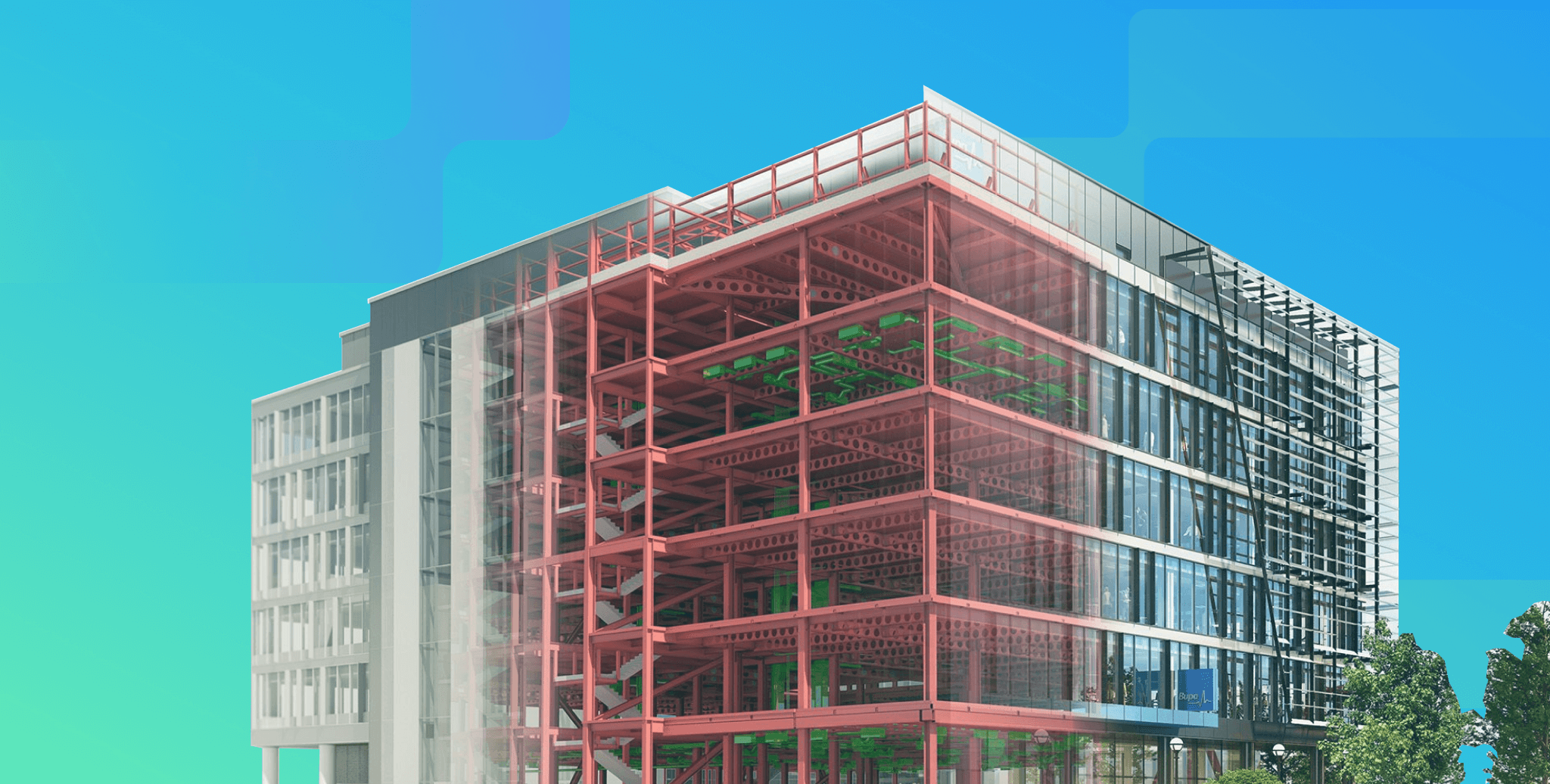
How is BIM Used in Urban Planning?
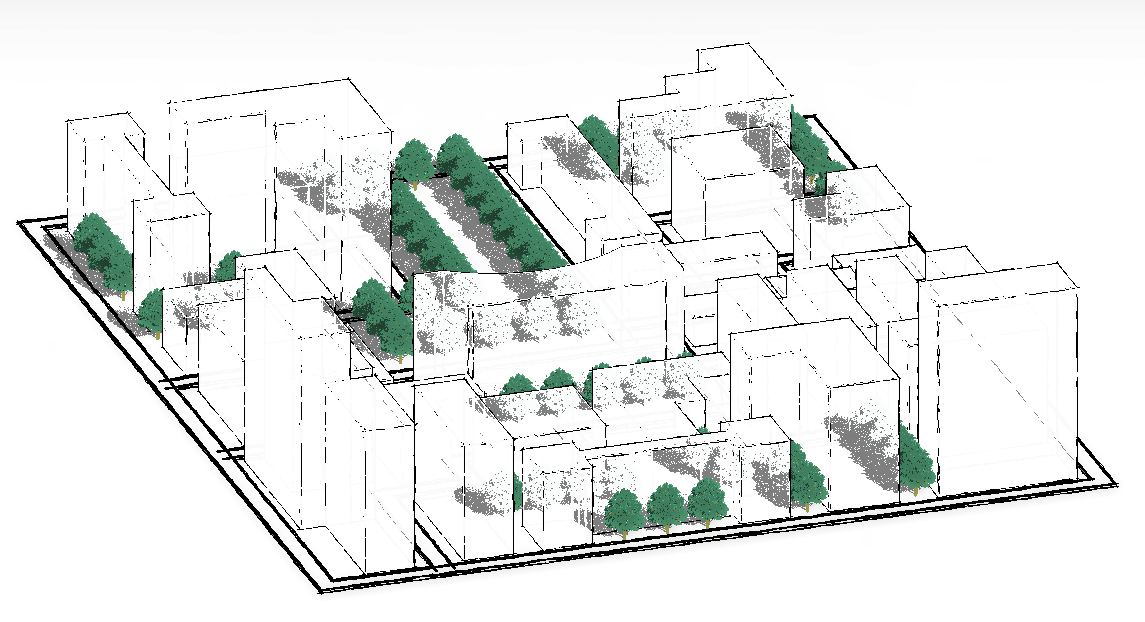
Table of Contents
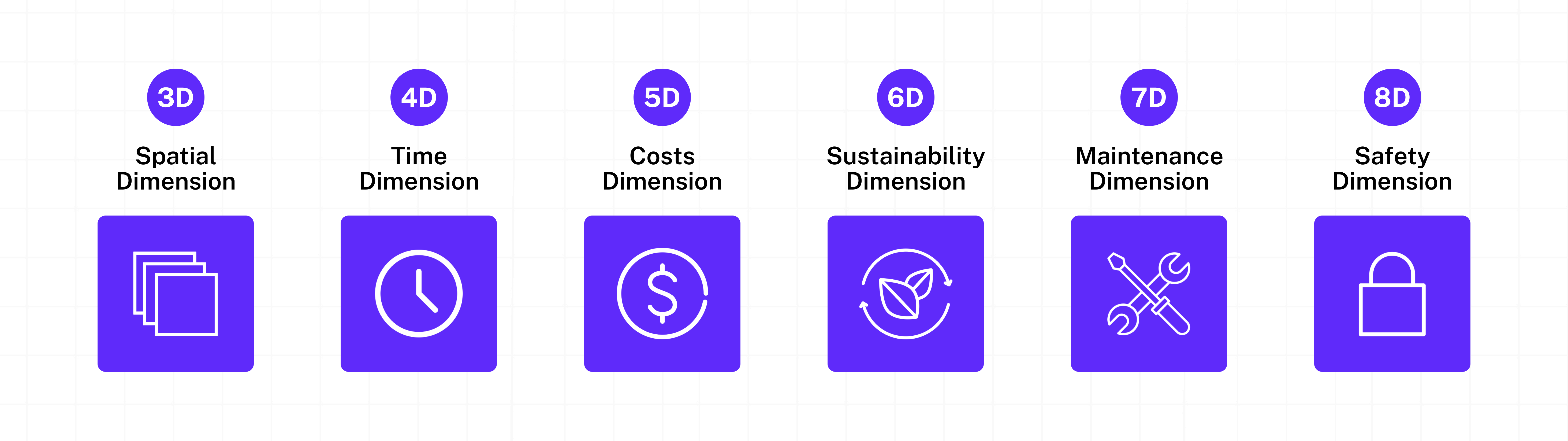
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a digital-first process of connecting the end-to-end design journey of a construction project. It creates and manages information about a built asset from a project’s conception stage to its completion, even assisting with operations and maintenance. It enables the flow of information to all the key stakeholders of the project team using tools and technologies like Revit, Navisworks, Dynamo, BIM 360, and more. BIM modelling goes beyond the traditional 2D and 3D models to incorporate 4D, 5D, 6D, 7D and 8D into a single visualisation and enables collaborative project execution with minimum errors.
This guide explains the benefits of BIM in urban design, showing how BIM enhances collaboration, accuracy, sustainability, and data-driven decision-making in large-scale city planning. It covers BIM–GIS integration, smart city applications, site analysis, and future trends. Ideal for urban designers, planners, architects, and AEC professionals looking to leverage BIM for smarter, sustainable, and future-ready urban infrastructure.
Using BIM, professionals in the AEC industry have streamlined the building process while reducing their cost, time, wastage, and much more. The significance of BIM technology, especially with the rapid digitization in construction projects across the world, has increased manifold. For instance, countries like the UK and Turkey have made BIM mandatory for all government projects while others highly prefer its use.
Given its benefits, BIM’s application in various verticals of the AEC industry is being implemented by design professionals and BIM managers across firms, and data suggests that it will only increase in the next few years thereby skyrocketing the need and demand for skilled BIM professionals. One such vertical that has found great value through the BIM modelling processes is Urban Planning. Let’s dive in!
What is Urban Planning?
Urban planning shapes how cities use land, roads, utilities, housing, and public spaces. It blends design and policy to improve daily life, manage growth, reduce risk, and support sustainable development through data-backed planning decisions.
Urban planning is a technical and socio-political process that focuses on land use and the surrounding built environment including public and private infrastructure, as well as public accessibility. It employs tools like land zoning, geographic mapping and analysis, park space analysis, water supply survey, population growth prediction, identifying transportation patterns, recognizing food supply demands, allocating healthcare and social services, and land use impact analysis to draw up the most optimised infrastructural plans. In its current form, urban planning focuses on city planning as a tool to improve the health and well-being of people while ensuring sustainable development.
How Does Urban Planning Help Urban Growth?
Urban planning guides safe expansion by aligning transport, housing, water, jobs, and public services with population needs. It reduces congestion, supports healthier neighborhoods, protects resources, and helps cities grow in a more organized and inclusive way.
Urban planning is an intricate blend of technical expertise and socio-political acumen, strategically shaping the growth and development of urban areas. Through a meticulous process that encompasses land use, infrastructure, and public accessibility, urban planning leverages a toolkit that includes land zoning, geographic mapping, park space analysis, etc. By employing these tools, urban planners create optimised infrastructural plans that cater to the growing population’s evolving needs.
In the contemporary context, urban planning emerges as a powerful instrument for fostering communities’ physical and social well-being. It goes beyond mere city development; it is a holistic approach aimed at enhancing people's lives while ensuring sustainable progress. As cities become hubs of dynamic growth, urban planning stands as a pillar, steering urban expansion towards a future that is not only thriving but also resilient and inclusive.
Also Read: Singapore Smart City: A Leading Model for Urban Innovation
What is the scope of BIM in Urban Planning?
BIM supports city-scale planning by creating data-rich models of buildings and infrastructure. It strengthens coordination, scenario testing, and performance analysis, helping teams plan smarter systems for mobility, utilities, resilience, and long-term maintenance.
The world’s urban population is rapidly increasing with thinly stretched resources. The global population currently stands at a little over 8 Billion and the latest projections suggest that it possibly will reach ~10 Billion by 2050, with 68% projected to live in urban areas. Cities alone account for 70% of worldwide emissions with the building and construction industry accounting for ~40% of the global carbon footprint.
Naturally, growing urbanisation puts immense pressure on the natural resources of cities to compete with the increasing demands for housing, transportation, water, energy systems, education, health care, waste management, access to public spaces, and more.
The biggest challenge faced by urban planners, then, is how to formulate master plans that cater to the needs of its citizens while ensuring they help achieve the goal of “net-zero carbon by 2050”.
This is where BIM comes in!
BIM in Urban Planning and the case of Smart Cities
In urban planning, BIM is used as an analysis tool to create information-rich, digital models consisting of streets, buildings, water supply, parks, and other infrastructure. These models are then visualised and analysed to assess the proposed development’s efficacy and impact. Using BIM models, planners can build urban ecosystems that are data-backed, tech-fuelled, interconnected, innovative, citizen-centric and most importantly, inspire sustainable construction– a standard revered by many but achieved by a few. A case in point is the Smart City model.
Smart Cities - The embodiment of a smart and sustainable urban future
Smart Cities are tech-forward, planned urban areas that leverage information and communication technologies (ICT) to gather specific data and use it to optimise the way the city functions while improving the quality of life for its citizens. In India, they fall under the urban renewal and retrofitting program by the government to make cities more people and environment-friendly.
Smart city projects use master planning of urban areas with multiple professionals and agencies involved in the infrastructural development- both public and private. Working in a vacuum from other components means falling for the same traditional decision-making and operational pitfalls. These may include last-minute monumental changes in the built structure, data corruption, delayed project completions, monetary and resource loss, public inconvenience, a higher carbon footprint, and so on. Additionally, Smart Cities built with BIM are inherently tech and data-forward. Hence, any planning warrants the use of tools compatible with the core values of the city.
At the core of smart cities lies the Internet of Things (IoT) - a network of connected devices like sensors in home appliances, vehicles, etc., that can communicate and exchange data. This data is stored in the cloud/servers which is then used to create an amalgamation of the digital and physical city components for better planning and governance by urban designers.
- sustainability,
- increased efficiency, collaboration and communication,
- equitable information dissemination,
- time and cost-effectiveness,
- powered by data,
- transparency, and so on.
Smart cities are just one example where BIM can help urban planners build optimised and smart infrastructure that meets the needs of the citizens and accommodates green building standards. With the goal of achieving net zero emissions, initially set by the Paris Agreement, efforts are being made globally to reduce the carbon footprint of the construction industry.
So far we have explored what BIM technology is and its scope in urban planning. But before we get into the how of things, let us look at why planners should use BIM in urban infrastructure projects.
What are the Benefits of Using BIM in Urban Planning?
The benefits of BIM in urban design include better coordination across agencies, fewer design errors, faster reviews, and clearer visual models for public and stakeholder feedback. BIM also supports schedule planning and greener choices through early analysis.
The current trend of planning and design and development of Smart Cities offers us a sneak peek into the scale of BIM and other technological adoption that will occur in the next couple of decades. It is expected to completely transform the way the AEC industry operates. For urban planners too, there are many upsides to tech adoption. Let’s look at some of the key benefits urban planners can reap by using BIM:
1. Better collaboration
The essence of BIM is that it facilitates the collection and dissemination of information through every stage of the building process. As discussed above, urban development projects like smart cities, metros, etc. are usually large-scale and have multiple design teams and agencies involved. BIM eliminates the communication gap that leads to increased collaboration between teams and agencies and fosters an environment of data-led decision-making.
2. Greater accuracy
Every BIM project is grounded in data. Urban planning techniques like site analysis and data visualization coupled with seamless data sharing enable early error detection in the plan laid out.
Take the example of Dubai’s Museum of the Future designed by the architectural firm, Killa Design. Using BIM software, the team created immersive visualizations in the planning & design stage that allowed all professionals across the industry and decision-makers (public & private) to walk through the entire museum and examine each element for flaws. Similarly, urban planners too can create visual models, find design flaws in the early stages, geographically analyze the design’s interaction with surrounding elements and environment, incorporate the observations and fully optimize master plans with increased accuracy at the time of building.
3. Early error detection
Early error detection means fixes to the plan are made before starting the actual building process. Using BIM technology, urban planners can reduce the margin of error and waste of resources like money, labour, and time considerably thereby increasing the accuracy of the design process.

4. Reduced public inconvenience
Urban Planning projects are undertaken to improve the quality of life of inhabiting citizens but given their scale, the construction process itself can cause inconveniences to the users. Restricted access to excavated roads and land in urban infrastructural projects can cause traffic, pollution, etc. BIM technologies allow urban designers and planners to explore modular prefabricated construction - a method where components of a built environment are constructed elsewhere and only brought to the actual project site for assembly. It decreases on-site construction time and helps maintain the surrounding residents' quality of life and safety. BIM is transforming the experience of urban infrastructural developments for both planners and citizens.
5. Reduced project delays
With BIM-driven collaboration, accuracy, early error detection, pre-fabrication, robust visualization, and more, the end-to-end process of planning and building becomes highly streamlined with each stakeholder aware of the project elements dependent on them. There is greater visibility, transparency and structure to the way urban infrastructures are planned and developed which results in shorter project timelines.
6. Increased sustainability
Better collaboration between project teams leads to early problem detection, refined accuracy, expedited project deliveries and less public inconvenience. These are the operational benefits of using BIM in Urban Planning. There is a larger, more critical benefit that urban planners and the community as a whole can reap - a sustainable, energy-efficient, long-lasting built environment.
BIM’s inherent transparency, data collection and dissemination, and the ability to use advanced analytics to predict a building's operational performance before it is even built enable architects and urban designers to instil elements of energy efficiency into the built structure from the very outset of the project.
BIM-driven urban projects also increase construction sustainability by reducing waste. Using BIM, planners can create detailed virtual models of the entire plan, analyse how the proposed built environment interacts with surrounding and pre-existing city components, and identify clashes and design errors before starting construction to reduce the total waste generated in the entire project lifecycle. They can then leverage BIM 3-D modelling to find construction materials with the least ecological footprint by examining and comparing the embodied energy and global warming potential of different materials.
To summarize, urban planners can leverage BIM technology to plan and create smarter, healthier, liveable cities that can sustainably cater to the needs of the ever-expanding urban population.
Also Read: 15 Best Urban Design & Planning Software To Learn
BIM Techniques for Urban Planning
Urban teams use BIM for site analysis, phasing, and simulation, then connect it with GIS layers for deeper location insights. This supports evidence-based decisions on zoning, access, utilities, environmental impact, and sustainable infrastructure planning.
1. Site analysis with BIM
Site analysis is the pre-design stage of planning that entails examining the site’s geographical, climatic, demographic, historical, legal, and infrastructural conditions. It is one of the most critical elements of a planning process as building infrastructures does not happen in isolation from the environment in which it is being built from the socio-political, topographic and morphological elements.
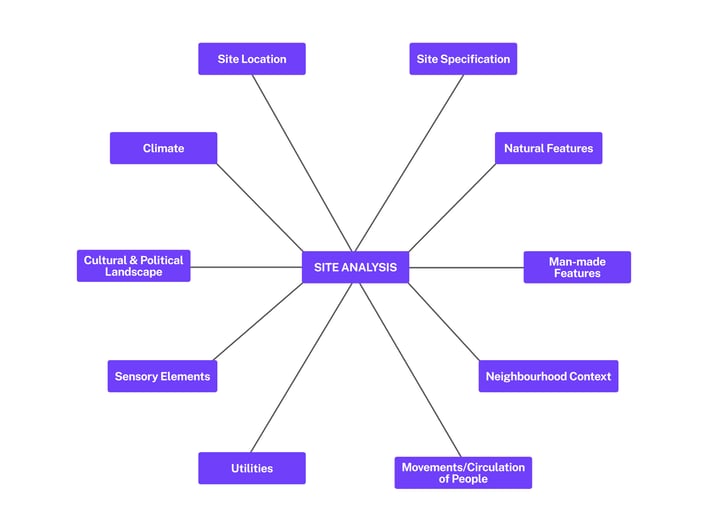
Collating all these data points in the BIM 3-D model helps planners visualise the site in its entirety and collaborate efficiently with all stakeholders for early error detection and plan optimization.
Additionally, we are at a critical stage in human history where our very existence as a species is under threat due to the rapidly changing climate and its subsequent effects on our planet. Building materials, structures, utilities, etc. that work today may become redundant in the next few years. Additionally, even the soil on which the structures, roads, etc. are built today may fundamentally transform its nature in the next decade or so as a result of climate-triggered change.
Therefore, planners need to combine site analysis with climate change scenarios which can only be achieved by leveraging technologies like BIM, Geographic Information System (GIS), etc. Precipitation and satellite data can help account for the future possibility of floods, landslides, and extreme precipitation. Temperature predictions can help planners plan for future droughts or heat waves. The list is endless and the opportunities are ready to be tapped into. BIM technology lets urban planners analyse historical, current, and future contexts in their site analysis which helps in the construction of future-ready built environments that can withstand the test of time.
2. Integrating BIM and GIS for data-driven urban planning
Geographical Information System (GIS) is a computer system that creates, stores, analyses and maps geographical data. It gathers spatial and attribute data (or tabular data), and combines the two for the best possible visual plotting of any part of the earth. The pin location of a hospital, for example, is spatial data. Additional information about the hospital like its name, treatments it offers, capacity, etc., are attributed data.

Put simply, much like BIM, GIS leverages gathered raw data to visually represent the characteristics of unique locations. Visualisation of this data is done in multiple ways ranging from Point Data (e.g. exact pin location on a map) to Polygons (e.g. mapping entire cities or states).
In recent years, AEC professionals have increasingly started using BIM for construction or advocating for its use – starting from the planning stage to building and maintenance. And the goal of achieving net neutrality gives it an added push. Naturally, BIM usage has also been gaining impetus in urban design and planning.
For instance, the London Underground Station’s Capacity Assessment Tool – a software that integrates BIM and GIS improves passenger flow management. It uses BIM data to create 3D models of the stations and GIS data to create passenger flow simulations, enabling planners to optimize station design for reduced congestion.
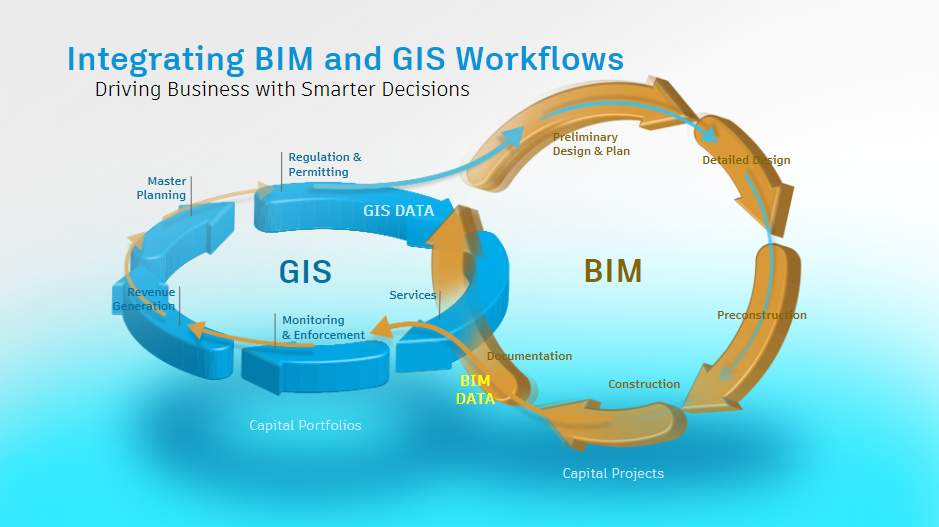
The most crucial upside to integrating BIM & GIS is the precision with which it allows urban planners to seamlessly move from a bird’s-eye-view analysis to examining specific elements and features of the built infrastructure’s plan, and then going beyond the site plan to the larger city, state, country or even the world - all backed by data.
Also Read: The Ultimate Career Guide to Urban Designer: Roles & Salaries
3. BIM and Sustainable Urban Planning
We’ve already explored much of how using BIM in urban planning can lead to a more sustainable future in the previous sections – less wastage, energy-efficient building plans, pre-fabrication with greater accuracy, and infrastructures with longer lifetimes. The example of Smart Cities detailed above is one key example of how BIM-tech fits into the global mission of forging a sustainable future.
The images above show different design visualisations of a single urban development project. Such visualization has only been made possible with the introduction of technologies like BIM in urban planning and design. By feeding pedestrian and traffic movement data gathered during the site analysis phase, planners can run multiple life-like stimulations, visualize pedestrian and traffic movement, and find the best possible layout that will suit the current as well as future population.
Without BIM use, planners risk proposing plans that limit the way the public accesses the built infrastructure but also end up demolishing and re-developing what’s been built based on the flawed plan. This leads to increased wastage, a shorter lifecycle of the built environment, and higher carbon emissions - a vicious cycle yesteryear planners constantly struggled with.
By becoming the single source of data and truth, BIM helps plan and execute more sustainable, better risk-managed urban planning that can accommodate current and future demands without putting a strain on available natural resources and existing urban infrastructure.
Future of BIM in Urban Planning
BIM is moving toward smarter, connected city systems through BIM–GIS workflows, digital twins, and real-time data from sensors. This supports faster planning updates, better risk forecasting, and more sustainable development across growing urban regions.
Consider these two statements -- Construction and buildings account for ~40% of the global carbon footprint.
- At the 2026 United Nations Climate Change Conference of the Parties (COP27), the United States launched the Net-Zero Government Initiative, inviting governments to lead by example and achieve net-zero emissions from national government operations by no later than 2050.
Urbanization is at its peak. Climate change is the reality of the hour. So how do urban planners and designers accommodate the needs of the rapidly growing urban population for various amenities like housing, water, transportation, recreation, energy systems and more?
BIM adoption in urban planning in recent years has increased manifold and is only expected to rise further. Countries like the US and UK that are at the forefront of BIM adoption have undertaken massive efforts to accelerate its integration with initiatives like mandated BIM application for all major construction and renovation projects, setting up BIM standards and guidelines, establishing task forces for ensuring effective BIM implementation, introducing BIM in educational curriculums, to name a few.
In Asia, Singapore has set the benchmark for using data for urban planning and BIM adoption. Winning the award of the smartest city in the world drives the point home!
Can you guess what’s common between these urban infrastructure projects – the Central Vista in Delhi, the Personal Rapid Transit System at Amritsar, the Bangalore International Airport, the Nagpur Metro Rail Corporation and the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation?
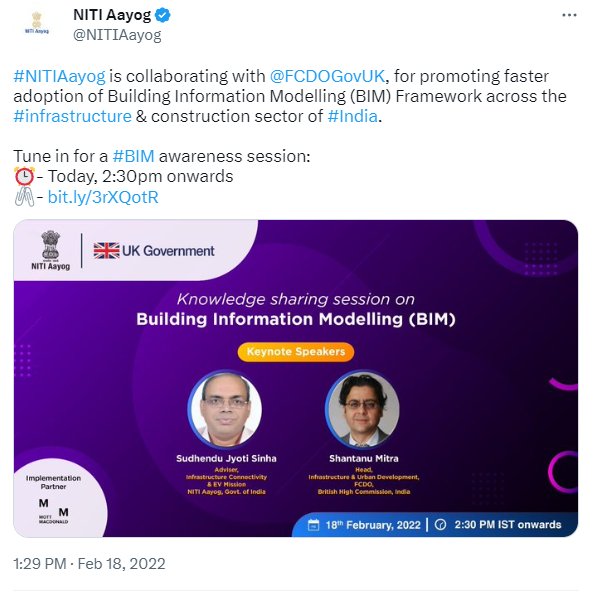
They are all large-scale government projects that are BIM-driven! And, the recent collaboration between NITI Aayog (a public policy think tank of the Government of India) and the UK Government is another step towards increased BIM adoption in India meaning more demand for BIM-skilled professionals.
Best 3 Places to Learn Urban Planning
In the dynamic urban planning field, it's crucial to align oneself with educational platforms that provide theoretical knowledge and practical insights into contemporary tools. Given below are three different courses for aspiring urban planners, offering immersive educational experiences that go beyond traditional paradigms. Through a blend of theoretical frameworks and hands-on tools, these platforms empower students and professionals to contribute meaningfully to the evolution of our cities.
1. Novatr's BIM Professional Course
We have talked about how BIM is used in Urban Planning extensively and in order to stay updated with the industry trends and applications, one must upskill at the right time! Novatr's BIM Professional Course offers a unique perspective by integrating BIM technologies. This course is an excellent choice for individuals seeking a broader understanding of urban development, incorporating innovative tools and methodologies. By exploring the intersection of BIM and urban planning, participants gain insights into the evolving landscape of city design and infrastructure development. Novatr offers one-to-one mentorship and guaranteed placement assistance.
2. BIM-Ready Complete Course by TechnoStruct Academy
Technostruct Academy offers a BIM-Ready Complete course that covers Architectural, Structural, Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing, and Fire suppression (ASMEPF) along with open BIM and Interoperablity. One can learn about all BIM software, optimal methodologies, multiple project lifecycles, and end-to-end project workflow. This academy also offers a Final Project Internship and personalised mentorship along with daily guidance and interaction from industry experts. Technostruct also offer placement opportunities that is tailored to your passion and career path.
3. BIM for Infrastructure by BIMLabs
BIM Labs offer BIM for Infrastructure for students interested in learning and understanding urban planning. The institute provides the platform and the required tools to plan, design, construct, and manage buildings and infrastructure. The main categories in this course are Road development and Land development that provide insights to plan, design, and build highways and bridges. BIMLabs also offer placement opportunities after the course completion.
Also Read: Navisworks Courses and Tutorials Guide
Conclusion
Owing to growing urbanisation, projections are that in the next 25 years, we will build infrastructure which will be equivalent to the total built development in the last 200 years. This mammoth feat can only be pulled off with the optimum confluence and use of technologies like BIM, GIS, Computational Design, etc. It’s safe to say that BIM is guaranteed to play a central role in major urban development and redevelopment projects globally.
A beacon in this paradigm shift,
the BIM Professional Course for Architects offered by Novatr provides a gateway to understanding and mastering BIM. For those ready to ride the wave of change, explore additional insights on BIM and its potential through our Resource Page.
FAQs
1) What are the benefits of urban design?
Urban design improves walkability, safety, and public space quality. It supports smoother traffic flow, stronger local identity, better access to parks and services, and more resilient neighborhoods through thoughtful layout, lighting, and human-scale planning.
2) What are the four pillars of BIM?
The four pillars of BIM are people, process, technology, and data. Together, they support consistent modeling standards, clear collaboration workflows, reliable tools, and accurate information sharing across design, construction, and long-term operations.
3) What are the 5 D’s of urban planning?
The “5 D’s” often refer to Density, Diversity, Design, Destination accessibility, and Distance to transit. These factors shape how people move, how neighborhoods function, and how cities reduce congestion while supporting healthier mobility options.
4) What is BIM and its advantages and disadvantages?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) creates a shared digital model for planning and delivery. Advantages include coordination, clash checks, and stronger accuracy. Disadvantages can include training costs, software expense, and workflow change during early adoption.
5) What are the 7 C’s of urban design?
The 7 C’s of urban design commonly focus on comfort, connectivity, convenience, clarity, character, choice, and community. Together, they support safer streets, easier navigation, stronger public spaces, and neighborhoods that work well for daily life.


 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!
.jpg)
.png)