Laser Scanning in Construction: Everything You Need to Know
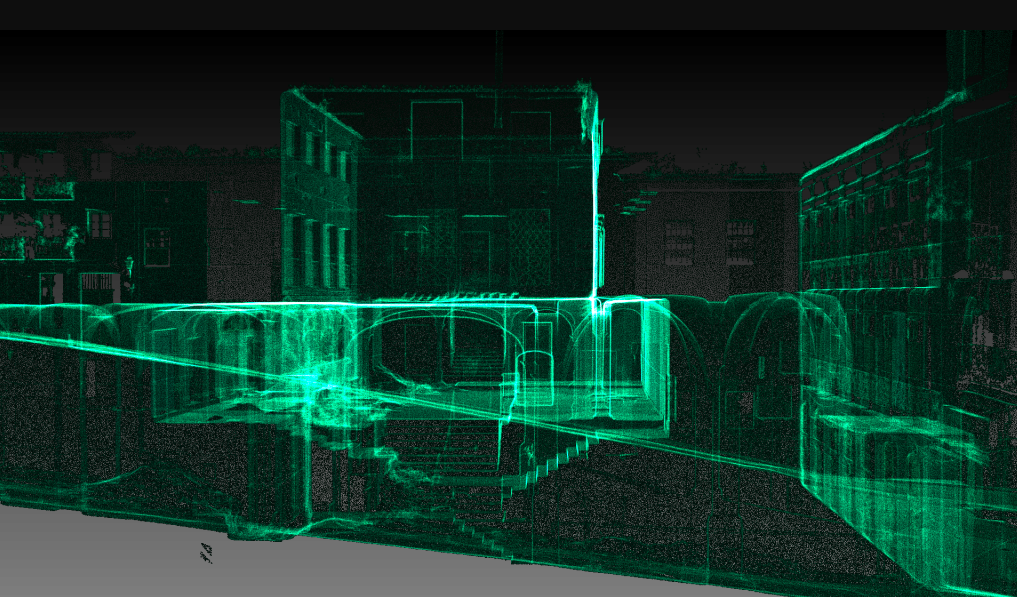
Table of Contents
Laser scanning is not a new technology, albeit it only started getting implemented in the architecture, engineering and construction (AEC) industry around the 1990s. According to industry research, owing to the accuracy of 3D laser scanning of buildings in the construction industry, the demand for the technology has increased by 57%, with the market expected to grow by 10 billion USD by 2026.
What is Laser Scanning in Construction Industry?

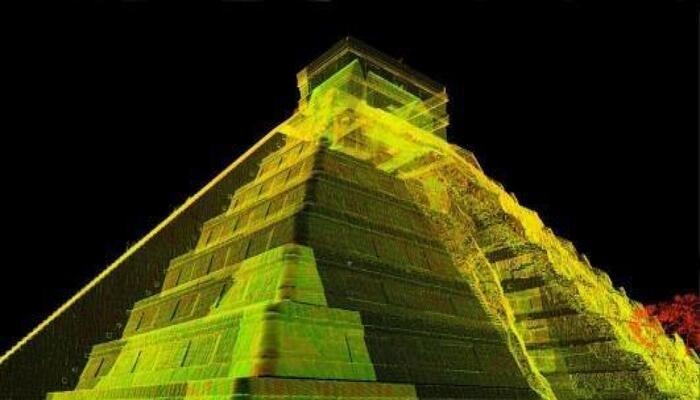
3D Laser scanning, also known as high-definition surveying (HDS) or reality capture, is a technology that uses laser beams to create precise 3D models of construction sites, buildings, and structures. It works by capturing millions of data points forming a point cloud that accurately represents the scanned environment. This technology enhances accuracy, reduces errors, and streamlines project workflows.
In construction, laser scanning is used at various stages of a project:
1. Pre-Construction & Design:
Before building begins, laser scans provide detailed site measurements, helping architects and engineers create accurate Building Information Modeling (BIM) models and identify potential design conflicts.
2. During Construction:
By detecting clashes between systems like electrical, plumbing, and HVAC, laser scanning improves coordination and prevents costly errors. It also allows teams to track progress by comparing the actual build to the original plans.
3. Post-Construction & Maintenance:
Once the project is completed, the 3D scans serve as as-built records, assisting with facility management, renovations, and future expansions.
By incorporating laser scanning into construction projects, teams can improve efficiency, enhance collaboration, and ensure greater precision throughout the building process.
Read: Site Analysis Categories You Need to Cover For Your Architecture Thesis Project
5 Benefits of 3D Laser Scanning in Construction Industry
3D laser scanning is empowering the AEC industry to think, design, and build better, one scan at a time. Leica Geosystems, Trimble Inc., Topcon Corporation, and Autodesk Inc. are some of the fundamental global companies leading the way forward for 3D laser scanning in the AEC industry.
Let’s have a look at the benefits of 3D laser scanning in construction industry.
1. Enhanced Accuracy and Quality
Laser scanning captures exact measurements of construction sites with millimeter-level accuracy. This reduces human error, ensures that designs fit real-world conditions, and minimises costly mistakes or rework. It is especially useful for complex projects where precision is critical.
2. Rapid Data Collection
Unlike traditional surveying methods, laser scanning collects millions of data points in seconds, allowing teams to document entire construction sites quickly. This speeds up project planning, reduces site visit requirements, and provides real-time insights for better decision-making.
3. Cost Reduction
By reducing manual labor, preventing rework, and streamlining workflows, laser scanning helps lower overall project costs. Fewer site visits, quicker inspections, and early detection of design issues contribute to savings of up to 50% compared to conventional methods.
4. Improved Collaboration and Coordination
Laser scanning provides a highly detailed 3D model that serves as a single source of truth for all project stakeholders. Architects, engineers, and contractors can use this model to detect design clashes.
5. Comprehensive Documentation
The technology creates precise as-built records that serve as a valuable reference for facility management, future renovations, and expansions. These digital records help ensure that any modifications are based on accurate existing conditions, improving long-term maintenance and operational efficiency.
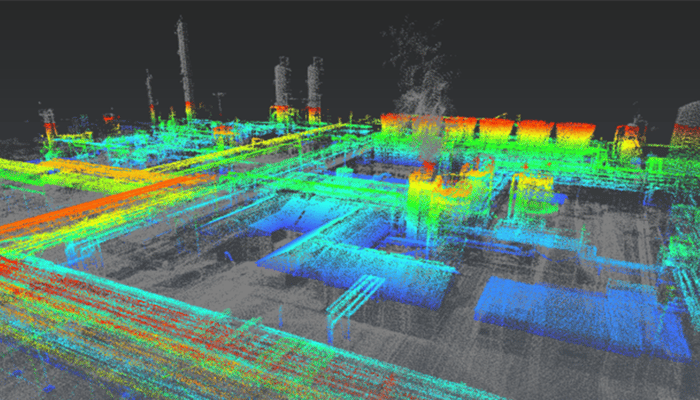
Application of 3D Laser Scanning in the AEC Industry
Ranging from site documentation and design to construction sequencing and building systems management, 3D laser scanning has wide applications in the AEC industry. Let’s have a look at the fundamental 3D laser scanning applications in the design and build sector.
1. As-Built Documentation Drawings
3D laser scanning is a speedy and accurate method for conducting as-built surveys. It enables professionals to capture existing building conditions and generate highly detailed point cloud data. This information serves as the foundation for structural modifications, renovations, and retrofitting projects, enhancing space usage optimization and eliminating the need for manual measurements and minimizing errors in project documentation.
2. Construction Planning and Management
3D laser scanning plays a vital role in verifying construction progress and ensuring adherence to design intent. By comparing point cloud data with working drawings, professionals can identify discrepancies, clashes, or deviations early in the construction process. 3D laser scanning can also help in manufacturing rightly-sized and shaped prefabricated building components. It also enables sequencing and scheduling thereby allowing project stakeholders to reduce conflicts, optimize construction workflows, and improve overall project efficiency.
Read: BIM 360: The Essential BIM Construction Management Tool For All Stakeholders
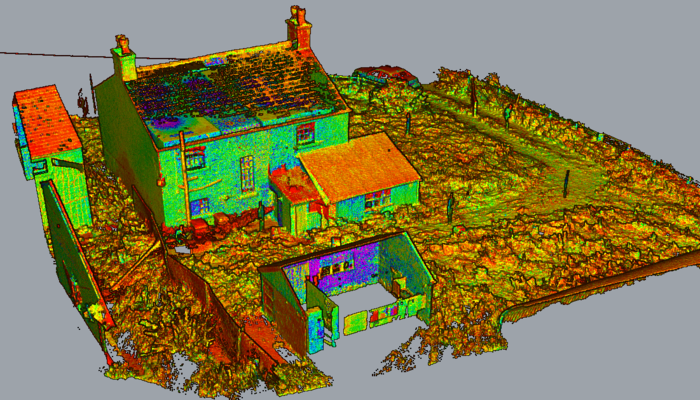
3. Architectural Documentation and Historical Preservation
In architectural documentation and historical preservation projects, 3D laser scanning is invaluable. It captures intricate details of heritage sites, buildings, or artifacts with exceptional accuracy. This data serves as a comprehensive digital archive, aiding in documentation, analysis, restoration, and preservation efforts. 3D laser scanning for heritage buildings ensures the preservation of cultural heritage while enabling experts to study and restore structures appropriately.
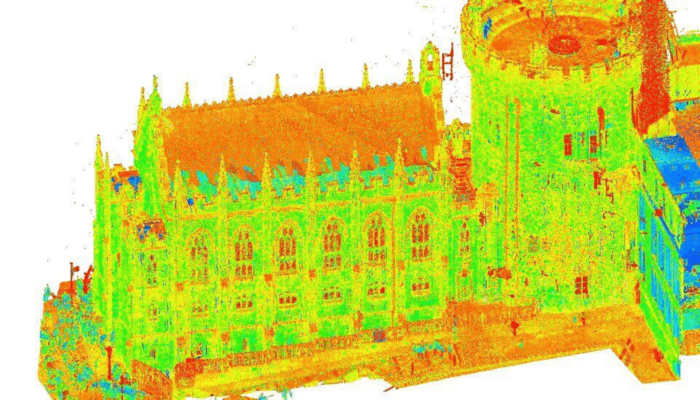
Read: The Powerful Influence of Colonization in India: History and Architecture
4. Virtual Design and Construction (VDC)
3D laser scanning integrates seamlessly with Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) workflows. By combining point cloud data with BIM models, VDC professionals can create immersive virtual environments for design visualization, stakeholder engagement, and project coordination. This technology enhances communication and collaboration among project teams, resulting in improved project outcomes.
5. Facility Coordination
In large-scale facilities, such as factories, warehouses, or hospitals, 3D laser scanning assists in facility coordination. It enables professionals to capture precise measurements of complex built environments, including equipment, utilities, and structural elements. This data aids in facility management, maintenance planning, and operational efficiency.
6. Collecting Geospatial Data
3D laser scanning is instrumental in collecting geospatial data for various applications. By combining laser scanning with Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) or aerial LiDAR, professionals can create highly accurate 3D models of terrain, landscapes, or infrastructure. This data is essential for urban planning, environmental analysis, and geospatial mapping.
7. Creating Digital Twin Solutions
In recent times, the concept of digital twins has gained traction in the AEC industry. 3D laser scanning can play a crucial role in creating digital twin solutions by capturing the as-built conditions of structures. These digital twins provide real-time insights, allowing stakeholders to monitor performance, conduct simulations, and optimize operations throughout the lifecycle of a project.
Challenges in Laser Scanning
1. Environmental Challenges:
Rain, fog, and extreme lighting can interfere with laser accuracy, while reflective or transparent surfaces (like glass and water) may cause distortions.
2. Hardware & Cost:
High-end scanners are expensive, have limited range, and require frequent recharging, making large-scale or outdoor scanning challenging.
3. Data Processing Issues:
Large file sizes demand powerful computing, while software compatibility and noise removal add complexity to post-processing.
4. Scanning Limitations:
Hard-to-reach areas, occlusions from obstacles, and scanning moving objects can result in incomplete or inaccurate data.
Essential 3D Laser Scanning Equipment for the AEC Industry

The equipment required for scanning a building with a 3D laser scanner would depend upon the scale of a structure, the desired level of detail, and project requirements. Having said that, below are the key equipment that are vital to undertake a 3D laser scanning job.
1. 3D Laser Scanner
A 3D laser scanner is the primary device used to capture detailed 3D measurements of objects and structures. There are various types of laser scanners available such as terrestrial scanners, handheld scanners, and mobile scanners, each with different capabilities and applications.
2. Tripod or Mounting System
A stable tripod or mounting system is used to securely position the laser scanner at the desired height and angle during scanning. It ensures consistent and accurate data capture.
3. Targets or Reference Points
These are markers placed strategically in the scanning area to aid in the registration and alignment of multiple scans. Targets can be retro-reflective spheres or specialized targets recognized by the scanning software.
4. Laptop or Tablet
A high-performance laptop or tablet is required to control the scanner, manage the scanning process, and store the captured data. It should meet the system requirements specified by the scanner manufacturer and have sufficient storage capacity.
5. Batteries and Chargers
Laser scanners are typically powered by rechargeable batteries. It's important to have spare batteries and chargers to ensure uninterrupted scanning sessions, especially when working in remote locations.
6. Data Storage
Since 3D laser scanning generates large datasets, it's crucial to have ample storage capacity. External hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), or network storage solutions can be used to store and manage the captured point cloud data.
7. Software
Specialized 3D scanning software is required to control the scanner, process the captured data, and create detailed 3D models. Examples of popular software include Autodesk ReCap, Leica Cyclone, and Faro Scene.
In Conclusion
Technologies such as 3D laser scanning are enabling the AEC industry to become smarter. With time, the portability and accessibility of 3D laser scanning technology is expected to improve, thus making it more feasible for on-site and remote scanning applications. Additionally, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms with 3D laser scanners will also contribute to automated data interpretation. This will enable faster and more accurate analysis of complex datasets thereby opening new avenues for design thinking and construction.
If 3D laser scanning processes interest you, you must check out Novatr’s cohort-based program called BIM Professional Course. By enrolling for the course, you can master 7+ BIM software and industry workflows, learn from industry stalwarts, and work on a capstone project to hone your skills. Explore the course today.

 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!
-1.png)
.png)






