What Does a Computational Designer Do and How to Become One? Updated}
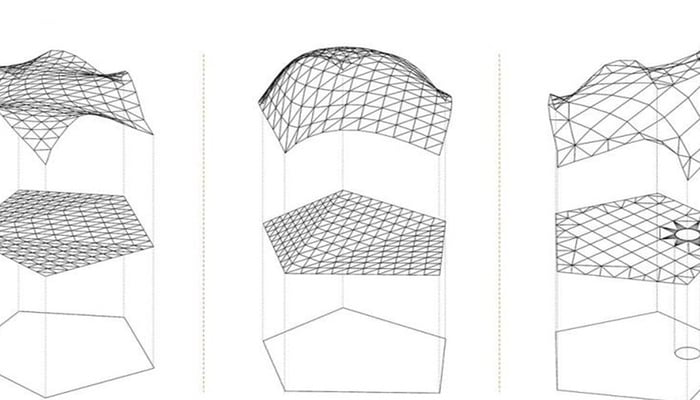
Table of Contents
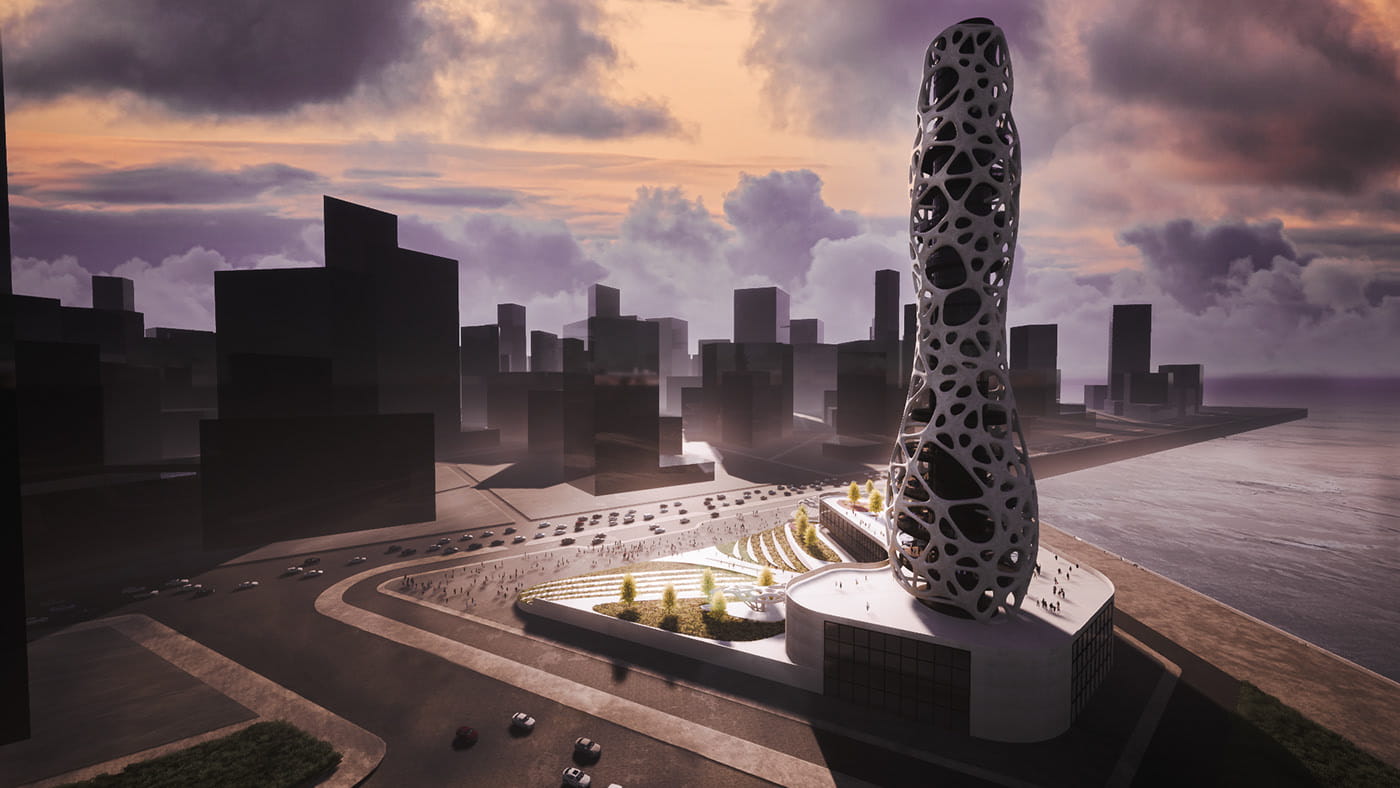
In the rapidly evolving landscape of the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry, the role of a computational designer is increasingly becoming prominent. Using data-driven processes like automation and visual programming, these innovators are pushing the boundaries of conventional design methodologies to design better-built environments.
While architects and engineers traditionally rely on intuition and experience to solve design problems, computational designers can enhance that process through visual programming, thus creating an impact both at the project as well as company level. This niche field includes various subsets like parametric modelling design, generative design, sustainability analysis, and digital fabrication, to name a few. Today, computational designers form an indispensable part of the AEC industry.
In this blog, we will describe the role of a Computational Designer in detail and examine how one can become a Computational Designer.

What is Computational Design?
Computational design employs a blend of parameters and algorithms with the assistance of advanced computer processing that addresses design challenges. This software program uses data parallel to project-related parameters to create algorithms, further generating design models or completing design studies.

What does a Computational Designer do?
To understand the role of a Computational Designer, let us first understand what all is included in Computational Design.
Computational Design is an immensely broad and complex field, encompassing various terminologies and subsets. In the simplest terms, Computational Design involves using data-driven processes to optimise the various stages of the design process, including creation, presentation, analysis, evaluation, interaction, and aesthetic expression. With digitalization accelerating at an unprecedented rate, Computational Design is gaining prominence across the AEC industry.

Read more: Understanding Computational Design (The Ultimate Guide)
The various subsets that come under it include Parametric Modelling Design, Generative Design, Algorithmic Design, and Form Finding, to name a few. As the prevalence of Computational Design grows in architectural spheres, it has led to the creation of a defined role: The Computational Designer.
A Computational Designer’s roles and responsibilities includes:
-
Developing and using computational design tools such as algorithms and scripts, to streamline design processes, including creation, presentation, analysis, evaluation, interaction, and aesthetic expression.
-
Collaborating with architects, engineers, and construction professionals to integrate computational design into the design and construction process.
-
Creating and managing digital models, simulations, and visualisations to support decision-making throughout the design and construction process.
-
Developing custom tools and workflows to automate routine tasks and improve design quality and efficiency.
-
Ensuring that computational design tools and processes adhere to industry standards and best practices.
-
Staying up-to-date with the latest developments in computational design and related technologies.
-
Providing technical support and training to team members as needed.
-
Participating in project meetings and providing input on design and construction issues.
-
Communicating design concepts and solutions to clients and other stakeholders.
Overall, the role of a Computational Designer is critical in the AEC industry as it helps to bridge the gap between design and construction and to make the design process more efficient, accurate, and cost-effective.
Scope and Future of Computational Design
Computational Design has the power to completely alter the landscape of the AEC Industry. Some of the key trends and developments in the field of computational design architecture include:
1. Use of AI and Machine Learning
Increased use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to improve design processes and outcomes.
2. Implication of Immersive Technologies
Greater integration of virtual and augmented reality technologies to support design visualisation and communication.
3. BIM Software and Tools
Development of new software and tools for building information modelling (BIM) that allow for more sophisticated simulation and analysis of building systems and performance.
4. Efficient Collaboration
Growth of interdisciplinary collaboration between design professionals, data scientists, and engineers to create more integrated and efficient design processes.
5. Emerging New Technologies
The emergence of new design methodologies and approaches, such as generative design leverages computational methods to generate multiple design options and optimise design solutions.
The scope of this field is not only limited to computational design architecture but this technology can also be applied to the Gaming Experience and Metaverse Design, Fashion Design, Automobile Design, Automation and Robotics etc.
Skills Required to become a Computational Designer
Computational Designer requires to have a strong technical skill set. Here are a few competencies that can help you with this design method:
1. Programming skills:
Proficiency in programming languages such as Python, C++, or Grasshopper, as well as the ability to write scripts and algorithms to automate design tasks.
2. BIM and 3D modelling skills:
Knowledge of building information modelling (BIM) software and 3D modelling tools, such as Revit, Rhino, or SketchUp.
3. Visualisation skills:
Ability to create visualisations, simulations, and animations to communicate design concepts and solutions.
4. Data analysis and management skills
Knowledge of data analysis and management tools and methods, such as Excel or SQL, to support the analysis and manipulation of design data.
5. Design software skills
Familiarity with design software and tools, such as AutoCAD, for creating and refining design drawings.
6. Problem-solving skills:
The ability to analyse complex design problems and develop innovative computational solutions.
7. Project management skills:
Understanding of project management principles and experience working with project teams to coordinate design tasks and meet project deadlines.
8. Interdisciplinary collaboration skills:
The ability to work effectively with architects, engineers, and construction professionals to integrate computational design into the design and construction process.
In addition to these technical skills, a computational designer in the AEC industry should also have excellent communication and interpersonal skills, as well as the ability to think creatively and outside the box. Furthermore, staying up-to-date with the latest developments in computational design and related technologies is also crucial for success in this field.

Read more: Benefits of emerging Computational design developments in the AEC industry
Career Progression of a Computational Designer
Now that we have a sufficient understanding of the skills required for you to become a Computational Designer, let us look at the Career Progression of a Computational Designer.
| Years of experience | Possible role(s) | Salary range (UK) |
| 1–2 | Computational Designer Parametric Designer Environmental Analyst |
40-50 K GBP |
| 3+ | Computational Design Specialist Design Technology Specialist |
50-70 K GBP |
| 5+ | Computational Design Lead Design Technology Lead Senior Computational Designer |
50-70 K GBP |
| 7+ | Computational Design Manager Design Technology Manager |
70-100 K GBP |
| 10+ | Director of Technology Studio Regional Head |
70-100 K GBP |
| 15+ | Chief Technical Officer | 100K + GBP |
Note: The salaries are an estimation based on Novatr’s primary research. To Know more about Salaries of computational designer read this blog.
How to Become a Computational Designer?
Computational Design architecture has brought a paradigm shift in design processes, broadening the scope of design and opportunities. This is one of the most promising fields in the AEC industry, bringing sustainable design, better project management, and increased efficiency and effectiveness to the table. With the augmenting use of Computational design, the demand for professionals is only going to rise.
Here are two major ways in which one can become a Computational Designer:
Option 1: Master’s Degree
One of the ways in which you can become a Computational Designer is by taking the traditional route of a Master’s in Advanced Computation. Several universities around the world offer this course, allowing students to investigate new design opportunities and critical perspectives at the intersection of design and computation. Although a Master offers an in-depth understanding of the subject, it is costly and often requires students to move to a new country.
Option 2: Upskilling Courses
Another option includes pursuing online upskilling courses, which are a great way to upskill yourself while staying in the Industry. One great example of this is the Novatr’s Master Computational Design Course for Architects and Engineers. The 10-month online course is designed and delivered by industry professionals from coveted AEC firms with extensive experience in computational design. This ensures an industry-relevant curriculum that focuses highly on real-world application to help learners break into advanced careers in the industry.

Conclusion
Computational design is shapeshifting with the evolution of modern design. Promising to solve potential problems like energy crisis, healthcare needs, and global warming, it's fair to say that we are walking the path of sustainability, and the future of design looks computational. So that’s it! I hope this blog gave you the inspiration to pursue Computational Design as well as insight into defining your career in this field.
For more insights on AEC careers, software and tools, and industry trends — head to our Resources page.
If you too want to be a part of meaningful redevelopment interventions, you must upskill in such future-relevant technologies. You can learn them by enrolling in the Master Computational Design Course offered by Novatr. The course offers you the opportunity to learn in-depth about computational design processes, tools, and workflows. Check out the course TODAY!

 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!



/827x550/images/blog/blogHero/Ami_Nigam_Oneistox.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)






