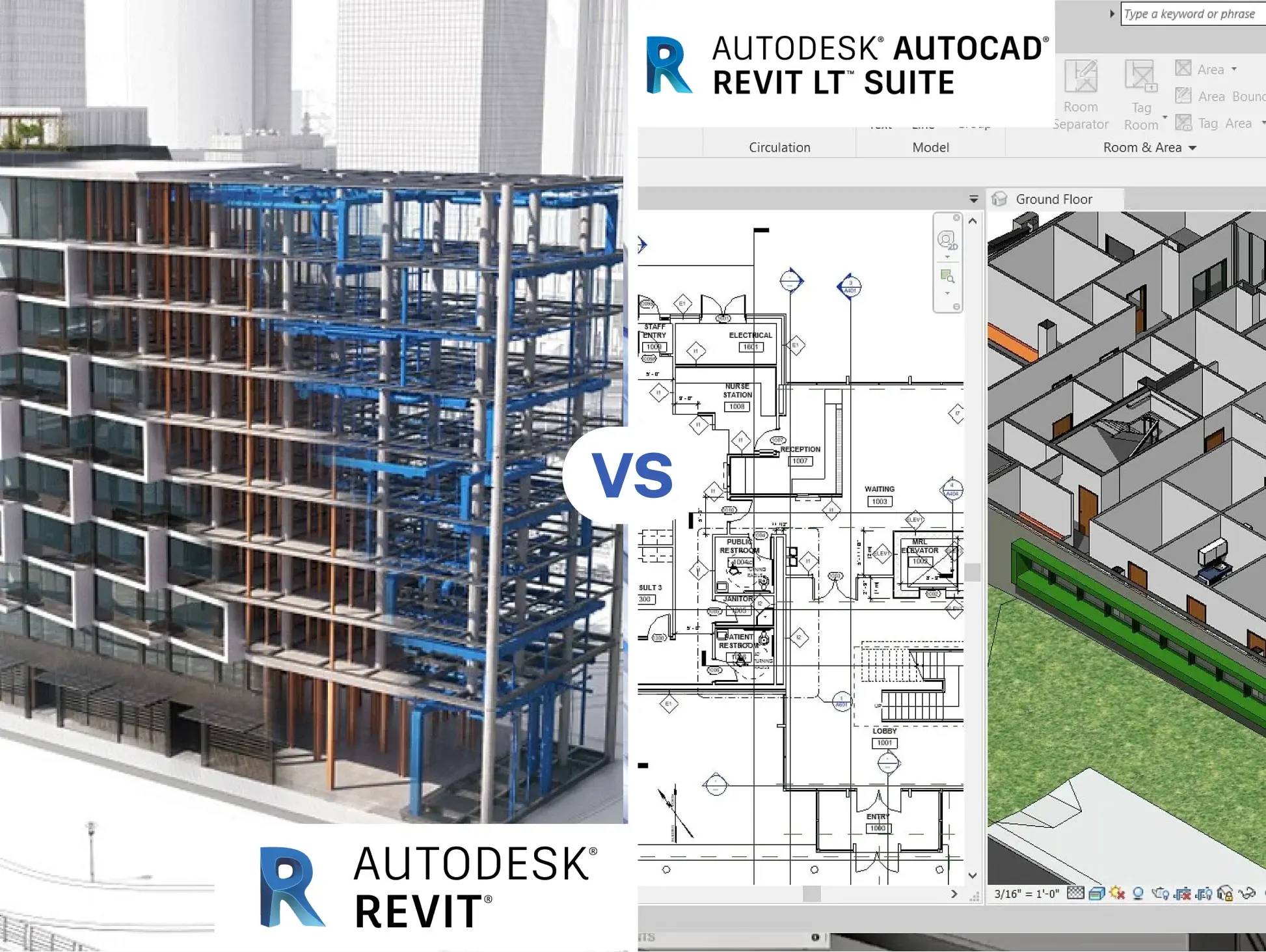
Revit v/s Revit LT are two of Autodesk’s most popular BIM tools, but they serve different needs within the AEC industry. Professionals are increasingly comparing them to decide which software aligns with their workflow, design requirements, and long-term BIM goals. Revit offers a full BIM environment with multidisciplinary modeling, collaboration, automation, and simulation tools suited for complex projects, whereas Revit LT provides streamlined architectural modeling and documentation at a lower cost. This difference makes the choice between them highly dependent on project scale, team structure, and budget.
This guide compares Revit vs Revit LT, covering pricing, features, collaboration, rendering, analysis tools, and modelling capabilities, to help AEC professionals pick the best BIM software for their workflow. Ideal for architects, small studios, freelancers, and large multidisciplinary teams deciding whether they need full-scale Revit for advanced collaboration and analysis or Revit LT for affordable architectural modelling and documentation.
Key Differences between Revit and Revit LT
|
Revit |
Revit LT |
|
|
Price |
$2910 per year |
$420 per year $55 monthly payment |
|
Overview |
Revit software helps architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) teams create high-quality buildings and infrastructure. |
Simplified 3D BIM tool for producing 3D architectural designs and documentation. Not suitable for structural, mechanical, electrical, or piping engineers. |
|
Collaboration |
Multiple users can work in the same Revit model at the same time. |
Multi-user environments are not allowed. |
|
Simulation |
Area analysis, Route analysis, MEP systems analysis, Energy Optimization for Revit, Lighting Analysis with Autodesk Rendering, Solar analysis, Sun and shadow studies, and Structural analysis available. |
None of the analysis tools are available. |
|
Point Clouds |
The process for importing point clouds into Revit is simple and user friendly. |
Point Clouds cannot be used in Revit LT. |
|
APIs and Automation |
All features available. |
There is no API (Application Programming Interface) |
|
In-product Rendering |
In-product rendering available. |
Revit LT renders in the cloud. No in-product rendering. |
|
System Requirements |
Processor: 2.5-3+ GHz Microsoft Windows: 10, 64-bit Disk space: 30 GB RAM: 8-32 GB |
Processor: 2.5-3+ GHz Microsoft Windows: 10, 64-bit Disk space: 30 GB RAM: 8-32 GB |
Revit v/s Revit LT

Revit
Revit is Autodesk’s full-scale BIM platform built for multidisciplinary AEC workflows, enabling teams to model architecture, structural systems, and MEP services within a single coordinated ecosystem. It supports real-time collaboration, in-product rendering, advanced analytical simulations, customizable automation through APIs, and shared model environments required for large, data-heavy construction projects.
Developed by Autodesk in 2000, Revit software helps architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) teams create high-quality buildings and infrastructure. It also has an extended cloud functionality for rendering and analysis. Revit software includes additional features and functionality such as work sharing, analysis, and in-product rendering.
If you’re new to Revit, Novatr offers a one-of-a-kind BIM Professional Course that features a specialised career-relevant curriculum designed and delivered by BIM experts from leading firms.
To understand the difference between AutoCAD and SketchUp, check out: Revit Vs SketchUp: Which Software is Better & Why?
Revit LT
Revit LT (or Revit Lite), as the name suggests, is a more cost-effective, streamlined BIM software for architecture professionals and studios - a slightly lower version of the full-scale version of Revit.
While Revit includes features for architectural design, MEP, structural engineering, and construction, Revit LT was derived from Revit software as a stepping stone for smaller architectural design firms looking to move towards a BIM workflow.
Unlike Revit, Revit LT only supports less advanced modelling.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Revit and Revit LT
|
Revit |
Revit LT |
|
A more robust version of the LT one, Revit offers a range of additional features such as work sharing, analysis, and in-product rendering. |
Absence of various features. |
|
Tailored for architectural professionals and studios. |
Suitable for smaller architectural practices. |
|
Comparatively expensive |
More cost-effective. |
|
Allow multiple users to work in the same Revit model at the same time. |
Lacks the feature. |
|
Revit offers 3D modelling and mechanical and structural tools. |
Revit Lite does not support any MEP tools and also lacks certain features such as slanted columns, conceptual massing, adaptive components etc. |
|
Revit comes with some additional features such as work sharing, analysis, and in-product rendering. |
Revit Lite lacks these features. |
|
Revit offers a range of analysis tools such as Area analysis, Route analysis, MEP systems analysis, Energy Optimization for Revit, Lighting Analysis with Autodesk Rendering, Solar analysis, Sun and shadow studies, and Structural analysis. |
Revit LT lacks these tools. |
|
Revit offers complete features when it comes to Revit families and templates. |
Revit LT offers limited In-place Families (can only model in-place walls), and no view filter functionality (although they can be applied via View Templates) |
|
Revit offers decal creation or in-product rendering. |
Revit LT clouds rendering capabilities. |
Conclusion
Selecting between Revit and Revit LT ultimately depends on the scale of your projects and the BIM capabilities you need in 2026. If your work involves multidisciplinary collaboration, detailed analysis, and advanced 3D modelling, Revit provides the full ecosystem required for complex AEC workflows. However, if you operate as an independent architect, freelancer, or small design studio seeking affordable BIM adoption focused mainly on architectural modelling and documentation, Revit LT offers a streamlined and budget-friendly entry point without unnecessary features.
To strengthen your BIM and architectural design expertise, professional training plays a critical role. The BIM Course for Architects offered by Novatr equips learners with industry-relevant BIM workflows, hands-on software training, and real project exposure, enabling architects to build future-ready skills and transition confidently into advanced BIM roles.
Visit our resource page to explore more insights, tutorials, and expert-led guidance on BIM careers, architecture tools, and AEC industry trends.
FAQs
1. What is the basic difference between Revit and Revit LT?
Revit LT (or Revit Lite), is a more cost-effective version of Revit and is derived from Revit software as a stepping stone for smaller architectural design firms.
2. Can Revit LT open Revit files?
A project can go back and forth between Revit and Revit LT, and can be opened, modified, and saved several times. You can save a Revit LT project using Revit, use Revit to make and save changes, and then open the project in Revit LT again.
3. What is Revit LT good for?
Revit LT offers a simplified BIM tool for creating 3D architectural designs and documentation. Although the software does not offer features for mechanical consultants, it provides basic structural modelling, interoperability, and data management, as well as presentation and visualisation features.
The software is targeted at the architecture community only. Smaller Architecture firms can subscribe to “Autodesk AutoCAD Revit LT Suite”, which helps them transition to BIM with both, Revit LT and the familiar drafting tools of AutoCAD LT, available together in one suite.
Was this content helpful to you







-1.webp)


-1.webp)