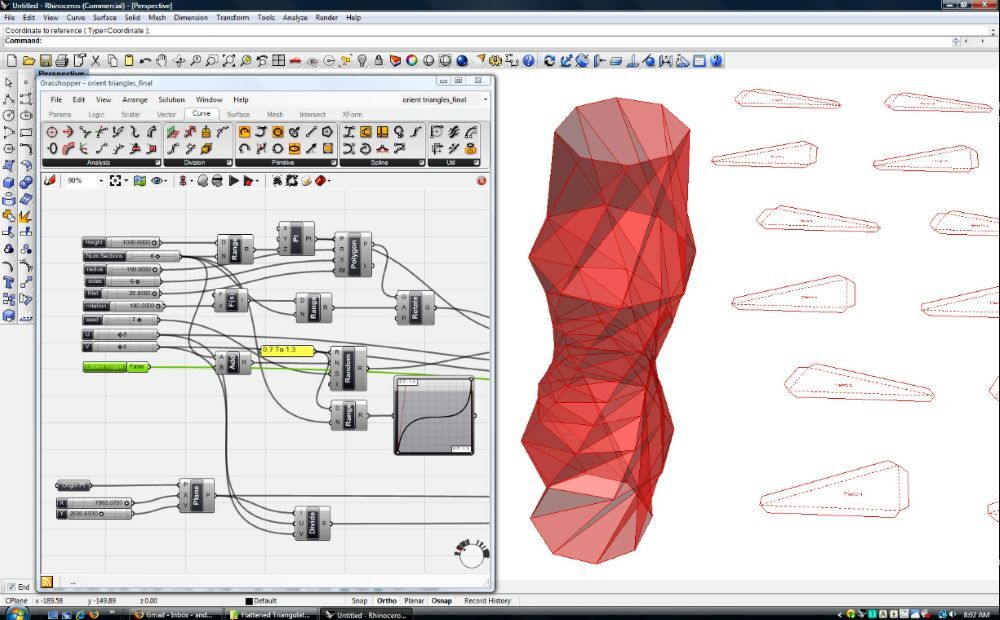
The demand for efficient and adaptable healthcare infrastructure is growing rapidly in the U.S. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, hospitals account for nearly 8% of total building energy use, making design optimization crucial for performance and sustainability. This has led architects and planners to adopt computational design in healthcare, a data-driven approach that improves how hospitals and labs are planned, built, and managed.
By using digital simulations and performance-based models, architects can achieve hospital optimization architecture that meets both patient needs and operational goals. This approach enhances design efficiency and ensures healthcare spaces remain adaptable in an ever-evolving medical landscape.
What is Computational Design?

Computational design combines design logic with algorithms to create intelligent systems that optimize outcomes. Instead of drawing manually, designers use software to set parameters such as light, ventilation, or circulation to generate multiple design options automatically.
In healthcare, this means creating flexible, functional, and efficient facilities that respond to real-world conditions. From testing various hospital building plan design layouts to evaluating energy performance, computational tools make it possible to design based on measurable outcomes rather than assumptions.
Why Healthcare Facilities Need Computational Design
Hospitals and labs are complex systems requiring precision and adaptability. Here’s why healthcare facilities benefit from adopting computational workflows:
- Improved Space Utilization – Algorithms can simulate patient movement and staff flow to create an optimized layout of a hospital, reducing congestion and improving accessibility.
- Energy and Resource Efficiency – Data-driven modeling ensures facilities meet environmental standards while minimizing energy use.
- Enhanced Patient Experience – Computational analysis helps balance privacy, comfort, and safety through light, acoustics, and circulation design.
- Scalability and Adaptability – Hospitals can easily evolve as technology and medical needs change.
- Precision in Planning – Automated modeling allows teams to adjust hospital layout optimization strategies in real-time, ensuring error-free coordination across departments.
Adopting computational workflows leads to healthcare spaces that are efficient, resilient, and patient-centered.
Challenges in Healthcare Architecture

Designing healthcare environments involves intricate challenges that balance technology, efficiency, and human well-being.
Key challenges include:
- Complex spatial requirements – Hospitals must accommodate diverse functions, from emergency care to specialized labs.
- Compliance and safety regulations – Meeting strict healthcare codes and accessibility standards can limit design flexibility.
- Energy consumption and sustainability – High energy demands impact operational costs and environmental goals.
- Workflow inefficiencies – Poorly planned layouts lead to wasted time and movement for medical staff.
- Future adaptability – Healthcare facilities must evolve with advancing technology and patient needs.
These challenges demand a design approach that’s flexible, data-informed, and performance-oriented, with qualities embedded in computational design methodology.
How Computational Design Solves These
Computational design in healthcare addresses these challenges by integrating simulation, automation, and optimization directly into the design process.
Key ways it solves architectural constraints include:
- Parametric modeling – Enables quick iterations of design solutions for different medical programs using parametric healthcare design methods.
- Performance analysis – Tests environmental factors like light, air circulation, and thermal comfort for maximum efficiency.
- Workflow simulation – Analyzes real patient and staff movement data to enhance hospital optimization architecture.
- Resource management – Ensures materials and systems are optimized for energy performance and sustainability.
- Predictive planning – Uses data to anticipate future facility needs and scalability.
Through these methods, computational design translates complex architectural data into actionable design solutions that enhance functionality, promote sustainability, and elevate the overall patient experience.
5 Hospital Designs Created Using Computational Design
1. Maggie’s Centre, London
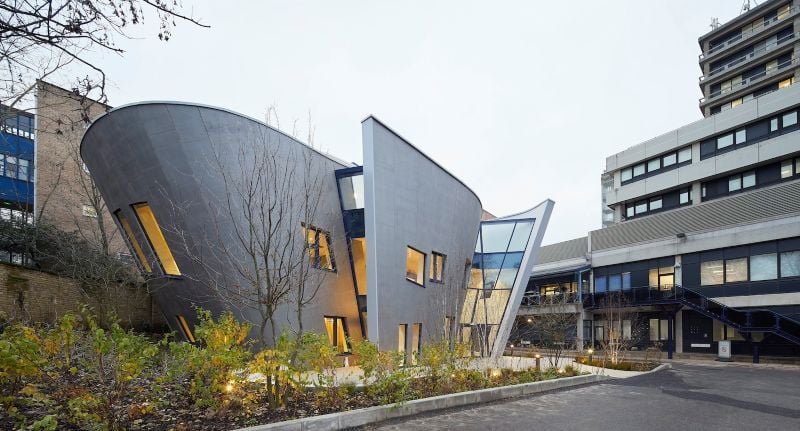

This facility uses algorithmic modeling to enhance daylight optimization and healing-focused spatial flow. Computational design helped balance emotional well-being with performance-driven efficiency.
2. Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, Singapore
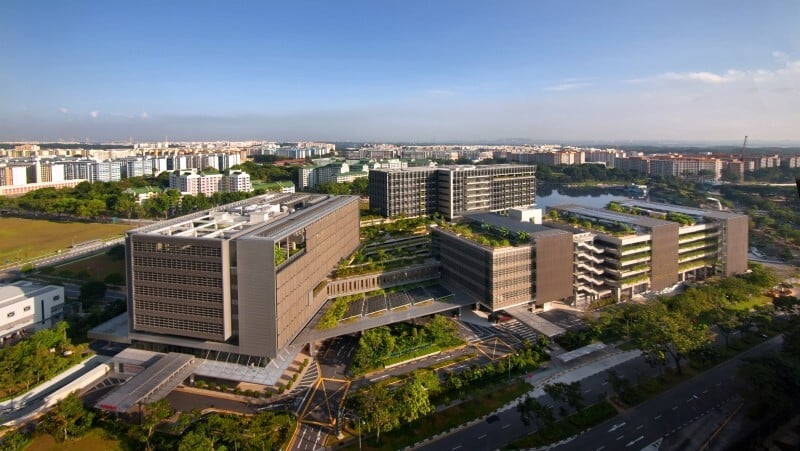

Designers applied computational tools to integrate energy-efficient systems and natural ventilation strategies, creating a biophilic environment that improves recovery rates.
3. Cleveland Clinic, Abu Dhabi
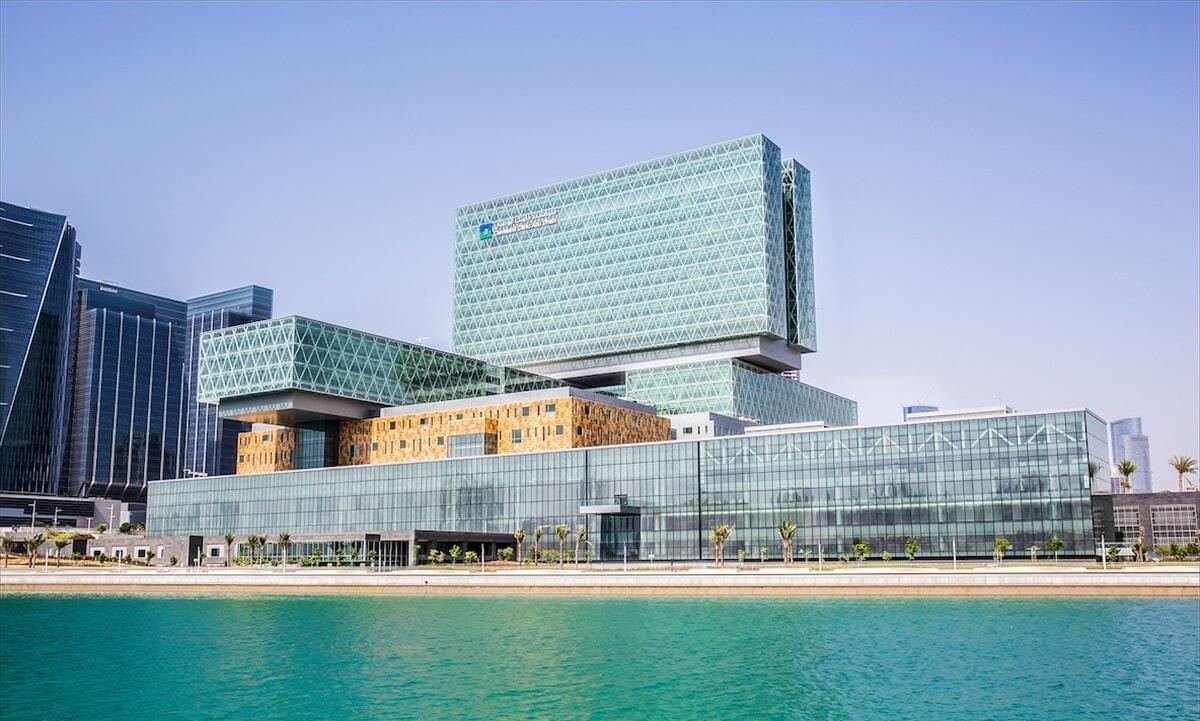

Digital simulations guided the optimization of building orientation and circulation routes, improving staff workflow and patient accessibility across departments.
4. Karolinska University Hospital, Sweden
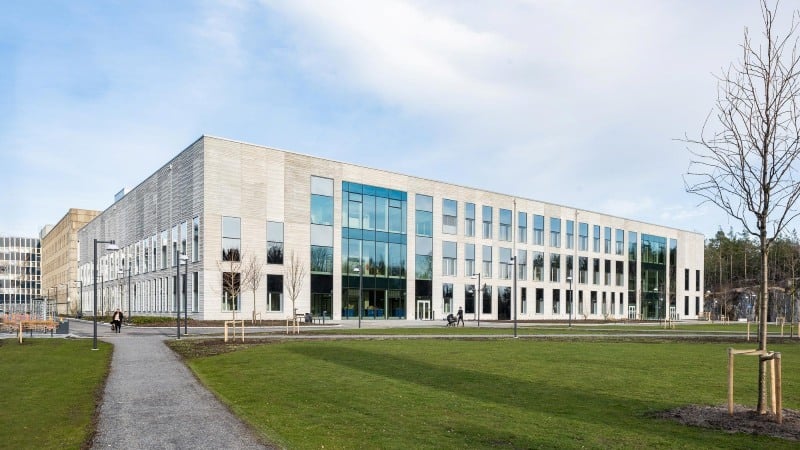

Data-driven modeling was used to refine infection control layouts and optimize operational efficiency across multiple specialized medical units.
5. Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital, California
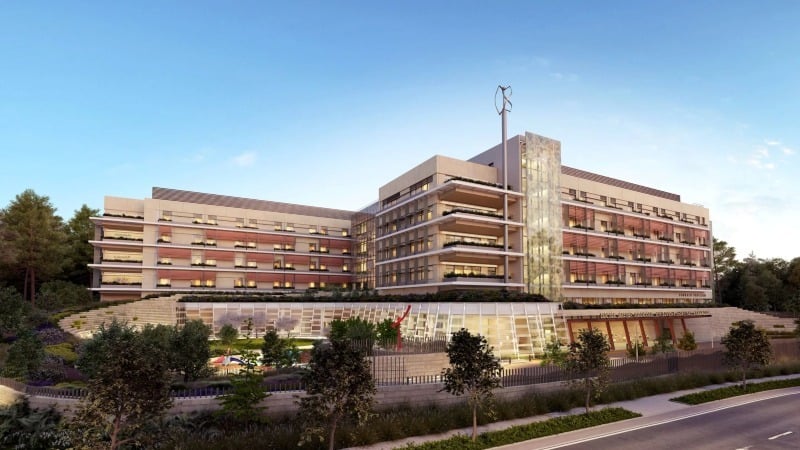

Computational analysis enhanced patient visibility, natural lighting, and movement efficiency, resulting in a warm, responsive healing environment.
These projects show how computational methods shape hospital building plan design that merges technology with human-centered care.
Learn Computational Design!
As computational tools become integral to healthcare architecture, professionals need advanced skills to apply them effectively. Transform how you design and think with Novatr’s Master in Computational Design course, a hands-on program built to help architects and designers future-proof their careers. Through expert-led training, you’ll learn how to combine creativity with technology to solve complex design challenges.
Here’s what you’ll learn in detail:
- 5 powerful industry tools – Grasshopper, Rhino 3D, Flux.ai, ComfyUI, and D5 Render.
- Master popular plugins like Paneling Tools, DeCoding Spaces, Anemone, Galapagos, Wallacei, LunchBox, Open Nest, and Horster Animation to create smarter, faster design workflows.
- Build parametric and generative design workflows used by top global firms.
- Automate repetitive tasks and explore AI-driven creativity to produce high-quality renders for presentations.
- Develop a professional computational design portfolio showcasing project-based learning.
- Earn dual certification from Novatr and NSDC (National Skill Development Corporation) and step confidently into the world of future-ready architecture and design.
Disclaimer: Course details, including curriculum, duration, fees, and related information, are for informational purposes only and may change at the company’s discretion without prior notice. Please visit the official course page or contact our admissions team for the latest updates.
Conclusion
As healthcare infrastructure becomes more complex, computational methods are proving essential for achieving efficient, patient-centered outcomes. From hospital layout optimization to sustainable planning, computational tools enable architects to design smarter, safer, and more adaptive spaces.
To build the skills needed for the current shift, upskill with the Master Computational Design course by Novatr, which offers a practical way to strengthen your understanding of computational workflows and real-world design efficiency.
Visit our resource page to get started and receive expert guidance on advancing your career.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Is computational design suitable for labs and research facilities?
Yes, computational design supports efficient lab layouts by analyzing workflow, ventilation, and safety zones, leading to optimal performance and adaptability.
2. How does computational design improve hospital and lab layouts?
It uses data simulation to refine the layout of a hospital, enhancing accessibility, energy use, and staff efficiency through precise spatial analysis.
3. What skills do architects need to apply computational design in healthcare?
Architects should understand parametric healthcare design, data modeling, and visualization tools to generate optimized outcomes for healthcare projects.
4. What is computational design in healthcare architecture?
It’s a data-driven design approach that enhances hospital optimization architecture through automation, simulation, and performance-based modeling.
5. What are the main challenges in healthcare facility design?
Balancing patient needs, compliance standards, and sustainability while ensuring flexibility and efficiency across complex healthcare systems.
Was this content helpful to you



.jpg)