Singapore Smart City: A Leading Model for Urban Innovation
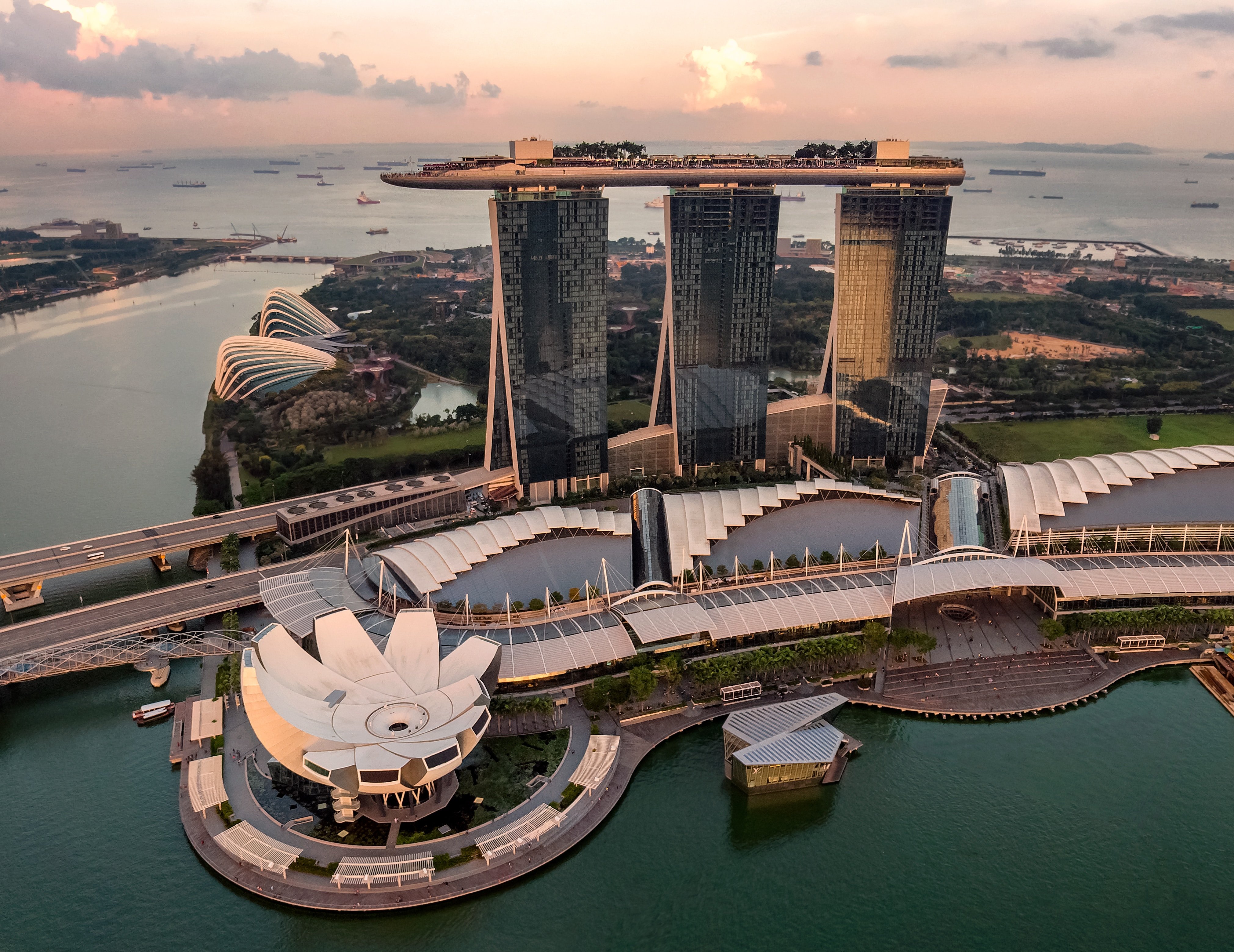

Table of Contents
Singapore is widely recognized as one of the world's leading smart cities. To enhance the standard of living for its citizens and make the city more sustainable, practical, and livable, the city has put into practice a wide range of technologies and initiatives.
In 2014, Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong launched the Smart Nation initiative and three years later benefited from a government injection of SGD$2.4 billion. Today 90% of Singapore’s population uses smartphones making it easy to digitalise systems be it education or healthcare.
In this blog, we will explore what makes Singapore one of the most innovative cities in the world. We will look at how Singapore has leveraged technology to improve various aspects of urban living, including transportation, public safety, and health care.

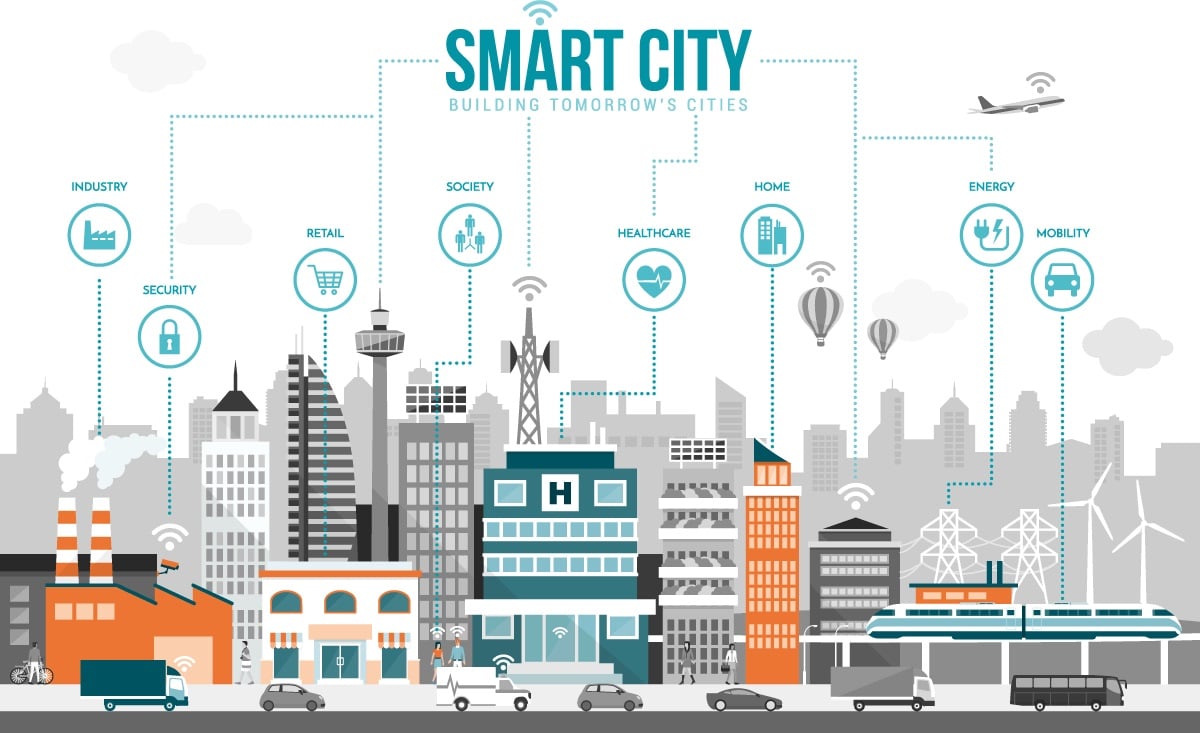
What is a Smart City?
A smart city describes a city that uses technology and data to improve the quality of life for its residents by making the city efficient, sustainable, and livable.
A smart city incorporates a variety of technologies in its design, such as sensors, data analytics, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and artificial intelligence (AI) systems to collect and analyze data about the city's infrastructure, environment, and residents. This data can be used to make informed decisions about how to improve city services, reduce energy consumption, optimize transportation systems and enhance public safety, among other things.
Smart cities can also leverage technology to provide citizens with access to information and services, including mobile apps that enable them to pay bills, access transportation schedules, report issues to the city, and participate in civic engagement activities.
Overall, the goal of a smart city is to create a more connected, sustainable, and equitable urban environment that enhances the quality of life for all its residents.
Singapore is perhaps one of the most advanced cities in the world when it comes to applying the latest technologies for improving the quality of life of its citizens. The city-state, located in Southeast Asia, is well-known for its high living standards, excellent public infrastructure, world-class education system, and easy, efficient access to information and communication technologies. It is a city that can be described as a "smart city" in the true sense. Smart cities are the future and Singapore is leading the way.
Historical Urban Transformation of Singapore
The transformation of Singapore into a modern and prosperous city-state has been a remarkable achievement that has taken place over the past 50 years. Before its independence in 1965, Singapore was a small, overcrowded, and relatively poor trading port with few natural resources. However, through visionary leadership, strategic planning, and the hard work of its people, along with architects, urban designers and planners, and policymakers, it has achieved the status of one of the world's leading cities.
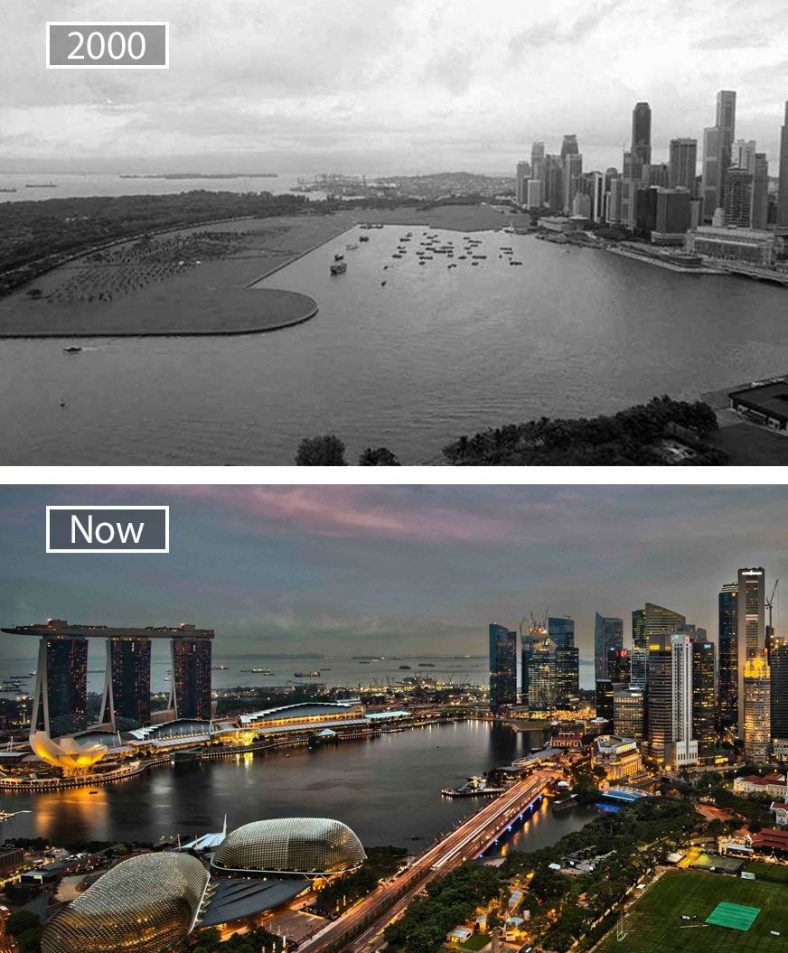

One of the key factors in Singapore's transformation has been its focus on urban planning and development. In the 1960s and 1970s, Singapore's government embarked on an ambitious program to develop new towns and public housing estates to accommodate its rapidly growing population. This program was aimed at improving living conditions for the city's residents, many of whom were living in slums and squatter settlements.
The Housing and Development Board (HDB) was established in 1960 to oversee the construction of public housing. By the 1980s, more than 80% of Singaporeans lived in HDB flats. These flats’ approach to public housing was innovative in many ways, including the use of prefabricated building components to speed up construction, the creation of high-density but livable communities, and the provision of public amenities such as schools, parks, and community centers.

Another key factor in Singapore's transformation has been its focus on economic development. In the 1960s and 1970s, the city's government pursued a policy of import substitution, seeking to develop a range of domestic industries to reduce the country's reliance on imports. This policy was later replaced by a focus on export-oriented industrialization, with particular emphasis on manufacturing, electronics, and services.
Also read: What's New in Architecture - Automation, Coding, and BIM!
The administration also put into effect several initiatives to encourage entrepreneurship and draw in foreign investment such as the formation of industrial parks, the creation of tax incentives, and the supply of funding and technical support to small and medium-sized businesses.
Singapore has implemented a range of initiatives to make the city a leading smart city.
Singapore's transformation into a smart city has been facilitated by constant investments in various fields, including transportation, healthcare, public safety, business development, and energy. Here are some examples of how these investments have contributed to Singapore's development as a smart city.
1. Transportation
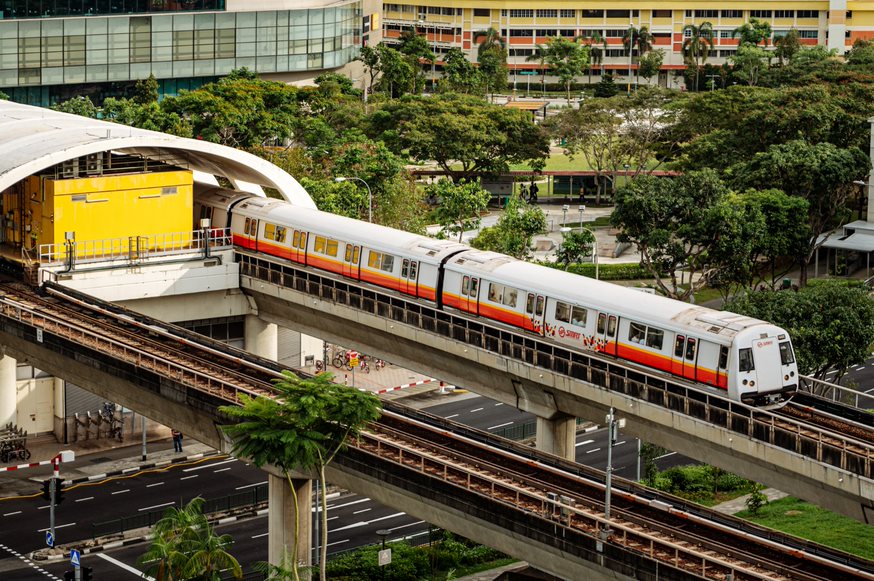
Singapore has one of the most advanced public transportation systems in the world, thanks in large part to its use of technology. The city's public transportation system is made up of buses, trains, and taxis, and each mode of transport is integrated seamlessly with the others through smart ticketing systems such as the EZ-Link card.
The city's Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) system is one of the most extensive in the world, with over 200 km of track and 119 stations. The system carries over 3 million passengers every day and is known for its reliability and efficiency. The system uses innovative technologies, including automatic train control, intelligent signaling systems, and real-time passenger information displays that provide information on train arrivals and departures. This not only helps commuters plan their journeys but also helps reduce overcrowding at individual stations.

In addition to the MRT, Singapore is also investing in driverless cars and drones to improve transportation. In 2016, the city-state launched a pilot program for autonomous taxis, which allows users to hail a self-driving cab using a specially designed mobile app. Meanwhile, the use of drones for crowd monitoring and security surveillance has also been successfully tested in Singapore.
2. Energy
Singapore is home to some of the most energy-efficient buildings in the world, thanks to the use of innovative building materials, energy-efficient systems, and technologies. The city-state has set a goal for 80% of its entire buildings to be green by 2030. The use of green buildings isn't just a matter of environmental responsibility; it's also a smart business decision. Green buildings are more energy-efficient than traditional buildings and can save on operational costs in the long run.
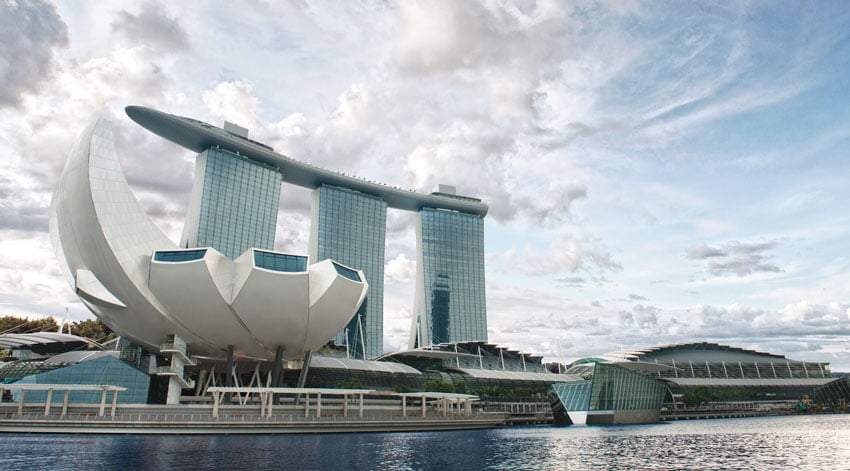
One of the most notable examples of energy-efficient buildings in Singapore is the Marina Bay Sands complex. The complex uses a range of technologies, such as rainwater harvesting and energy-efficient lighting systems to reduce its environmental impact. The complex's three towers are also fitted with a system that captures and recycles waste heat from air conditioning units, which is then used to heat the water in the hotel's swimming pools.

3. Waste Management
Waste management is an essential issue for any urban area and Singapore has been working towards resolving this problem through a combination of technology and innovation. One of the efforts towards this has come in the form of implementation of the National Recycling Program which encourages residents to recycle and compost their waste.
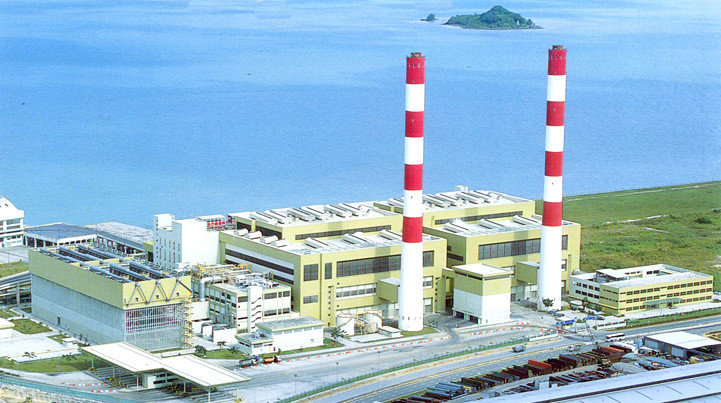

Singapore also has a groundbreaking approach to its waste management system. Instead of relying on traditional landfills, the city-state has built a waste-to-energy plant that converts waste into electricity. The Tuas South Incineration Plant is the world's largest waste incineration facility generating electricity by incinerating waste. The facility can reduce the city’s waste volume by 90% and generates enough electricity to power over 60,000 homes.
Also Read: How BIM is Enhancing Urban Design: A Comprehensive Guide
4. Public Safety
Singapore has long been known for its low crime rates and technology has played a significant role in maintaining public safety in the city-state. One of Singapore's most widespread systems for public safety is closed-circuit television (CCTV). The city-state is home to over 100,000 surveillance cameras that provide real-time surveillance of public spaces.
The city has also invested in facial recognition and biometric technologies to help identify and track potential threats in the city. For example, the island state has implemented a facial recognition system that can detect when a person is wearing a mask. This system is particularly useful for identifying potential security threats in public spaces.

5. Healthcare
Singapore has one of the best healthcare systems in the world, thanks to its focus on technology and innovation. The city-state has invested heavily in telemedicine which allows doctors to communicate with patients remotely. This has greatly improved access to healthcare, particularly for residents who live in remote areas of the country.
The city has also implemented a range of other technologies to improve the quality of healthcare in the city-state. For example, the country has a national electronic medical record system that allows doctors to access a patient's medical history from any hospital or clinic in the country. This not only improves patient care but also helps reduce waiting hours and saves time and money for patients.
Being a Smart City has benefitted Singapore in many ways.
- Improving Efficiency: Smart technologies and policies in Singapore have helped to improve the efficiency of various systems such as transportation, healthcare, and energy. It has enabled the city to operate more effectively, reduce costs, and provide better services to its residents.
- Enhancing Safety and Security: Smart technologies such as surveillance cameras, biometric systems, and real-time monitoring have helped improve Singapore's citizens' safety and security. This has helped to reduce crime rates and provide a greater sense of security for residents and visitors alike.
- Promoting Sustainability: Singapore's focus on sustainability has helped to reduce its carbon footprint and promote environmental stewardship. This includes initiatives such as renewable energy infrastructure, electric vehicle incentives, and the incorporation of sustainable building practices.
- Boosting Economic Growth: Singapore's investment in technology and innovation has helped attract talent and investment to the city, driving economic growth and creating new opportunities for its residents. This has helped to establish Singapore as a leading hub for technology startups and innovation in the region.
- Improving Quality of Life: Smart technologies and policies have helped to improve the overall quality of life for residents in Singapore by providing better access to services, reducing congestion and pollution, and promoting more sustainable and healthy lifestyles.
Cities around the world are increasingly looking to adopt smart city technologies and strategies to improve their functioning, enhance the quality of life for residents, and reduce their environmental impact. Here are some ways cities can make changes to become “smart”:
.png?width=1629&height=834&name=Screenshot%20(71).png)
-
Smart cities leverage a variety of technology-driven approaches to enhance the quality of life for their residents while promoting sustainability. To better understand the needs of its citizens and optimize city services such as traffic management, waste management, and energy consumption, they use data and analytics.
-
Smart cities also implement the Internet of Things (IoT) and other connected technologies to improve services such as lighting, parking, and public transportation, which helps reduce energy consumption, enhance public safety, and improve traffic flow. Sustainable transportation options like bike-sharing, car-sharing, and electric vehicles are prioritized to reduce traffic congestion and emissions, and technology is used to optimize traffic flow and improve public transportation systems.
-
Smart grid technologies and energy management systems are used to improve energy efficiency, reduce waste, and promote renewable energy sources. Public safety is enhanced through the use of technology such as video surveillance, gunshot detection systems, and emergency response systems. Citizen engagement is promoted through the use of technology such as mobile apps, social media, and online platforms, providing residents with access to information and services.
Finally, smart building technologies that employ sensors and automation to optimize building operations and reduce energy consumption are also implemented in smart cities.
In Conclusion
Singapore is a city that is constantly evolving, thanks in no small part to its focus on technology and innovation. It has leveraged technology to improve a range of urban services, including transportation, energy, waste management, public safety, and healthcare. With its current focus on becoming a smart city of the future, Singapore is well poised to lead the way in the development of advanced urban solutions that can help other cities across the world. As a result, Singapore has become one of the smartest cities in the world.
The city has been able to transform itself from a small, overcrowded trading port with few natural resources to a world-class smart city that uses technology and data to improve the quality of life for its residents. This transformation has been driven by visionary leadership, strategic planning, and the hard work of its people. Singapore has invested in various fields including transportation, healthcare, public safety, business development, and energy, to become one of the most innovative cities in the world. The city-state is a great illustration of how smart city projects may improve the quality of life for all citizens by making cities more connected, sustainable, and equal. Singapore is setting the bar for future smart cities.
Experience the future of urban living in Singapore – visit today and witness how the city-state has harnessed technology and innovation to create a world-class smart city. From advanced transportation systems to sustainable waste management, Singapore has it all. Be inspired by its visionary leadership, strategic planning, and hardworking people, who have transformed a small trading port into one of the most innovative cities in the world. Don't miss the opportunity to see how smart city projects can improve the quality of life for all citizens. Book your trip to Singapore now and witness the future of urban living!
Want to keep up with the transforming world?
Explore BIM Professional Course offered by Novatr. This course helps you understand the subject theory, master advanced tools, and build your expertise. The course helps you:
- Become a BIM expert in just 7 months of part-time, online study.
- Master 15+ BIM software and industry workflows.
- Learn from AEC professionals leading BIM at top-tier firms worldwide.
- Work on a live, RIBA-structured capstone project to practice your skills.
- Get placement assistance to land jobs in globally operating BIM firms.
Get your hands on BIM to be able to design for the future!

 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!
-1.png)

.png)


.jpg)



