Revit or Tekla Structure: Similarities, Differentiation, & Integration
Table of Contents
This guide breaks down Revit vs Tekla Structures, covering key features, major differences, similarities, and how both tools integrate in real projects. Perfect for architects, civil engineers, and structural designers evaluating the best BIM software for detailed modeling, coordination, and high-efficiency project delivery. Ideal for professionals choosing the top tools or planning to use Revit and Tekla together for smoother workflows and smarter BIM execution.
Revit and Tekla Structures are two prominent software solutions that have taken Building Information Modelling (BIM) and structural design to another level. They have redefined the way professionals approach their projects, offering robust tools for design, collaboration and project management. Naturally, choosing the right software can significantly impact the project’s success, influencing efficiency, accuracy and project outcomes. Despite Autodesk Revit’s widespread popularity for structural modelling, the question remains: will it outshine Tekla Structures in the long run? More importantly, which software should you choose for your needs?
Revit Overview
Revit is a multidisciplinary BIM software used in architecture, engineering, and construction to model, document, and coordinate building projects efficiently.
Autodesk Revit provides a unified BIM environment that enables architects, engineers, and contractors to design, model, and manage construction projects with precise documentation and seamless collaboration. Its parametric design capabilities and extensive component libraries make it a powerful tool for creating coordinated building models that update automatically when changes are made.
1. Features of Revit
A. Multi-Disciplinary Design Integration- Facilitates seamless collaboration between teams within a single model.
- Allows all project stakeholders to work simultaneously, ensuring consistency and reducing errors.
B. Parametric Components
- Uses parametric components to create building elements that be reused conveniently
- Allows users to create and edit families to meet specific project requirements
- Generates accurate construction documents, including sections, elevations, and floor plans
- Changes in any part of the model are automatically updated in all associated documentation, reducing work and ensuring consistency
- Integrates and works with other software like Navisworks, BIM 360, and AutoCAD, enhancing interoperability
- Supports open standards for efficient data exchange and collaboration
2. Pros and Cons of Revit
Pros
- Revit provides an all-in-one BIM platform that integrates architectural design, structural engineering, and MEP (Mechanical, Engineering, and Plumbing) systems, facilitating interdisciplinary collaboration.
- It has an intuitive interface, making it accessible for architects and engineers.
- The software excels in producing detailed drawings and documentation, which are essential for the design and construction phases.
- Revit supports IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) and integrates well with other Autodesk products, such as AutoCAD, Navisworks, and BIM 360, enhancing interoperability and collaboration.
- It supports cloud-based project management and collaboration through Autodesk BIM 360, enabling real-time communication and data sharing.
- Revit comes with an extensive library of components and families, which can be customised to meet specific project needs.
Cons
- Revit can become slow and less responsive when handling very large models, impacting productivity.
- While user-friendly, Revit has a steep learning curve for beginners, especially for advanced features and workflows.
- Revit's structural detailing capabilities are not as advanced as those of specialised software like Tekla Structures, limiting its use for detailed fabrication.
- Revit is relatively expensive, which can be a barrier for small firms and individual design firms.
- For advanced structural analysis, Revit relies on integration with other Autodesk products, which can be cumbersome and add to the cost.
Also Check out: The Evolution of Autodesk Revit: From Inception to Industry Standard
Tekla Structure Overview
Tekla Structures is a BIM software focused on advanced structural modeling, detailed steel and concrete fabrication, and construction-ready documentation.
Tekla Structures, developed by Trimble, is a powerful 3D modelling BIM software for structural engineering and construction. It helps create detailed, information-rich models for various structures, including steel, concrete, and timber. Tekla's strengths lie in its ability to handle complex geometries, manage large-scale projects, and provide accurate material takeoffs. Known for its precision and robustness, it is widely used by structural engineers, detailers, and fabricators to create, combine, manage, and share highly detailed 3D models.
1. Features of Tekla Structures
A. Multi-Material Modelling- Supports various materials like steel, concrete, timber, and composites
- Enables creation of detailed 3D models with complex geometries and connections
- Produces comprehensive drawings, reports, and schedules
- Facilitates accurate fabrication and construction documentation
- Integrates with software such as AutoCAD, Revit, and other design tools
- Supports open standards like IFC for seamless data exchange
- Allows multi-user collaboration on the same model simultaneously
- Includes project management tools for tracking progress and managing revisions
- Integrates with structural analysis software for direct analysis within the Tekla model
- Supports various design codes and standards
- Provides detailed fabrication information, including CNC data
- Enhances construction planning with clash detection and site layout planning
2. Pros and Cons of Tekla Structures
Pros
- Tekla Structures excels in detailed structural modelling, including steel and concrete detailing, making it ideal for fabrication and construction.
- The software includes advanced structural analysis and design capabilities, allowing for precise engineering calculations and simulations.
- It offers high levels of accuracy and detail, which are crucial for complex projects requiring exact fabrication details.
- Tekla supports IFC and integrates well with other Trimble solutions and various third-party software, enhancing data exchange and collaboration.
- It facilitates cloud-based collaboration through Trimble Connect, enabling real-time data sharing and project management.
- The software allows for extensive customisation and scripting, which can be tailored to meet specific project requirements.
Cons
- Tekla Structures has a more complex interface compared to Revit, which can be daunting for new users and requires extensive training.
- While highly specialised in structural engineering, Tekla lacks the comprehensive architectural and MEP capabilities of Revit, making it less suitable for multidisciplinary projects.
- Tekla Structures is also expensive, which can be a challenge for smaller firms and projects.
- The software can be resource-intensive, requiring powerful hardware to run smoothly, especially for large and complex models.
- The advanced features and capabilities come with a steep learning curve, requiring significant time and effort to master.
Revit & Tekla Integration: Bridging the Gap
While Revit and Tekla Structures are often seen as competitors, there's a growing trend towards integrating these two popular platforms. The ability to import Tekla to Revit and export Revit to Tekla has become increasingly important for seamless workflow in complex projects. The Revit Tekla integrator and Tekla Revit plug-in have been developed to facilitate this interoperability. These tools allow for smoother data exchange between the two software, enabling teams to leverage the strengths of both platforms throughout the project lifecycle.
Key Aspects of Integration between Revit and Tekla Structures
1. Data Exchange: Revit and Tekla Structures support Industry Foundation Classes (IFC), an open standard for BIM data exchange, enabling interoperability and collaborative workflows. IFC files can be imported and exported between the two software, facilitating seamless data transfer. Additionally, direct links and plugins, such as the Tekla Revit Link, enable the direct import and export of Revit models to Tekla and vice versa, streamlining the exchange process.
2. Workflow Optimisation: Integration between Revit and Tekla Structures optimises workflows from design to fabrication. Architects and structural engineers can create initial designs in Revit, focusing on architectural and structural components. Detailed structural analysis, connection design, and fabrication detailing can then be performed in Tekla Structures. This combined use enhances clash detection and coordination, with Revit’s robust modelling and coordination features complementing Tekla’s detailed connection design.
3. Collaboration: Integrated workflows between Revit and Tekla Structures improve coordination among architects, structural engineers, detailers, and fabricators. Shared models and data enhance communication and reduce errors across disciplines. Cloud-based collaboration platforms like Trimble Connect and Autodesk BIM 360 allow real-time sharing, reviewing, and coordination of models and data, further improving project efficiency.
4. Model Synchronisation: Consistent updates between Revit and Tekla Structures ensure that changes made in one software are reflected in the other, maintaining consistency and reducing rework. Tools and workflows are available to manage model synchronisation and track changes effectively.
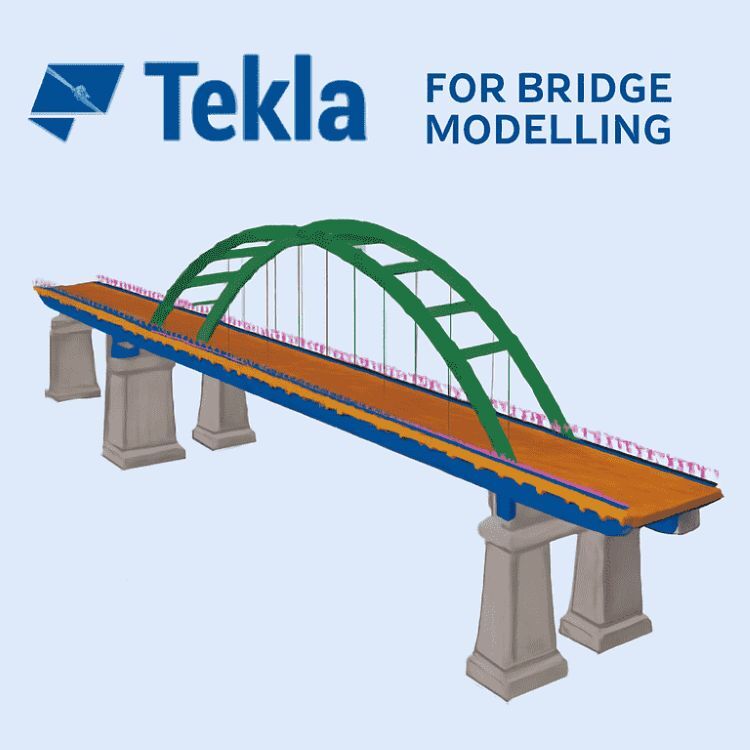
5. Common Use Cases: The integration is ideal for complex projects requiring detailed structural design and fabrication, such as high-rise buildings, industrial facilities, and bridges. It also enhances collaboration in multidisciplinary projects where architectural and structural components need to be seamlessly integrated.
6. Challenges and Considerations: Ensuring data fidelity and integrity during the exchange process can be challenging. Proper setup and validation of data exchange protocols are necessary to avoid information loss. Users must be proficient in Revit and Tekla Structures to make the most of the integration, requiring training and experience in both platforms. Ensuring software compatibility between versions is crucial, necessitating regular updates and maintenance of plugins and integration tools.
Steps to Integrate Tekla Structures With Revit
Integrating Tekla Structures with Autodesk Revit involves several steps to ensure seamless data exchange and collaboration. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you integrate these two powerful BIM software solutions:
1. Install the Tekla Revit Plug-In or Revit Tekla Integrator
- Download the appropriate plug-in from the Tekla or Autodesk website
- Ensure compatibility with your versions of Tekla Structures and Revit
- Close both Tekla and Revit before installation
- Run the installer and follow the prompts
- After installation, restart your computer to ensure proper integration
2. Prepare your Tekla Structures Model for Export
- Review your model for accuracy
- Check that all structural elements are properly defined
- Ensure that material properties, profiles, and grades are correctly assigned
- Verify that all necessary custom components and connections are included
- Clean up any unnecessary elements or working views that aren’t needed in Revit
3. Export the Tekla Model to a Compatible Format
- IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) is the most common format for this transfer
- In Tekla, go to “File”>”Export”>”IFC”
- Choose the appropriate IFC schema version
- Select the elements you want to export
- Configure export settings to include relevant property sets and classifications
- Choose a destination for the exported file
4. Open Revit and Use the Plug-In To Import the Tekla Model
- Launch Revit and open or create a project
- Locate the Tekla import tool in the Revit ribbon (usually under “Add-ins”)
- Select the IFC file exported from Tekla
- Choose import options, such as how to handle units, coordinates, and levels
5. Map Tekla Elements to Corresponding Revit Families and Types
- The plug-in will attempt to automatically map Tekla elements to Revit families
- Review the mapping suggestions and make adjustments as needed
- For custom or complex elements, you may need to create or modify Revit families
- Pay attention to parameters and properties to ensure they transfer correctly
- Consider creating a mapping template for future use if you frequently work with similar models
6. Review and Adjust the Imported Model
- Check the overall geometry and placement of elements
- Verify that material properties have transferred correctly
- Review structural connections and ensure they’re properly represented in Revit
- Adjust any elements that may have been imported incorrectly or with reduced detail
- Check for any warnings or errors in Revit and address them
- Coordinate the imported structural model with architectural and MEP elements if present
Also Check out: Advanced Revit and BIM Techniques
Differences between Revit and Tekla Structures
Revit and Tekla Structures differ in their primary focus, level of detailing, workflow, and analysis capabilities, which affects how AEC teams use each BIM tool for design, documentation, and fabrication.
|
Differences |
Revit |
Tekla Structures |
|
Primary focus |
Multi-disciplinary BIM tool for architecture, MEP, and structural design, offering an integrated platform for building design and documentation. |
Specialised BIM tool for structural engineering with deep steel and concrete detailing, focusing on highly detailed models for analysis, design, and fabrication. |
|
Detailing and Fabrication |
Provides strong modelling for design and documentation, with basic structural detailing, but does not offer the fabrication-level detailing and construction depth that Tekla delivers. |
Offers advanced detailing such as connections, rebar, and fabrication-ready drawings, and is widely used for producing shop drawings and managing the fabrication workflow. |
|
User Interface and Workflow |
Revit offers a user-friendly interface tailored to architects and MEP engineers. Its workflows are designed to support architectural design and coordination between different disciplines. |
Tekla’s interface is more specialised for structural engineers and supports detailed modelling and complex structural workflows, including advanced analysis and fabrication processes. |
|
Analysis Capabilities |
It includes basic structural analysis tools suitable for the initial design and documentation phases. For more advanced analysis, it relies on integration with other Autodesk products like Robot Structural Analysis. |
It has built-in advanced analysis and design capabilities, especially for structural engineering. It provides detailed analysis features for steel and concrete structures. |
Similarities between Revit and Tekla Structures
Both Revit and Tekla Structures support BIM-based 3D modeling, IFC workflows, and collaboration features that help project teams coordinate designs and construction data across disciplines.
Below are at the main similarities between Revit and Tekla Structures:
1. BIM Integration
Both Revit and Tekla Structures are BIM software, supporting comprehensive 3D modelling, data management, and collaborative workflows. They facilitate the creation of detailed building and infrastructure digital representations.
2. IFC Support
Both software solutions support Industry Foundation Classes (IFC), an open standard for BIM data exchange. This allows for interoperability and collaborative workflows between different BIM tools.
3. Collaboration and Coordination
Revit and Tekla Structures support collaborative workflows, enabling multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously. They both offer tools for clash detection and coordination, improving project efficiency and reducing errors.
4. Integration With Other Software
Both platforms integrate with other software solutions in their respective ecosystems. Revit integrates well with other Autodesk products like AutoCAD, Navisworks, and BIM 360. Tekla integrates with Trimble Connect, SketchUp, and other Trimble solutions.
In Conclusion
Choosing between Revit and Tekla Structures depends largely on the specific project needs and user expertise. Revit is ideal for multidisciplinary projects requiring a comprehensive BIM solution with strong documentation and collaboration capabilities. Tekla Structures, on the other hand, is the go-to choice for detailed structural design, analysis, and fabrication, particularly for complex projects where high accuracy and advanced detailing are crucial. Evaluating the pros and cons of each software based on your project requirements and your team’s expertise can help you make the right choice.
If you want to master Revit and Tekla Structures and 10 other BIM software, Novatr offers a BIM Professional Course for Civil Engineers and a BIM Course for Architects. You can learn from industry experts and test your theoretical knowledge on capstone projects by enrolling in these courses.
To learn more about the industry, visit our Resources Page.
FAQs
1. Is Tekla compatible with Revit?
Yes, Tekla Structures is compatible with Revit through IFC file exchange and plug-ins like the Tekla-Revit integrator, which let you share models, align coordinates, and coordinate structural and architectural data between both tools.
2. What is the difference between Revit and Tekla?
The key difference is focus: Revit is a multidisciplinary BIM software for architecture, MEP, and structural design, while Tekla Structures is specialized for detailed structural modeling, rebar, steel and concrete connections, and fabrication-ready drawings.
3. Is Tekla a BIM software?
Yes, Tekla Structures is a BIM software that helps structural engineers, detailers, and fabricators create accurate 3D models, generate drawings, and plan fabrication and erection for complex structures.
4. Which software is best for structural design?
For general structural design inside a full building model, Revit works well, especially when coordination with architecture and MEP is important. For highly detailed steel and concrete design, connections, and shop drawings, Tekla Structures is usually the better choice.
5. Can I use Revit for structural design?
Yes, you can use Revit for structural design. It supports structural elements, analysis integration, and coordination with other disciplines, making it suitable for creating and managing structural models within a BIM workflow.


 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!
.jpg)


.png)


.jpg)

-1.png)

