Need for Resilient Infrastructure in Strategic Landscape (2026)
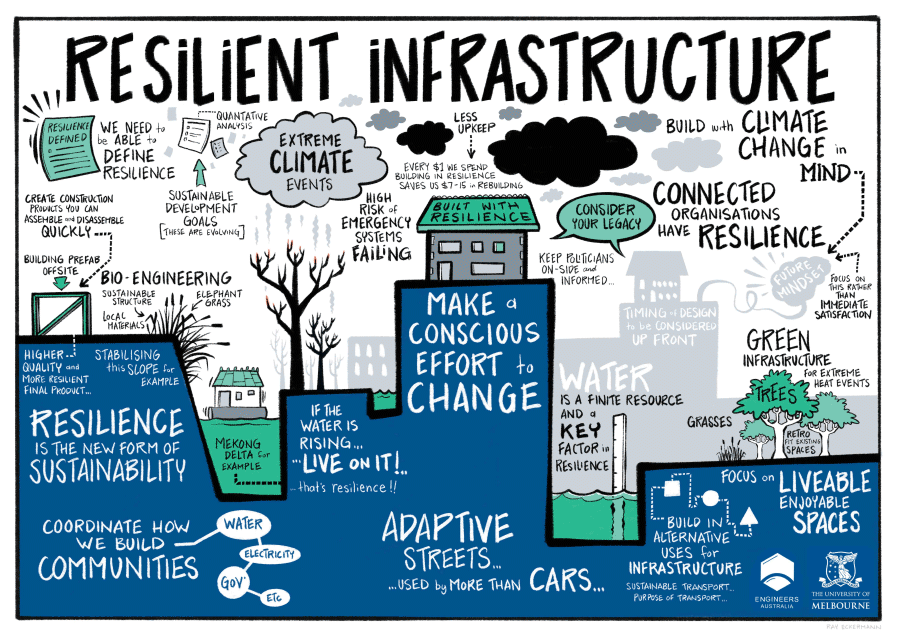
Table of Contents
Resilient infrastructure plays an important role in today’s strategic landscape, especially within the AEC industry, where technology, collaboration, and sustainable design are reshaping how cities and structures adapt to challenges.
What if we said that about 30-55% of the infrastructure industry gets affected during a flood? Hard to believe right? However, according to the OECD's modelling, the potential impact of a significant flood in Paris revealed that the infrastructure sector would bear 30% to 55% of the direct flood damages.
Also, take the example of the 2013 Kedarnath flood in Uttarakhand, India. This tragedy caused losses worth US $1 billion, and that’s only the calculated and reported amount. Be it a home, a hotel, a bank, or a commercial building, you name it and the structure was one of the many critically damaged buildings, leaving the citizens and tourists stranded for weeks.
Now look at this from an engineer’s point of view. Imagine the time, cost, and effort to build this place over many decades - all gone in just a few weeks. Why?
Whether we blame the geography or the climatic factors, the likelihood of a structure surviving any disaster comes down to precautionary steps taken during construction in line with the threats they may face.
Understanding What is Resilient Infrastructure?
Resilient infrastructure refers to the ability of physical systems and built environments to remain functional and adaptable under stress or disruption.
Disaster Infrastructure Resilience was introduced during the 1970s but started getting attention recently—it took experts some time to adapt to it and implement it for a better future.
Resilient Infrastructure refers to the ability of a system to anticipate, prepare for, respond to, recover from, and adapt to adverse conditions or disruptions while also maintaining essential functions, structures, and identity.
It is a comprehensive concept that describes a system’s ability to withstand and recover from critical situations due to humans or natural causes. Resilient Infrastructure is crucial for ensuring the continued operation and functionality of essential systems during natural disasters, cyber-attacks, and other unexpected events.
How Does Reselient Infrastructure Work? 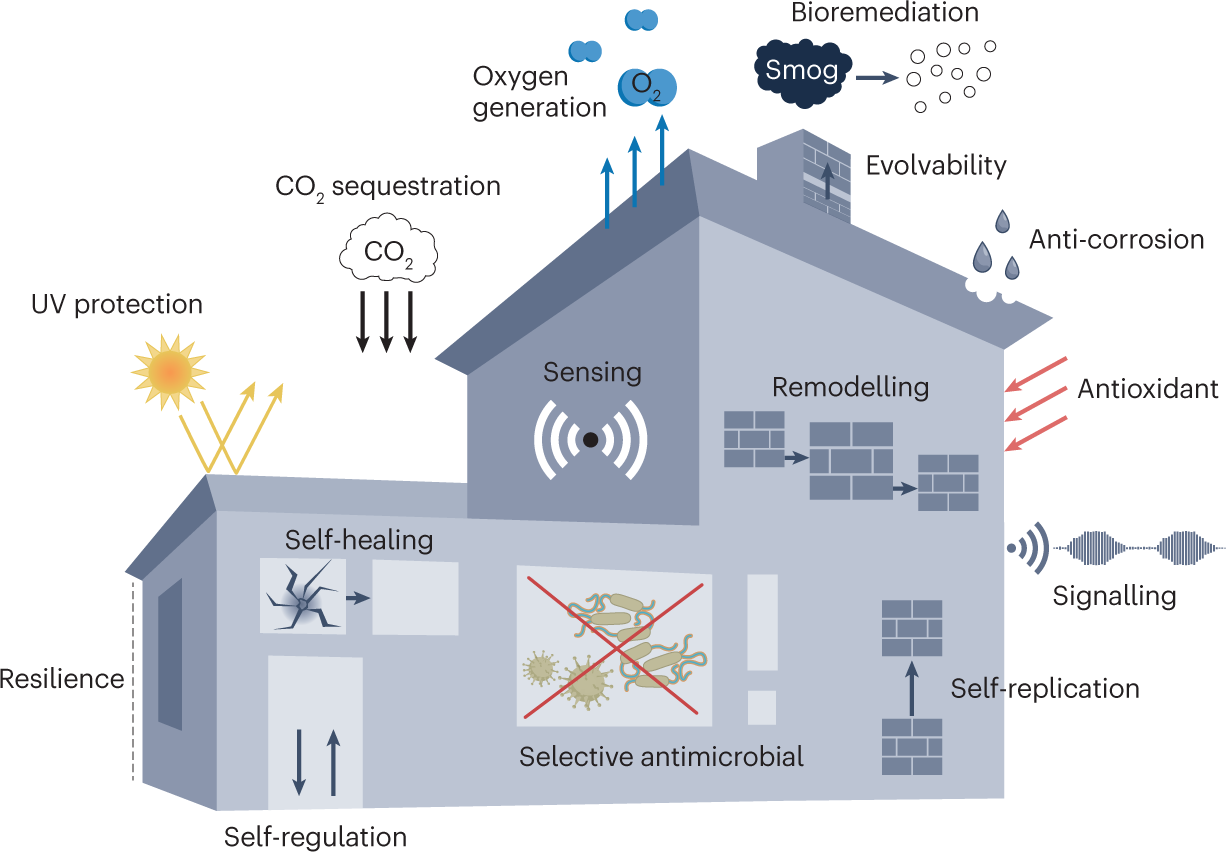
To explain it better, here are three major pointers in the form of a funnel:
Top of the Funnel
This step consists of risk assessment and preventive measures like identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities. Understanding natural hazards, potential human-made threats, and external vulnerabilities is the first step to a sustainable development project. Preventive measures include referring to the steps ideated to minimise the casualties and hassles within the system; a way to prevent potential risks. Factors involving infrastructure design, redundancy, and security measures are some of the preventive measures.
Middle of the Funnel
This part of the funnel includes developing plans and procedures to respond efficiently and effectively to any kind of disruptions. Protocols like communication, coordination, and mobilisation of resources during these emergencies are involved. This part involves backup plans, a data recovery system, and other required alternatives.
Bottom of the Funnel
This part includes learning from disruptions and being flexible along with scalability. It is crucial to analyse and understand what worked and what didn’t. This also involves having to look into what and how things could be improved. This chain of processes helps improve the whole hierarchy of systems and enhances its ability to adapt to future challenges. Thus, the designing systems have to be flexible and scalable, which allows them to adapt to the changing conditions and situations; be it a change in demand, or an upgrade in technology.
Key Measures for Strengthening Resilient Infrastructure
To strengthen resilient infrastructure, organizations must integrate cross-sector collaboration, technological innovation, and supportive regulations to build systems that endure stress and recover efficiently. Resilient infrastructure is a multidimensional concept that requires a dynamic and integrated approach. Here are a few key measures to strengthen resilience:

Cross-sector Collaboration:
-
Interconnection: Identifying and understanding that different sectors and areas are often interconnected is very crucial as it helps one understand that disruptions in one area can have cascading effects on others. For example, Nepal earthquakes mostly lead to tremors in Delhi and neighbouring areas.
-
Communication is the Key: Communication across the sectors and collaborative efforts between them such as private-public partnerships are quite essential for a holistic approach to resilient infrastructure. This leads to understanding the measures that can be taken collaboratively for the well-being of the sectors across.
Technological Resilience:
-
Smart Infrastructure: Here the architects make use of the technological aspect of the AEC industry, like — the Internet of Things (IoT), sensors, and data analytics, to enhance monitoring, early warning systems, and decision-making procedures during disruptions.
-
Cyber Security: When it comes to IT and critical infrastructure, safeguarding against cyber threats cannot be neglected. This step involves the implementation of robust cybersecurity, regular audits, and staying updated on emerging threats.
Regulatory Framework:
-
Adherence and Standardisation: Establishing and complying with regulatory frameworks along with standards and best practices helps to ensure that the infrastructure is built, operated, and maintained to withstand the challenges faced.
-
Involvement of Government: The Government is a crucial player in the whole process as it provides support, resources and a regulatory environment that pushes forward the resilience measures and enforces it on the system.
From strategic planning, technological investment, investment in infrastructure, cross-sector collaboration, and continuous adaptation to changes in the environment and industry, all of these factors build resilient infrastructure.
The ultimate goal is to build a system that not only withstands the obstacles but also evolves for a better and stable future.
Also Read: 5 Things to Keep in Mind Before Starting Your Career in BIM
The Importance of Resilient Infrastructure in 2026
If explained in one single sentence, resilient infrastructure aims to help communities prepare for disasters and build them back after; be it a natural disaster or human one. Here are a few points to further elaborate:

Time, Effort, Investment
In every other infrastructure, there is a huge amount of time, effort, and investment involved, so the instinct is to expect long-term benefits to society from it. Be it in terms of economic growth, wellbeing improvement, contributing to key policy priorities such as protecting biodiversity, being sustainable, making resilient societies, etc.
Economic Opportunity
Resilience is necessary to withstand the effects of negative shocks and it presents a special chance for nations to prepare for potential threats in the future as part of their recovery efforts. Additionally, as the economic case for sustainability gains traction among private investors, they demand that assets satisfy ESG standards to mitigate risk, comply with legal obligations, and support efforts like the EU Taxonomy for Sustainable Activities.
Service to the Community
With the increasing infrastructure changes globally, the need to consider the changing environment, community expectations, social connectivity and potential legal requirements is also important, as they are the key factors to achieve sustainable development and deliver an efficient project to society as a whole. If there’s strong community opposition, it can result in cost overruns, delays, and cancellations.
Reduction in Maintenance Cost
Latest technologies play a critical role in offering alternatives to the traditional infrastructure designing techniques, along with construction and maintenance. This leads to an increase in operational costs in the beginning but a massive reduction in maintenance costs in the future.
Improving Operational Efficiency
Technological development also contributes to identifying possible threats which cannot be avoided but dealt with precautionary measures. This strengthens the resilience of crucial systems by improving operational efficiency and enabling quick reactions to emergencies or changing circumstances.
Also Read: 10 Gravity-Defying Structures That Will Leave You Awestruck
How to Integrate BIM in Resilient Infrastructure in Today's Buildings and Structures?
Before we dive into the details headfirst, watch this video to understand the Building Information Model or BIM :
You can also dive into our blog here to learn more about Building Information Modeling(BIM).
Now that you are familiar with BIM and how it contributes to the AEC industry, let’s understand its role in resilient infrastructure and how it is integrated into today’s buildings and structures.
Role of BIM in Resilient Infrastructure
Here are a few points to elaborate on the role of BIM in resilient infrastructure :
-
Collaborative Planning: BIM leads to a holistic and integrated approach to the design and planning of infrastructure projects, enabling stakeholders to collaborate in real-time, identify potential vulnerabilities, and optimise designs for resilience; considering factors such as climate, geology, and local conditions.
-
Risk Analysis and Mitigation: BIM facilitates advanced risk analysis by simulating various scenarios and their potential impacts on infrastructure. This includes analysing the vulnerability of structures to earthquakes, floods, or extreme weather events.
-
Real-Time Monitoring and Response: Sensors and IoT devices integrated into the BIM model provide data on structural health, environmental conditions, and other relevant parameters. This data can be analysed in real time, enabling swift decision-making and response strategies to minimise damage during emergencies.
-
Enhanced Decision Making: BIM models can be shared with all stakeholders involved in a project, which can facilitate decision-making, monitor development, exchange information, address problems, and reduce disputes.
-
Cost-Effective: BIM identifies the problems and risks in the earlier stage, hence providing bandwidth with a wider range of scope and resolutions throughout the design process. This process is needless to say, time-saving and cost-effective, as it helps in avoiding the problems that can take place in the future.
-
Adaptability to Changing Conditions: BIM supports the entire life cycle of a project, from design and construction to operation and maintenance. This ensures that infrastructure remains resilient over time, with the ability to adapt to changing conditions; allowing for proactive measures and reducing the risk of sudden failures.
Also Read: How are Smog-Eating Buildings Leading the Way Forward for the AEC Industry?
How Resilient Infrastructure is Used in Sustainable Development
Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure is an important aspect of the AEC industry that focuses on the sustainable development of infrastructure-resilient communities.
The ability of an infrastructure to address the needs of the present case scenario without compromising on the ability to meet the requirements of future generations is referred to as Sustainability.
Whereas Resilience refers to the precautionary measures taken against unforeseen natural hazards and anthropogenic obstacles(like human errors) for an infrastructure. It revolves around the performance of the infrastructures built and modifying natural environments.
Conclusion
In the face of a rapidly changing world, resilient infrastructure has emerged as a critical aspect in building an infrastructure for it to stand the test of time. By embracing an integrated and collaborative approach to design, construction, and management, BIM is reshaping the way we build and maintain resilient infrastructure. As we continue to face new challenges, the adoption of BIM and implementation of resilient infrastructure plays a pivotal role in ensuring that our cities and communities are well-prepared for whatever the future may hold.
Novatr offers a professional and specialised course tailored for Civil Engineers. It’s time to dive into the world of Building Information Modeling (BIM), hone your skills, and become industry-relevant.
Our comprehensive programs, BIM Professional Course for Civil Engineers and BIM Professional Course for Architects equip professionals to leverage BIM tools for efficient project management and enhanced collaboration. Before investing time and resources in extensive training, explore our curated courses for Civil Engineers, offering practical insights and guidance.
Explore our Resources page to find more career insights in the AEC industry.
Freuqently Asked Questions:
1. What is resilient infrastructure?
Resilient infrastructure means systems or structures that can resist, adapt, and recover from natural or human-made disruptions while maintaining their functionality and safety.
2. Why is resilient infrastructure important in 2026?
In 2026, resilient infrastructure is crucial for ensuring urban systems can withstand climate risks, economic disruptions, and rapid development while supporting sustainable growth in the AEC industry.
3. How does BIM contribute to resilient infrastructure?
BIM improves collaboration, risk analysis, and predictive maintenance by using data-driven design. It supports smarter decisions, making infrastructure more adaptable and sustainable.
4. What are examples of resilient infrastructure projects?
Examples include flood-resistant bridges, energy-efficient smart grids, earthquake-ready buildings, and sustainable transport systems developed using advanced digital modeling.
5. How is resilient infrastructure related to sustainable development?
Resilient infrastructure supports sustainable development by ensuring long-term resource efficiency, minimizing maintenance costs, and creating safer, climate-ready cities.

 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!



.png)

-1.png)


-2.png)
