In modern construction, HVAC systems (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) are essential for maintaining safe, healthy, and efficient indoor environments. As part of MEP engineering, which combines mechanical, electrical, and plumbing services, HVAC ensures temperature regulation, air quality, and energy efficiency.
Whether in residential towers, commercial offices, or industrial facilities, HVAC in building services plays a pivotal role in occupant comfort and regulatory compliance. Understanding the role of HVAC in MEP is crucial for engineers and architects designing sustainable, high-performing buildings.
What are HVAC Systems and Why Are They Important in MEP Engineering?
What is an HVAC system?
An HVAC system is a network that delivers heating, cooling, ventilation, and humidity control within a building. It ensures year-round comfort by regulating indoor temperature and humidity, while also improving air quality through pollutant filtration and fresh air circulation.
What is MEP engineering?
MEP stands for Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing systems that keep MEP buildings' services functional and safe. Among these, HVAC is one of the largest and most energy-intensive services, making it a top priority during design and implementation.
The role of HVAC in MEP projects:
-
Comfort & Air Quality: Maintains thermal comfort, humidity balance, and healthy indoor air.
-
System Design & Coordination: HVAC engineers select equipment and work with electrical and plumbing teams to ensure seamless integration.
-
Energy Efficiency: Well-designed HVAC systems reduce energy waste, lower operating costs, and support green building certifications.
-
Compliance & Safety: Systems must align with regulations while ensuring occupant safety and performance optimisation.
In short:
HVAC is not just about comfort; it plays a central role in how MEP engineering achieves safety, compliance, and sustainability in modern buildings.
What are the Main Components of HVAC Systems in Buildings?

The design of an HVAC system may vary by project, but most systems rely on a few essential groups of components that work together to provide comfort, safety, and efficiency.
Key HVAC system components include:
-
Heating and Cooling Units – Furnaces, boilers, heat pumps, air conditioners, chillers, and VRF systems that regulate temperature.
-
Ventilation & Air Handling – Ducts, fans, vents, and AHUs that maintain airflow, fresh air supply, and proper circulation.
-
Air Distribution Network – Ductwork and zoning pathways that deliver conditioned air to different areas.
-
Controls & Monitoring – Thermostats, sensors, and automation tools that optimise performance and energy use.
-
Air Quality & Safety Systems – Filters, purifiers, exhaust systems, humidifiers, and dehumidifiers that ensure clean, healthy, and balanced indoor environments.
Together, these elements form the backbone of HVAC MEP systems, ensuring reliable, safe, and energy-efficient operation.
Also Read: Top 50 MEP Interview Questions & Answers 2026
How Do HVAC Systems Work with Plumbing and Electrical Systems in MEP?
In modern buildings, no system works in isolation. HVAC, plumbing, and electrical services are interdependent, and their successful integration is what makes MEP engineering both complex and critical. HVAC systems, in particular, rely on coordinated design and shared infrastructure to ensure efficiency, comfort, and safety.
-
HVAC relies heavily on plumbing for chilled water, hot water supply, and condensate drainage.
-
Boilers and cooling towers need constant plumbing integration to function effectively.
-
HVAC is powered by electrical systems, which support motors, compressors, controls, and emergency power backups.
-
How does HVAC integrate with MEP building services? The answer lies in coordinated design, where ducts, pipes, and wiring are planned together in shared spaces.
-
Control systems often tie into the Building Management System (BMS), which manages HVAC, lighting, and security under one platform.
-
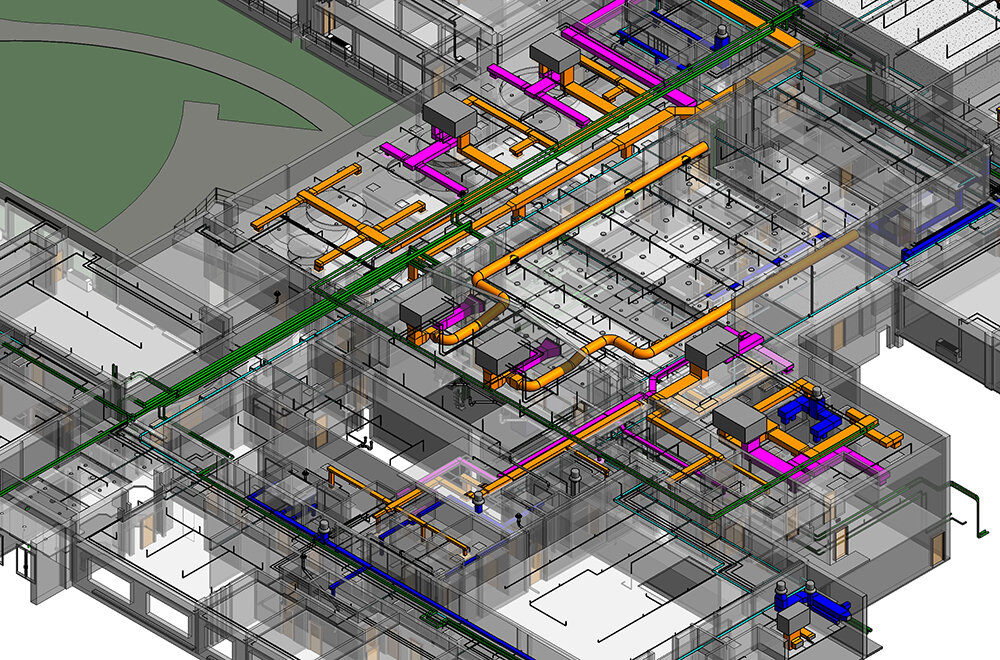
BIM modeling ensures that how HVAC systems are used in MEP projects avoids clashes with plumbing and electrical systems.
-
For engineers, this highlights the role of HVAC in MEP as a central, coordinating system.
What Role Do HVAC Systems Play in Energy Efficiency and Indoor Comfort?

-
HVAC systems in sustainable MEP engineering are critical for lowering carbon footprints and reducing energy costs.
-
Energy-efficient HVAC systems account for 40–60% of building energy use but can be optimised through smart controls and modern technologies.
-
Zoning systems improve comfort by conditioning only the required areas, saving energy.
-
How HVAC systems improve building efficiency in MEP: By integrating smart energy recovery systems, using renewable energy sources, and maintaining regulatory compliance.
-
The push toward energy-efficient HVAC systems makes skilled MEP engineers more critical than ever.
Which Tools and Software Help Design and Manage HVAC Systems Effectively?
Designing and managing HVAC systems in modern buildings is a complex task that demands precision, efficiency, and collaboration across multiple disciplines. To achieve this, MEP engineers rely on a range of advanced tools and software that streamline everything from initial system design and load calculations to energy simulations, coordination with other building services, and ongoing performance monitoring.
Modern tools help MEP engineers optimise HVAC MEP systems through design, coordination, and performance monitoring:
-
BIM (Building Information Modeling): Enables 3D coordination of HVAC with plumbing and electrical services.
-
AutoCAD MEP: Drafting and documentation of layouts.
-
Revit MEP: Advanced modeling and clash detection for HVAC in building services.
-
EnergyPlus: Open-source platform for performance modeling.
-
BMS Systems: Centralised control and integration of all MEP building services. These tools enable how HVAC systems are used in MEP projects to be more efficient, accurate, and sustainable.
Also Read: BIM for MEP: A Complete Guide 2026
Conclusion
HVAC systems are at the core of MEP engineering, ensuring safety, comfort, and sustainability in every type of building. By mastering the role of HVAC engineers in MEP system design, professionals can optimise indoor comfort, integrate systems effectively, and design energy-efficient HVAC systems that align with global sustainability goals.
As buildings become more advanced and regulations more demanding, the need for skilled MEP professionals is growing rapidly. Novatr’s BIM Course for MEP Engineers offers comprehensive training in HVAC MEP systems, BIM workflows, and industry-relevant projects, equipping engineers to design, coordinate, and manage modern HVAC systems in sustainable MEP engineering. This course is ideal for professionals aiming to excel in MEP roles and shape the future of smarter, greener buildings. For more insights, head to our Learning Hub.
Also Read: Boost Your MEP Engineering Career with BIM Mastery
FAQs
1. What does HVAC stand for in MEP engineering?
HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning, forming a critical part of mechanical systems within MEP engineering projects.
2. Why are HVAC systems important in modern buildings?
HVAC systems ensure indoor comfort, regulate temperature, improve air quality, enhance energy efficiency, and maintain compliance with building safety standards.
3. How do HVAC systems fit into MEP engineering?
HVAC integrates with plumbing and electrical systems, enabling seamless coordination across MEP building services to ensure comfort, safety, efficiency, and sustainability
Was this content helpful to you