Throughout history, humans have been fascinated with the idea of pushing the boundaries of architecture and engineering to create structures that seem to defy gravity itself. From structures with large overhanging cantilevers like the Museum of Tomorrow in Brazil to homogenous free-form structures such as the Heydar Aliyev Center in Azerbaijan, one can find many examples of anti-gravity buildings that leave viewers in awe. This article aims to list 10 such gravity-defying edifices. Whether you're an architecture enthusiast, a history buff, or simply someone who appreciates beautiful and inspiring designs, this list is sure to leave you amazed and inspired.
1. Museum of Tomorrow

Architect: Santiago Calatrava
Location: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Completed in 2015, the Museum of Tomorrow includes 5,000 square meters of temporary and permanent exhibition space, as well as a 7,600 square metres plaza that wraps around the structure. The museum is inspired by the Carioca culture and explores the relationship between the city and its surrounding natural environment. A cantilevered roof expands along the full length of the pavilion, 75 m on the side facing the square and 45 m on the side facing the sea. This highlights the extension of the museum from the dock into the bay. To realize this structure, the architects added roughly 2,500 steel piles to the building’s foundation.
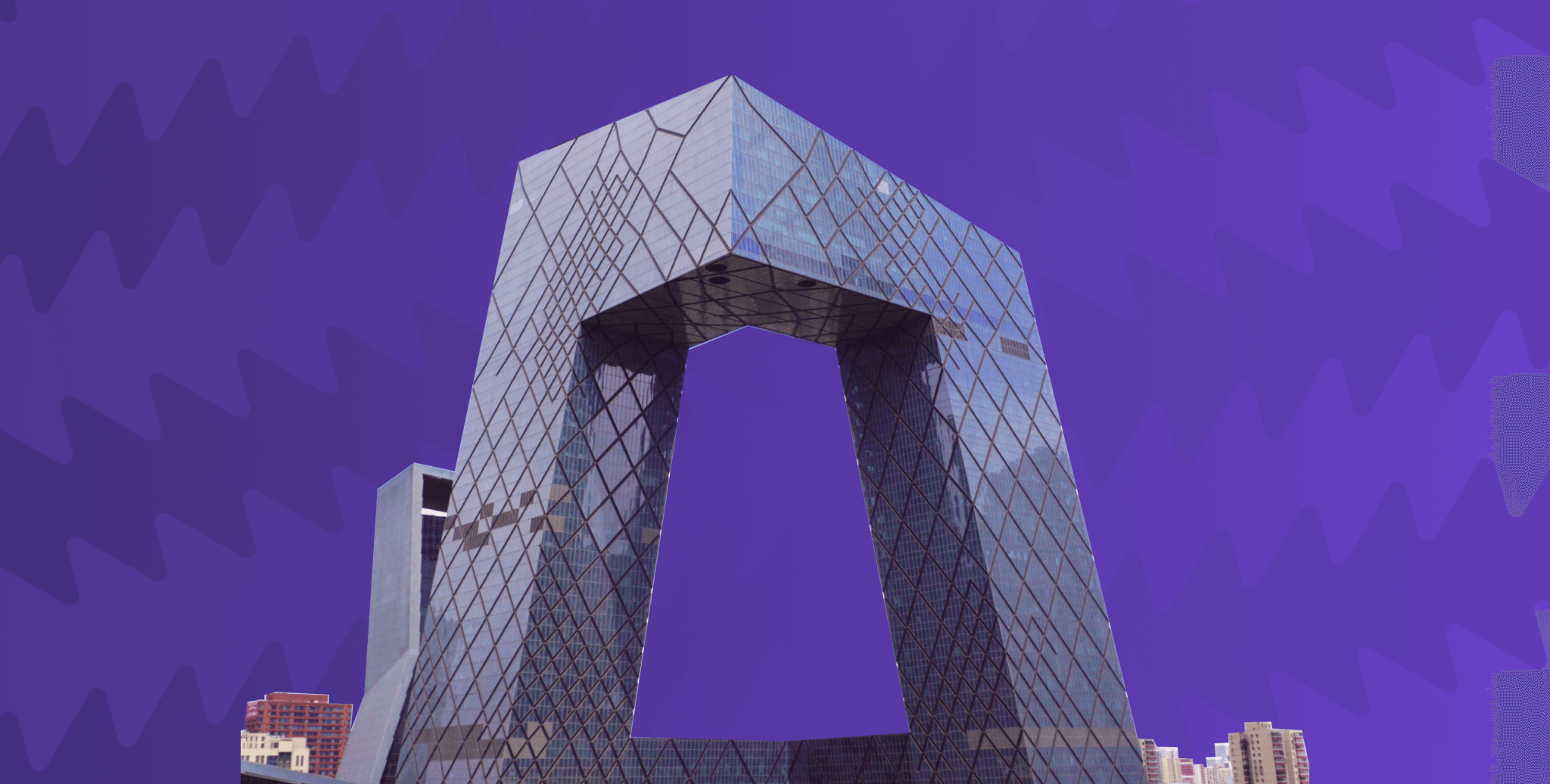
2. CCTV Headquarters

Architect: OMA
Location: Beijing, China
The CCTV Headquarters, completed in 2012, was designed as a reinvention of the skyscraper as a loop. The 234-metre tall building accommodates a range of spaces such as TV studios, offices, broadcasting, and production facilities, etc. Rising from a common platform, two towers lean towards each other and eventually merge in a perpendicular 75-metre gravity-defying cantilever. A web of triangulated steel brace adorns the facade of the building, highlighting its innovative structural solution. Because of this, the façade itself becomes a visual manifestation of the building’s structure.
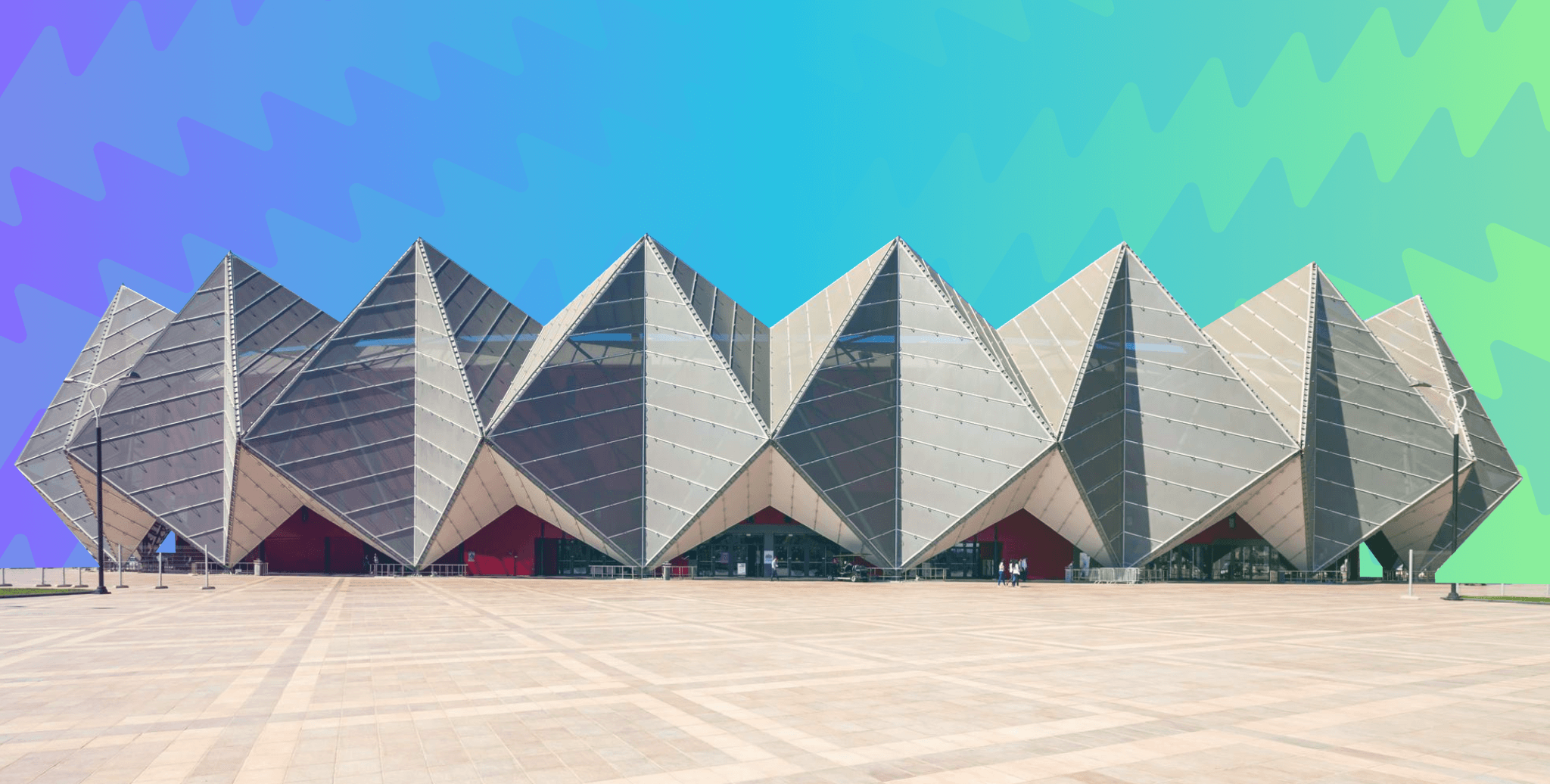
3. Heydar Aliyev Center

Architect: Zaha Hadid Architects
Location: Baku, Azerbaijan
Following a competition held in 2007, Zaha Hadid Architects were appointed as the design lead for the Heydar Aliyev Center. The center aims to become the primary building for the nation’s cultural programs. For its design, the architects wanted to establish a continuous, fluid relationship with its surrounding plaza and building interiors. A classic example of parametric architecture, the structure appears to defy gravity with formations such as undulations, bifurcations and folds. To design the homogenous free-form structure, advanced computing methods were used for the continuous control and communication of these complexities among the numerous project participants. In addition, vertical structural elements hidden by the envelope and curtain wall systems were used to help achieve the large column–free space in the center’s interior.
4. Needle Tower

Architect: Kenneth Snelson
Location: Hirshhorn Museum, Washington D.C, USA
The Needle Tower is a public artwork located outside the Hirshhorn Museum and Sculpture Garden in Washington, DC, USA. The tapering tower, constructed in the 1960s, was made using aluminium and stainless steel. It is interesting to note that the 60-foot tower has barely 14 inches of contact with the ground! The structural style displayed here is known as "tensegrity." A concept innovated by Buckminster Fuller, tensegrity structures are self-tensioning structures composed of rigid structures and cables, with forces of traction and compression forming an integrated whole. The structural components of the artwork consist of two different types of triangles made of steel wire. The result is a kind of lattice, making the structure stable.
Also Read: A complete guide to build modular homes in 2026
5. Museum of Rock

Architect: Cobe, MVRDV
Location: Roskilde, Denmark
Ragnarock, or the Museum of Rock, is an interactive museum delivering a multi-sensory experiential journey through the evolution of rock music and youth culture from the 1950s. The external facade of the building has a golden aluminium finish, paying homage to flamboyant lead singers of the era. The building hosts a colossal 20-metre cantilever that guarantees to have a physical impact on anybody standing under it. The cantilever houses the main museum centre which also includes an auditorium, administrative facilities and a bar.
6. Cube Houses

Architect: Piet Blom
Location: Rotterdam, Netherlands
Constructed in 1984, the Cube Houses in Rotterdam are a residential development complex designed as cubes, tilted inwardly over by almost 45 degrees. The structure resembles an abstract forest, with each triangular roof representing a treetop. The project attempts to breathe life into the city center and shift the emphasis from business to residential housing. Each cube is divided into three levels including a living space at the ground floor, bedrooms in the middle, and a sun lounge at the top. The cubes consist of structural timber-frame skeletons mounted on the edges of the floors and are supported by hexagonal pylons. These pylons are constructed by joining three concrete pillars with six cellular brick walls.
7. Balancing Barn

Architect: MVRDV: The Landscape Partnership
Location: Suffolk, United Kingdom
Situated by a small lake in the English countryside in Suffolk, the Balancing Barn is a 30-metre-long two-person home with a 15-metre cantilever. This means that 50% of the barn hangs in free space! Furnished to a high standard of comfort and elegance, the barn features a reflective metal sheeting exterior. It incorporates a kitchen, a large dining room, and four bedrooms with attached washrooms. Taking references from the local buildings, the structure balances on a central concrete core. It maintains its structural integrity by having the section that sits on the ground constructed from materials heavier than the cantilevered section.
8. Seattle Central Library

Architect: OMA + LMN
Location: Downtown Seattle, Washington, United States
The flagship library of the Seattle Public Library system, the Seattle Public Library, is an 11-storey glass and steel building in downtown Seattle. The building aims to redefine the traditional function of a library and aims to collect and store all forms of media. Generic flexible floors are designed by the architects so that they do not restrict the floor to one particular activity. The library can hold about 1.5 million books and other materials. It has a striking appearance, with several “floating platforms” wrapped in a large steel net. The structure is composed of both “load-bearing systems” and “seismic systems.” The load-bearing system, consisting of columns and beams, supports the floating platforms containing program spaces.
9. Montreal Tower

Architect: Roger Taillibert
Location: Montreal, Canada
Montreal Tower was part of the Olympic Stadium constructed for the 1976 Summer Games. At 175 meters and an inclined angle of 45 degrees (much larger than that of the Leaning Tower of Pisa), the Tower is the tallest inclined structure in the world! The secret to its extraordinary tilt can be found in its complex internal structure. It also hosts a retractable roof along with a range of other sporting facilities. While the building was originally planned to be built entirely of concrete, due to some structural setbacks, steel was later used to construct parts of the tower. The building also features an observation deck.
Related Read: 10 World's Best Stadium Designs in 2025!
10. One Central Park

Architects: Ateliers Jean Nouvel
Location: Chippendale, Australia
With One Central Park Apartments, the architects aimed to build an integrated experience for living in harmony with the natural world. The twin tower mixed-use development incorporates a public park that climbs the side of the floor to ceiling glass towers. 250 species of native Australian flowers and plants have been incorporated into the facade, making the structure a classic example of biophilic design. A gravity-defying cantilever crowns the pinnacle of the tower, which contains its most luxurious penthouses. The cantilever spans a length of 148 feet and weighs 120 tonnes. It is built using a steel truss system and hosts a reflective heliostat featuring 320 motorized mirrors.
In Conclusion
The age of digital design and production has opened up new opportunities in terms of innovative design methods and technologies. Various processes are used to realize these structures, including BIM and computational design. These technologies help simulate the behavior of these complex gravity-defying physical models and help enable more sophisticated, precise, and efficient simulations. They also help with the seamless collaboration of the design concepts among all the stakeholders.
Interested in getting started with computational design?
Novatr’s Master Computational Design Course for Real World Application course helps you:
- Become a Computational Design Specialist in just 8 months of part-time, online study.
- Learn from industry experts working at top firms like ZHA, Populous, and UNStudio.
- Master 6+ software, 15+ plugins and industry workflows.
- Build a core specialisation in High-Performance Building Analysis or Computational BIM Workflow.
- Get placement assistance to land jobs in globally operating firms.
Make sure to check out our Resources page for more informative reads.
Was this content helpful to you