, Canada
The New Champlain Bridge in Canada is a significant infrastructure project that spans the St. Lawrence River, connecting Montreal with its south shore. Spanning 3.4 kilometres, this bridge is designed by the Danish architect Poul Ove Jensen. Built to replace the original Champlain Bridge, the construction of the new cable-stayed bridge began in 2015 and was completed in 2019.
BIM played a vital role in this project, facilitating effective communication, project sequencing, and improving project coordination. By integrating BIM, stakeholders could visualize the bridge's complex design, optimize construction processes, and mitigate risks.
In Conclusion
Road and bridge construction projects help in designing cities with an improved quality of life. Using BIM for construction and infrastructure development projects can help in speedy, accurate, and effective construction. Using BIM can help these structures be future-relevant and adjust to the changing needs of people thereby enabling the creation of a healthier ecosystem.
If you too wish to build future-relevant roads and bridges, learning BIM would be a good start. You can check out the BIM Professional Course for civil engineers offered by Novatr. By enrolling for the course, you can master 12+ BIM software, plugins and industry workflows, learn from industry stalwarts, and work on a capstone project to hone your skills. Explore the course today.
Was this content helpful to you