Quality Control In Construction: A Comprehensive Guide

Table of Contents
Quality control is a crucial aspect of every construction project which ensures that every stage of development has strict standards, safeguarding the safety and durability of the structure. From thorough inspections to stringent standards, quality control ensures that every brick, beam, and bolt meets exacting standards. This fortifies the built environment and inspires confidence in the structures that shape our world. This blog explores the significance of quality control in construction, and its impact on safety, durability, client satisfaction, and industry reputation. It highlights its role as a catalyst for excellence and reliability in the dynamic construction landscape.
Understanding Quality Control in Construction
Quality control in construction focuses on monitoring materials, workmanship, and processes to ensure projects meet defined safety, durability, and regulatory standards, reducing defects, improving reliability, and ensuring consistent compliance across every project stage.
Quality control in construction is important for every aspect of a project that follows predefined standards and specifications. This is a systematic method which includes evaluating, monitoring, and maintaining high standards throughout the project, which includes picking out materials, ensuring quality workmanship, following safety protocols, and adhering to architectural and engineering plans. By using quality control techniques, construction projects can attain consistency and dependability and produce superior constructions that surpass the expectations of their clients. Ensuring public health, safety, and welfare through the implementation of building codes, safety laws, and environmental standards is a fundamental necessity for any construction project. By fostering consistency and interoperability, these standards lower risks and liabilities, enhance the credibility and image of construction companies and benefit society by resulting in structures that are more resilient, safe, and environmentally friendly.
Key Components Of Quality Control In Construction
Core components of quality control in construction include inspections, material testing, documentation, corrective actions, and continuous improvement practices that help track performance, identify deviations early, and maintain accountability throughout the construction lifecycle.
Key components of quality control in construction include:
- Maintaining detailed and precise documentation of all the processes, including materials used, inspections conducted, and also if any deviations from standards to track progress and make sure the accountability for that.
- Performing complete tests for the construction materials to ensure they meet specified quality standards and are accurate and suitable for future use.
- To monitor progress and guarantee accountability, keep thorough records of all procedures, including the materials used, the inspections carried out, and any deviations from the norms.
- As soon as possible, rectify any problems or deviations found during testing or inspections to avoid harming the project's overall quality.
- putting the suggestions and knowledge gained from earlier initiatives into practice by consistently enhancing the outcomes and quality control procedures.
Ensuring Safety and Compliance
Ensuring safety and compliance in construction includes robust safety protocols, adherence to building codes and standards, and strategic quality control measures. This is a complete approach to safeguarding the well-being of those involved and making sure the delivery structures meet the highest safety and regulatory standards. To maintain structural integrity and occupant safety, it is essential to meet and surpass industry requirements and building codes. Regulatory authorities establish building codes that specify the minimal criteria for structural design, construction, and occupancy. These codes address topics including environmental sustainability, fire safety, accessibility, and structural design. Along with fulfilling legal requirements, compliance protects against future liabilities and guarantees the durability of built structures.
Also Read: Explore 10 Best Online Architecture Courses in India in 2026
1. Mitigating Risks Through Effective Quality Control Measures
Quality control is an important role in mitigating risks throughout the construction process. With the Rigorous inspections, material testing, and adherence to construction standards, they become the integral components of quality control that helps to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. By implementing measures, such as identifying weak points in structures or addressing construction deviations promptly, quality control acts as a safeguard against safety hazards and non-compliance. It fosters a culture of accountability, continuous improvement, and risk reduction, thereby contributing to the overall safety and compliance objectives of construction projects.
2. Enhancing Project Efficiency
By reducing rework and delays and maximising resource utilisation, quality control increases a project's efficiency and ensures that it is finished on schedule. Project teams can attain more efficiency and uphold the highest standards of performance and quality by incorporating quality control into every facet of the construction process. Project teams can minimise rework and delays while still achieving their goals with the aid of this strategy.
3. Impact of quality control on project timelines
- Early problem detection and resolution will help to avoid future setbacks that could interfere with project timelines.
- minimises the need for rework and remedial actions, keeping the project on schedule and under budget.
4. Minimising rework and delays
- Assist in quickly identifying flaws or deviations to reduce the need for repairs or rework later on in the building process.
- It guarantees that construction proceeds smoothly and on time and lessens the possibility of delays brought on by rework.
Also Read: 6 Emerging Technologies Transforming the Construction Industry Today
Cost Savings and Budget Management
1. The Financial Implications Of Poor Quality Control
- Inadequate quality control can cause expensive rework, delays, and repairs, which can have a big financial impact on projects.
- Poor quality will increase remediation costs, legal ramifications, and reputational harm, which will compound financial strains.
2. Cost-Effective Strategies Through Quality Assurance
- Regular testing of materials and inspections will help to find problems very early and fix them by reducing the need for expensive revisions or rework.
- Cost savings can be achieved by minimising waste, maximising resource utilisation, and avoiding unnecessary expenses through the implementation of efficient building processes, utilisation of premium materials, and adherence to industry standards..
3. Long-Term Savings And Return On Investment
- Investing in quality control, may require expenditure for long-term savings and a higher return on investment.
- High-quality construction leads to durable, low-maintenance structures by reducing lifecycle costs and enhancing asset value.
- The reputation and credibility of the project in the construction firm lead to great opportunities for future projects and higher client satisfaction.

Implementing Effective Quality Control Practices
Implementing strategies for quality control in construction firms can uphold project standards, empower personnel, and utilise technology for efficient management throughout the project lifecycle. These strategies ensure the successful delivery of construction projects by establishing and maintaining robust protocols.
1. Establishing Quality Control Protocols
- Define comprehensive quality standards and performance criteria for all project aspects
- Develop detailed quality control plans with specific procedures, responsibilities, and checkpoints
- Implement document control procedures to ensure the accuracy and accessibility of project documentation
- Schedule regular inspections and audits to monitor compliance with quality standards and address deficiencies promptly
2. Training And Empowering Personnel
- Offer comprehensive training programs on quality control protocols and procedures to educate personnel.
- Designate individuals and teams as quality champions to oversee quality control efforts and promote a culture of continuous improvement.
- To find and fix quality problems early, project team members, suppliers, and subcontractors must work together and communicate openly.
- Educating people about the value of quality control through frequent communication, workshops, and award systems to foster a sense of pride in producing high-calibre work.
3. Utilising Technology For Efficient Quality Management
- Leverage technology solutions like construction management software, mobile apps, and cloud-based platforms for efficient quality management processes.
- Utilising remote technologies like IoT sensors and cameras to monitor construction activities and quality performance remotely.
- use BIM to enhance design and construction phase coordination, visualisation, and clash detection.
- Utilise predictive and data analytics to find trends, patterns, and risk factors that influence quality performance and proactively put preventive measures in place.
Also Read: How Automation in Construction is Leading the Way for the AEC Industry
Case Studies and Examples
Quality control is important for architecture which makes sure that the buildings are safe, durable, and meet the intended design standards. In architecture, quality control practices are essential to identify and rectify potential issues during the design, construction, and maintenance phases. This ultimately ensures the safety, durability, and functionality of built structures. Here are a few examples that illustrate the importance of quality control in architecture.
1. Fallingwater by Frank Lloyd Wright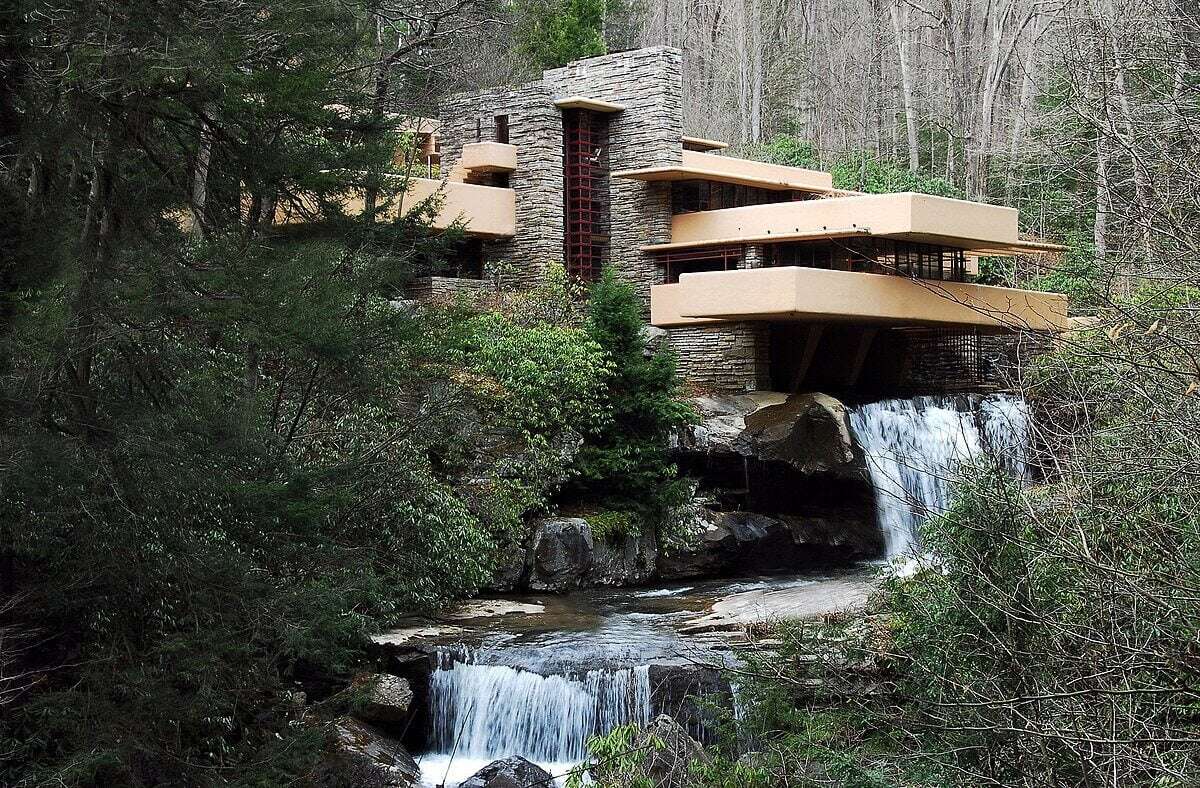
Frank Lloyd Wright created "Fallingwater '' as a masterpiece of organic architecture. It was completed in 1939 and is known for its surrounding area covered with nature, particularly the waterfall over which it is built. The initial construction was impeded by inadequate waterproofing and structural support. But afterwards, the cantilevered balconies started sagging, and water penetration became a major problem. To preserve it for long-time, the structure was stabilised, its construction improved and corrected, and also the waterproofing issues were addressed in the 1990s.
2. Millennium Bridge in London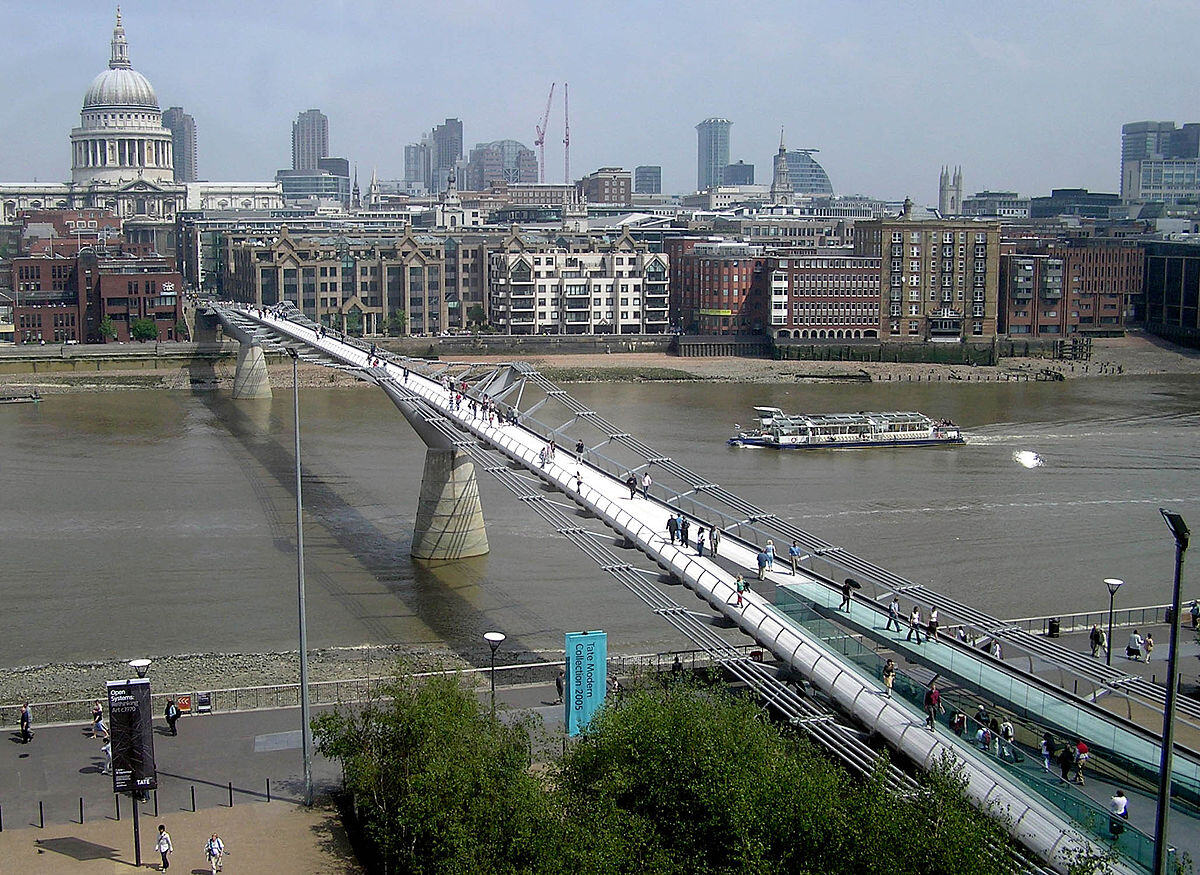 
The Millennium Bridge is a pedestrian suspension bridge which spans the River Thames in London. It was designed to be an architectural masterpiece. However, when it opened in 2000, it experienced unexpected lateral movement under pedestrian roads, leading to its closure shortly after inauguration. The issue was attributed to the bridge's natural frequency coinciding with the footsteps of pedestrians, causing excessive swaying. Subsequent modifications, including installing dampers, helped mitigate the problem, highlighting the importance of comprehensive quality control and testing in structural design.
3. The Leaning Tower of Pisa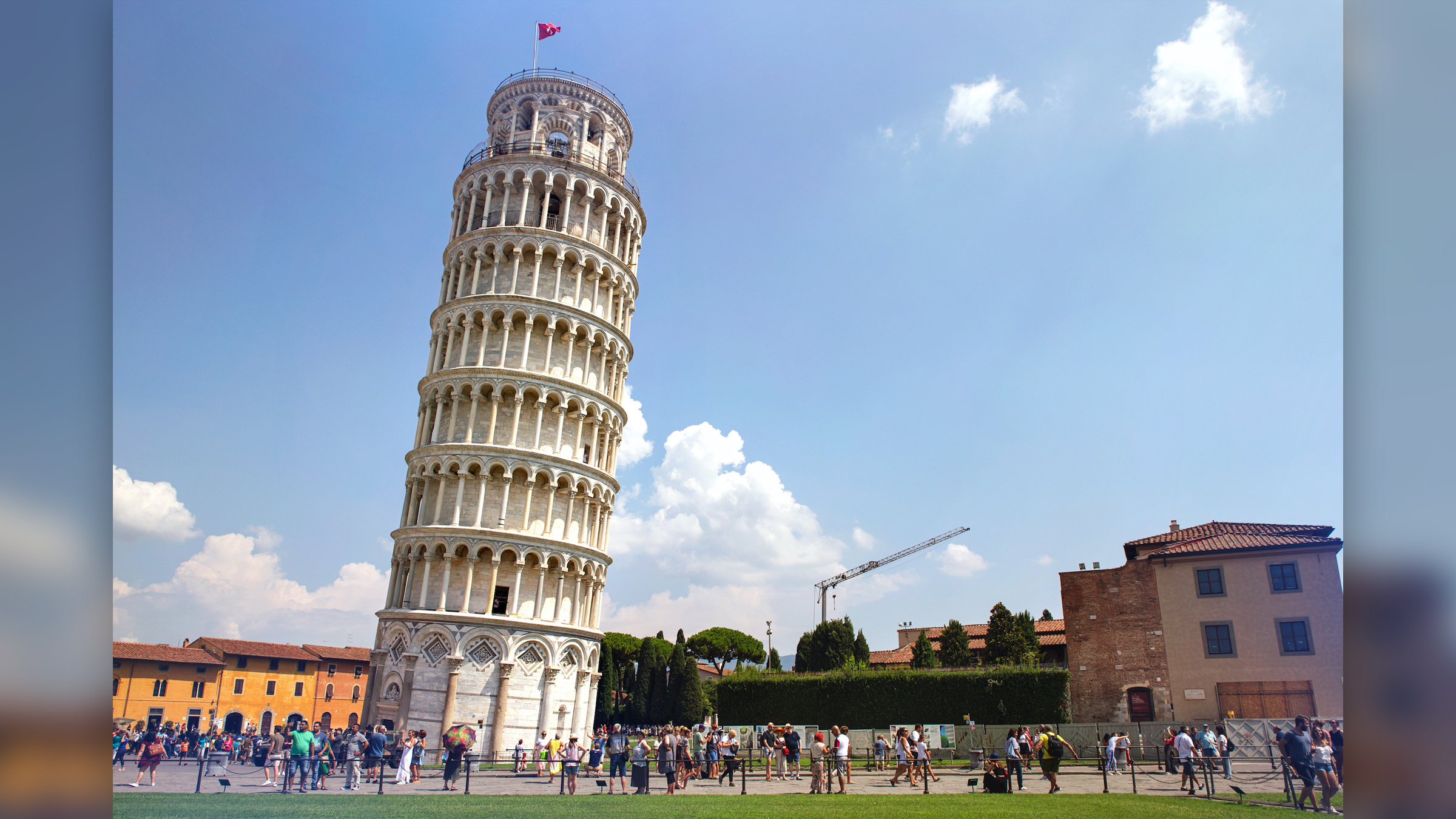
The Leaning Tower of Pisa is a historic bell tower in Italy that is well-known for its unexpected tilt. Construction began in the 12th century on unstable ground, resulting in the tower's progressive learning. Despite numerous attempts throughout the years to remedy the lean, but the tower continues to tilt. Extensive restoration operations in the late twentieth and early twenty-first centuries stabilised the building, ensuring its status as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
4. Taipei 101 in Taiwan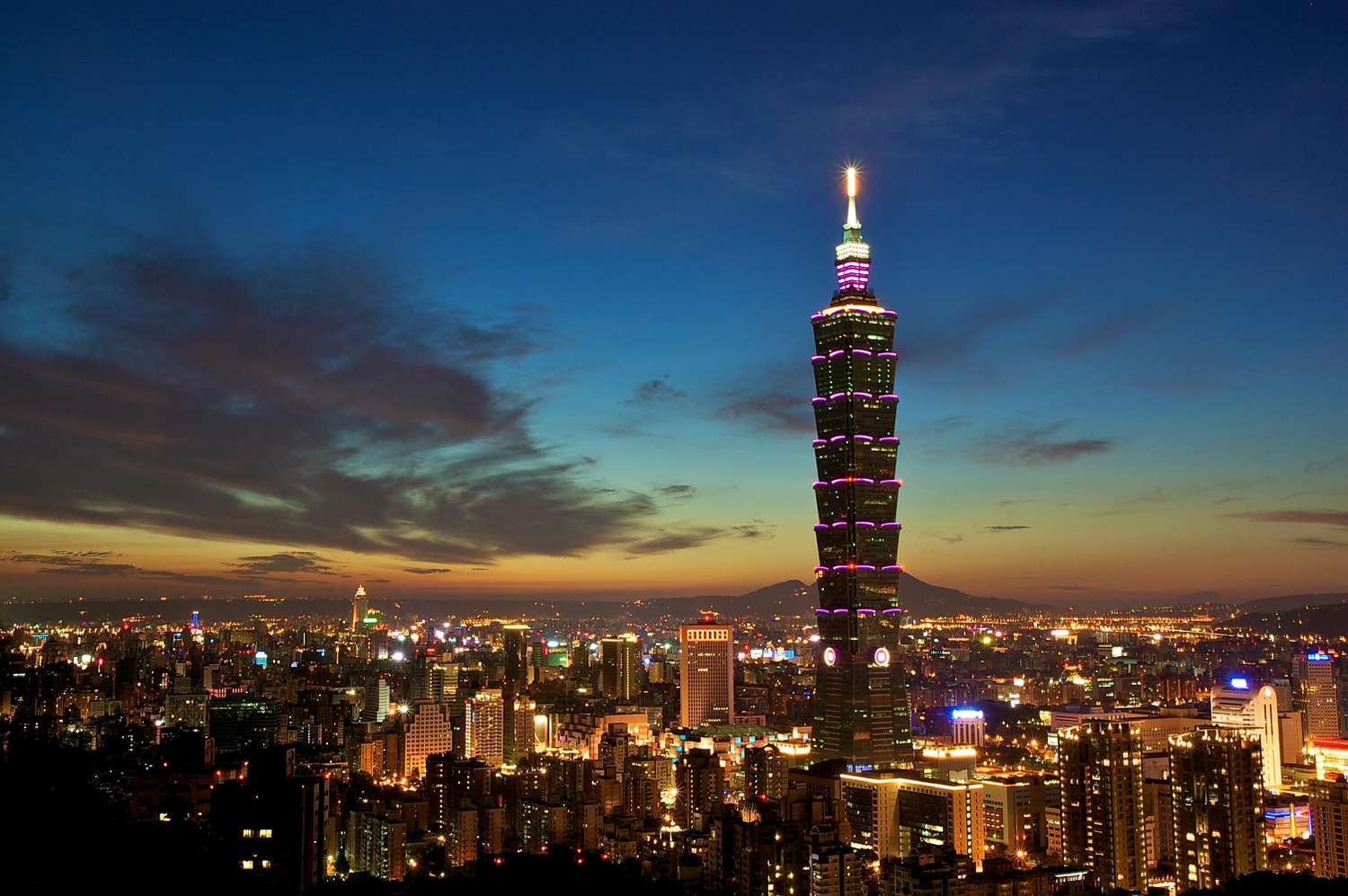
The world's tallest building, Taipei 101, was finished in 2004. Thorough quality control methods were implemented during the design and construction stages, and it is designed to survive the typhoons and earthquakes that frequently occur in the area. In order to provide occupant stability and safety, the building has a tuned mass damper system, which is a massive pendulum-like mechanism located near the top to offset the building's swaying caused by external pressures.
5. The Shard in London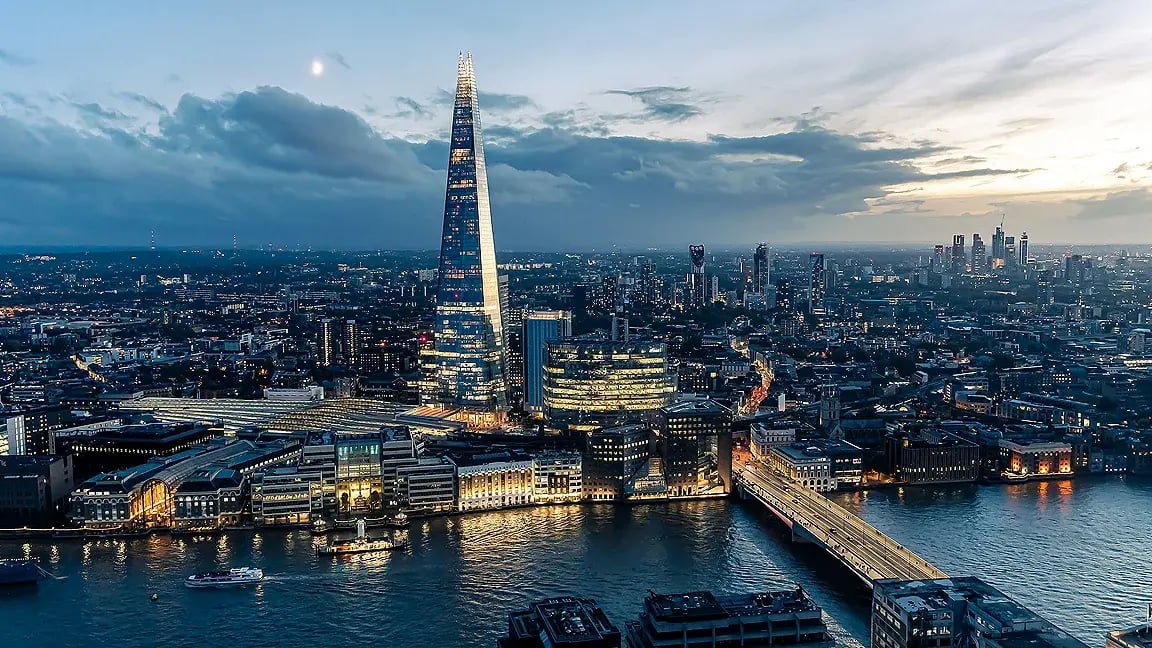 
One of the most famous skyscrapers dominating the London skyline is The Shard, designed by legendary architect Renzo Piano. Outstanding engineering and sustainability are highlights of this 2012-completed project. For the reason to guarantee structural integrity, safety, and performance, quality control was essential throughout the building phase. As a prime example of the importance of quality control in finishing big architectural projects, the building's decreasing form and unique façade systems were carefully engineered and tested to withstand wind loads and environmental stresses.

Future Trends and Innovations
The integration of technologies like BIM, UAVs, AR/VR, and IoT is revolutionising construction quality control practices. Trends like prefabrication, advanced materials, data analytics, and collaborative project delivery are also transforming the future of construction quality assurance.
Emerging technologies in quality control
Here are some emerging technologies that help in quality control:
1. Building Information Modeling (BIM):
BIM continues to revolutionise the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry by enabling comprehensive digital representations of buildings and infrastructure. In quality control, BIM facilitates clash detection, coordination, and visualisation of building elements, enhancing coordination and reducing errors during the design and construction phases.
2. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
These technologies offer immersive experiences that aid in visualising and simulating construction projects. Quality control processes benefit from AR and VR applications for virtual inspections, design validation, and training purposes, enhancing collaboration and decision-making among project stakeholders.
3. Internet of Things (IoT):
These devices enable real-time monitoring of environmental conditions, structural health, and equipment performance. This data-driven approach to quality control allows for proactive maintenance, predictive analytics, and optimization of construction processes.
Also Read: Architecture Thesis Topics: A Comprehensive List of 30 Topics to Pick From
Trends shaping the future of construction quality assurance
1. Prefabrication:
These methods gain popularity by their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and quality control benefits. By fabricating the building components off-site under controlled conditions reduces on-site errors and improves construction quality by minimising waste and enhancing precision.
2. Advancement in Materials:
advanced materials, such as carbon fibre, engineered timber, and self-healing concrete, offer opportunities to enhance structural performance, durability, and sustainability in construction projects. Quality assurance efforts focus on ensuring the integrity and performance of these innovative materials throughout their lifecycle.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Data analytics and AI-driven technologies are increasingly utilised for predictive quality control and risk management in construction projects. Machine learning algorithms analyse vast datasets to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and optimise construction processes, leading to improved quality outcomes and cost savings.
4. Integrated Project Delivery (IPD):
IPD promotes collaboration and integration with the project stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and owners. It aligns the incentives, sharing risks and rewards, by fostering a complete commitment to the quality for the project's success. Rapidly growing innovation and continuous improvement in construction give quality assurance.
Also Read: The Role Of Fabrication in Construction Industry and its Significance
Conclusion
Quality control is important for the success of any construction project. This ensures that each stage of development meets precise standards, guaranteeing the safety and longevity of the structures we inhabit. From rigorous inspections to strict protocols, quality control measures help maintain the integrity of every component, from bricks to beams to bolts. This, in turn, strengthens the built environment and ingrains confidence in the structures that shape our world. Quality control is an unchanging cornerstone of the construction industry, even as the industry evolves. By adopting effective techniques and staying up-to-date with emerging trends and technologies, construction firms maintain the highest levels of quality and empower their employees to build structures that are functional, safe, sustainable, and long-lasting.
Novatr provides a BIM Professional Course for Architects, wherein professionals with years of practical experience in the area teach. You will also have the opportunity to work on actual capstone projects. If you'd like additional information about similar occupations and software, visit our Resources page.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the role of quality control in construction?
QC or quality control varies from one construction to another. It improves product quality by minimising any kind of inconsistencies. Quality control ensures that the quality methodologies are applied correctly, with labour performance efficiency. The major responsibilities of QC is testing finished goods and services to ensure adherence with QC standards.
2. What is the quality control process in construction?
Quality control is a set of steps to ensure that a construction project is in compliance with the quality standards. These steps generally include defining standards that establish regulation, codes and quality standards, creating an inspection plan, conducting regular inspections and analyse. Quality control in construction also includes quality assurance, training and documentation.
3. What are the 4 pillars of quality control in construction?
The four pillars of quality control in construction are planning, inspection, corrective action, and continuous improvement, ensuring consistent standards, early defect detection, accountability, and long-term quality enhancement across projects.
4. What is a QC salary?
A quality control professional’s salary varies by experience and location, typically ranging from entry-level site inspectors to senior QC managers, with higher compensation linked to technical expertise, certifications, and large-scale project involvement.
5. What is QA in construction?
Quality assurance in construction focuses on preventive systems, processes, and standards that ensure work is done correctly from the start, supporting quality control efforts by reducing errors, improving consistency, and maintaining long-term compliance.

 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!
-1.png)
.png)