The Impact of BIM on Landscape Architecture: A Comprehensive Guide

Table of Contents
The Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) Industry is constantly evolving and actively embracing technology to make processes more efficient. Building Information Modelling (BIM) is one such technology that has significantly impacted various fields within the AEC industry, including landscape architecture. BIM has significantly impacted the landscape architecture field and helped landscape architects enhance collaboration, streamline their workflows, and improve overall project efficiency.
To learn more about the role of BIM in Landscape Architecture and how you can upskill yourself, continue reading the blog.
Also Read: Top 7 Places to Learn BIM (Building Information Modelling) in India
Role of BIM in Landscape Architecture
BIM is a technology that enables landscape architects to work collaboratively with architects, engineers, and other stakeholders in a shared digital environment, fostering better coordination and communication. It also allows for detailed 3D visualisation, facilitating better communication of design intent to clients, stakeholders, and the wider project team.
BIM serves as a centralised platform for managing project data, ensuring consistency and accuracy in documentation. BIM tools also offer analysis and simulation capabilities, allowing landscape architects to optimise designs for environmental considerations. BIM also supports facility management by providing a comprehensive digital record of landscape elements, useful for ongoing maintenance, renovations, and future developments.
For landscape architects, BIM allows for sustainability integration, allowing them to optimise designs for factors like water efficiency, energy use, and ecological impact. BIM also facilitates regulatory compliance.
Applications of BIM in Landscape Architecture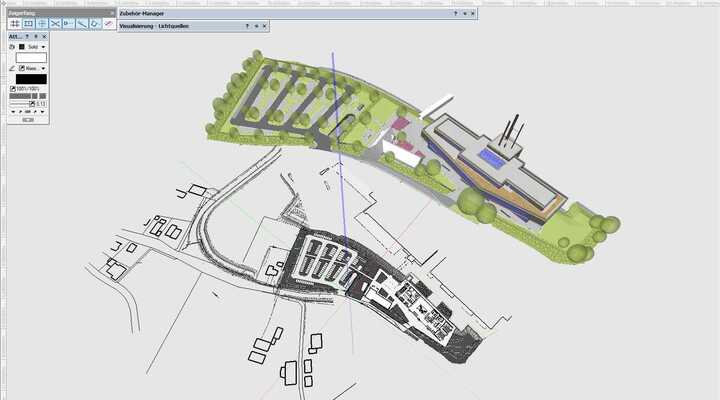
BIM in landscape architecture simplifies project management by enhancing vegetative selection and plantation management, optimising irrigation layouts, and contributing to risk mitigation by identifying and resolving conflicts early in the design process. Its holistic approach improves collaboration, visualisation, and decision-making throughout the entire lifecycle of a landscape project.
Take a look below at the applications of BIM in landscape architecture:
1. Project Management
BIM works as a centralised model that allows real-time sharing and coordination of information, reducing errors and improving communication. It also provides 3D visualisation of the landscape design, helping stakeholders to understand the project better. This leads to early detection of conflicts or design issues and better decision-making.
2. Vegetative Selection
BIM is used to create a database of plant species providing detailed information on their characteristics, maintenance requirements, and environmental preferences. This helps landscape architects select the most suitable vegetation for a project based on factors like climate, soil conditions, and aesthetics. It also allows for the simulation of plant growth over time, helping designers anticipate how the landscape will evolve and mature.
3. Plantation Management
BIM also helps determine the optimal quantity and spacing of plants within a design. This ensures proper coverage and aesthetics while considering factors like growth patterns and maintenance requirements. The BIM 3D models include information on maintenance schedules, helping landscape architects and maintenance teams plan and execute tasks such as pruning, fertilisation, and pest control.
4. Irrigation Layout
BIM helps design and simulate irrigation systems, considering factors like topography, soil conditions, and plant water requirements. This ensures efficient water distribution and helps in optimising irrigation layouts. BIM also plays a crucial role in water conservation as it helps landscape architects analyse water usage patterns and identify opportunities for water conservation. This is crucial for sustainable landscape design and aligning with environmental best practices.
5. Risk Mitigation
BIM enables clash detection by identifying conflicts or clashes in the design early in the planning phase. This is crucial for avoiding issues during construction and ensuring that all components, including vegetation and irrigation systems, can coexist harmoniously. BIM models can be used for accurate quantification of materials and resources required for a landscape project. This aids in cost estimation and risk assessment, allowing for better financial planning.
Popular BIM Software and Tools for Landscape Architects
Before zeroing in on BIM software, landscape architects need to consider project needs, collaboration level, and software capabilities for landscape-related elements like terrain modelling, planting, and hardscape design. BIM software is crucial for designing, analysing, and managing projects in a collaborative, data-rich environment. Popular BIM software and tools for landscape architects include:
1. Autodesk Revit
Autodesk Revit is a popular tool in the AEC industry, enabling the creation of 3D models with better design elements. It includes tools for documentation, analysis, and collaboration. Although primarily used for building design, Revit's flexibility makes it suitable for landscape architecture, such as site planning and conceptual design, though it may not be as specialised as other tools.
2. ArchiCAD
ArchiCAD is a BIM software developed by Graphisoft, offering 3D modelling, collaboration, and documentation tools for architectural design. Its user-friendly interface makes it suitable for landscape architecture applications, enabling site modelling, planning, 3D model creation, documentation generation, and stakeholder collaboration in landscape architecture.
3. VectorWorks Architect
VectorWorks Architect is a versatile BIM software that supports architectural and landscape design, offering 2D drafting and 3D modelling tools, collaboration features, and landscape design capabilities. It enables landscape architects to create detailed site plans, plant schedules, and hardscape elements, with its Landmark module specifically catering to landscape architecture needs.
Also Read: Landscape Architecture: Definitions, Types, Elements & More (2026)
4. Bentley’s AECOsim
Bentley’s AECOsim is a BIM platform for infrastructure projects, enabling multidisciplinary collaboration and 3D modelling, simulation, and analysis. It is also useful in landscape architecture for site planning and design, integrating various design disciplines and providing data-rich models for better decision-making.
5. Trimble SketchUp
Trimble SketchUp is a popular 3D modelling tool for conceptual design and visualisation in various fields, particularly in landscape architecture. Its intuitive capabilities make it ideal for creating quick 3D models of outdoor spaces, facilitating quick conceptualisations, presentations, and client communication.
6. Rhino/Grasshopper
Rhino is a versatile 3D modelling software, while Grasshopper is a visual programming language that allows parametric design. These tools are useful in landscape architecture for generative design and complex form creation, allowing architects to explore iterations, create parametric landscapes, and analyse environmental factors.
Case Studies of BIM in Landscape Architecture
Today, BIM has become a transformative tool for landscape architects, reshaping design processes and enhancing project outcomes. BIM helps in centralising data, streamlining collaboration, and simulating real-world scenarios. Take a look below at the case studies depicting the diverse applications of BIM within landscape architecture:
1. Brooklyn Bridge Park, USA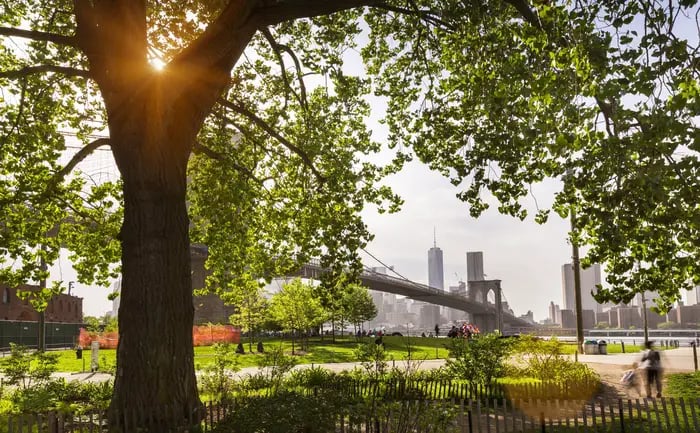
Brooklyn Bridge Park, a sustainable urban park in New York City, spans 85 acres along the East River waterfront. It features recreational spaces, sports facilities, and natural habitats, with the successful implementation of BIM.
BIM Implementation
Brooklyn Bridge Park used BIM to streamline design and construction processes. Landscape architects created a detailed 3D model of the park, integrating vegetation, hardscape features, and irrigation systems. This collaborative approach improved communication among stakeholders, enabling real-time visualisation of design concepts and early conflict identification. BIM also helped optimise the park's maintenance plan for long-term sustainability.
2. Gardens by the Bay, Singapore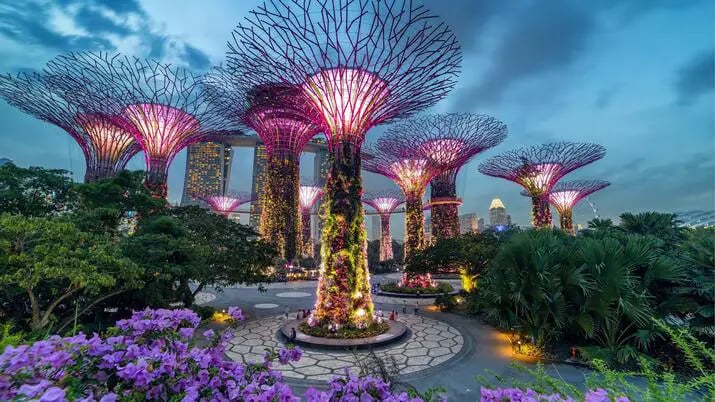
Gardens by the Bay, a Singaporean horticultural attraction, aims to create a sustainable garden environment. BIM played a crucial role in achieving intricate designs and facilitating seamless collaboration among diverse project teams.
BIM Implementation
BIM was used to model complex structures and landscape elements at Gardens by the Bay, integrating designs from architects, landscape designers, and engineers. Its 3D capabilities helped visualise intricate relationships between architectural and landscape components. BIM also created an intelligent facility management system, embedding data on plant species, climate control systems, and structural elements, providing a comprehensive database for maintenance teams.
3. Olympic Park, London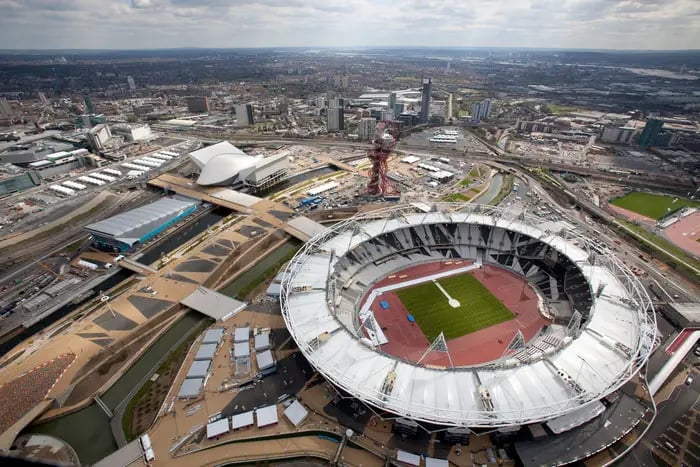
The London Olympic Park, designed for the 2012 Summer Olympics, is a sustainable urban park featuring waterways, green spaces, and iconic structures like the Olympic Stadium, with BIM playing a crucial role in the project's success.
BIM Implementation
This project uses BIM to create a detailed 3D model, integrating architecture, landscape architecture, and engineering disciplines. BIM facilitated the coordination of complex interactions between structures and landscapes, ensuring sustainability and accessibility. Clash detection was a key feature, reducing construction costs and providing crucial data for maintenance and future developments.
Also Read: Architecture Thesis Topics: A Comprehensive List of 30 Topics to Pick From 2026
Top BIM Courses for Landscape Architects
Landscape architects should choose a BIM course based on their skill level, industry-specific software tools, and desired knowledge. Courses with real-world case studies and practical exercises can enhance learning and prepare professionals for implementing BIM in their projects. As BIM adoption grows across the world, there are various courses and training programs designed to equip professionals with the necessary skills. Top BIM courses cover fundamentals, applications, implementation strategies, and project management.
1. BIM Professional Course by Novatr
The reimagined BIM architecture course offered by Novatr empowers participants with the skills needed to carve a unique path to success. It caters specifically to the architects' needs and offers a comprehensive program with essential knowledge and software skills crucial for BIM. Whether you’re a recent graduate or a professional, this course teaches you the application of BIM concepts through hands-on training and real-world projects. Under the guidance of industry experts, this course provides training in more than 15 BIM tools, allowing participants the chance to apply their knowledge in a RIBA capstone project. Additionally, participants receive invaluable placement support, making Novatr’s course a go-to choice for architects looking to excel in their careers.
2. BIM for Landscape Architects by LinkedIn Learning
The BIM for Landscape Architects course by LinkedIn Learning provides landscape professionals with essential skills in Building Information Modelling (BIM). This course covers the fundamentals of BIM, focusing on its applications in landscape design and planning. Participants will learn how to create detailed 3D models and effectively manage project data. Emphasis is placed on integrating BIM with other disciplines, such as architecture and civil engineering, to foster collaboration and improve project outcomes. Additionally, the course explores efficient project management strategies using BIM, enhancing decision-making and resource allocation. By completing this course, landscape architects will be well-equipped to leverage BIM technology for successful project delivery and innovative design solutions.
3. BIM Fundamentals for Landscape Architects by Udemy
This beginner-friendly course delves into BIM concepts with a strong emphasis on their application to landscape architecture. It provides a clear introduction to the essential tools used within BIM platforms, guiding learners through the model creation process, which is fundamental for visualising and managing landscape projects. The course also highlights collaboration strategies, ensuring landscape architects can work seamlessly with other disciplines like architecture and engineering. By focusing on BIM's role in project workflows, it illustrates how BIM enhances efficiency, precision, and coordination, allowing for better decision-making and resource management throughout a project’s lifecycle.
4. Advanced BIM Implementation for Landscape Architects by edX
The Advanced BIM Implementation for Landscape Architects course by edX is tailored for professionals who already have a foundational understanding of Building Information Modelling (BIM). This advanced course delves into sophisticated BIM strategies and implementation techniques specifically for landscape architecture. Participants will explore data integration methods that enhance project workflows and learn effective project coordination practices. The course emphasizes best practices that enable landscape architects to maximise the benefits of BIM technology in their projects. Through practical examples and case studies, learners will develop the skills necessary to tackle complex design challenges and improve collaboration among multidisciplinary teams, ultimately leading to more efficient and innovative landscape solutions.
5. BIM Execution Planning for Landscape Architecture Projects by Coursera
The BIM Execution Planning for Landscape Architecture Projects course by Coursera is designed to highlight the critical importance of planning and execution strategies for successfully integrating Building Information Modelling (BIM) into landscape architecture. This course provides in-depth insights into creating effective BIM execution plans that align with project goals. Participants will learn about collaboration protocols essential for fostering teamwork among various stakeholders, as well as the project standards necessary for maintaining quality and consistency. The course also covers workflow management techniques that streamline processes and improve efficiency. By the end of the course, landscape architects will be equipped with the knowledge and skills to implement BIM effectively, ensuring successful project delivery and enhanced design outcomes.
Also Read: How BIM is Transforming Landscape Design: Key Applications & Benefits
Learning to Use BIM for Landscape Architects
Learning BIM for landscape is important as it provides a holistic and collaborative approach to the design, construction, and management of landscape projects. Here's a breakdown of why landscape architects need to understand the fundamentals of BIM, its application in their field, implementation strategies, and its role in project management:
Fundamentals of BIM
BIM fundamentals are crucial for landscape architects to participate in collaborative design processes, create detailed digital representations, and use data for decision-making. Implementing strategies like interoperability and standardisation are essential for successful integration. Understanding BIM's role in project management optimises workflows, detects conflicts, and improves communication throughout a project's lifecycle.
Application in Landscape Architecture
BIM enables landscape architects to integrate design elements with other disciplines like architecture and civil engineering, ensuring seamless coordination of landscape features. It also provides data-driven decision-making, enabling informed choices about plant selection, material choices, and project feasibility. To successfully implement BIM, landscape architects must ensure interoperability between different software platforms and adhere to industry standards and protocols. This involves effective information exchange between different disciplines in the project. Understanding BIM standards is crucial for successful implementation, ensuring consistency in data exchange and collaboration.
Project Management
BIM provides a centralised platform for information sharing, allowing landscape architects to save time and reduce errors. It also helps in the early identification of design conflicts or clashes, preventing issues during construction. It also enhances communication and collaboration within project teams, ensuring everyone is on the same page. Therefore, landscape architects must be proficient in using BIM tools for effective communication and collaboration.
Conclusion
Integrating BIM in Landscape Architecture has helped improve communication, minimise errors, and simplify the entire design and construction process. It also helps in creating comprehensive 3D models but also in its capacity to facilitate data sharing, analysis, and decision-making among various stakeholders.
BIM in Landscape Architecture offers a holistic view of projects, allowing designers to consider environmental factors, sustainability, and long-term maintenance from the beginning. This improves design efficiency and contributes to more sustainable landscapes. The future of BIM in Landscape Architecture is promising, with enhanced interoperability between software platforms, increased cloud-based collaboration, and the integration of artificial intelligence for design optimisation. As technology advances, BIM will play a crucial role in shaping tomorrow's landscapes.
Additionally, the landscape architecture community can benefit from specialised courses catering to the industry's evolving demands. Novatr's updated BIM Professional Course for Architects is now inclusive of landscape and urban design, reflecting a forward-thinking approach. Urban designers, as integral members of the landscape architecture process, can harness the power of BIM to create more cohesive and sustainable urban environments. Novatr's commitment to incorporating the latest advancements in BIM technology ensures that professionals have the skills and knowledge necessary to thrive in the dynamic landscape architecture field.


 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!
-1.png)
.png)





