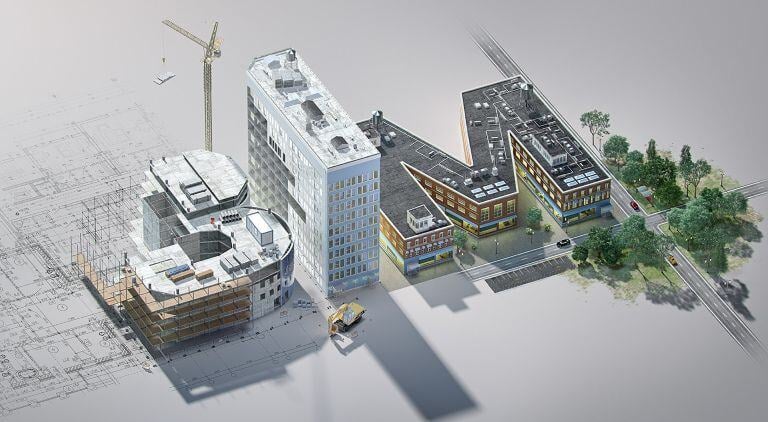

The world of AEC is changing faster than ever.
Wondering what the centre of this shake-up is?
Building Information Modelling.
But what is BIM Technology? BIM (Building Information Modelling) is a holistic approach used to design, document, and manage AEC projects. It is helping professionals to work remotely with improved project management and execution.
But how does that go about?
BIM uses 3D models as a central storage for data, which helps in planning, designing, constructing, and managing infrastructure.
It’s the foundational building block for the future of the AEC industry, driving the shift toward digital tools and methods across all stages.
Upcoming BIM Industry Trends
The Building Information Modeling (BIM) landscape is changing quickly as new technologies and ways of working are now changing how AEC professionals get their work done. Therefore, here are some of the more monumental changes in the BIM industry trends that are moving the industry forward to success.
Cloud-Based BIM Platforms
The adoption of BIM has shifted from a niche technology to a mainstream practice. One powerful trend in the BIM industry is the adoption of cloud-based BIM platforms, which promote collaboration between teams that may be physically dispersed, which allows team members to easily access the most current project information and facilitates more effective communication. This is particularly useful on large projects that have multiple stakeholders from various locations.
Data Analytics within BIM
The large amount of data included in BIM models can be analysed to mine useful information on project performance and inform decisions at all stages of the project lifecycle, while possibilities exist to potentially predict project risk and delay. Using data while engaging it with BIM is what creates a smooth and error-free decision-making process.
Sustainability
BIM tools are increasingly being used to analyse the impact that they have on building designs, optimise energy performance, and select sustainable sources. This allows AEC professionals to design and construct buildings that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient.

Integration of Emerging Technologies
Technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are being integrated with BIM and creating connectivity referred to as smart buildings, automation, predictive maintenance and so on
Looking ahead, several exciting BIM industry trends will further shape the AEC sector, few being:
- Stronger AI Integration (Autodesk): Anticipate that Autodesk will introduce more AI-powered capabilities into its platforms, including generative design optimization, tasks currently performed manually (clash detection, drawing generation, quantity take-offs), and predictive analytics. Learn Autodesk revit with our online courses.
- Cloud-Based Collaboration and Data Management (Autodesk): Emphasize a more connected data environment that incorporates more enhanced Common Data Environments (CDEs) and interoperability between products and an "outcome-based BIM".
- Digital Twins and Asset Management (Autodesk): Greater adoption of Autodesk Tandem with tighter integration with design and construction platforms for creation and management of lifecycle data and integration of real-time data.
- Sustainability Focus (Autodesk): This is embedded in BIM platforms to optimise carbon emissions and energy consumption.
- Extended Reality (XR) (Autodesk): This is the continued integration of AR and VR software that are used for design visualisation, on-site collaboration, and immersive training.
- Digital Twins: Taking BIM industry trends to the next level, Digital Twins are virtual representations of physical assets and other processes. These go beyond static models by including real-time data from sensors and other sources. This allows for continuous monitoring, analysis, and optimisation of performance.
- Generative Design: It is an AI-supported process that applies algorithms to consider a tremendous range of design alternatives based on premeasured constraints and goals. Designers and engineers provide information for the process to execute, such as goals for building performance, site condition data, or cost requirements to generate several design options. This design process can facilitate novel and more efficient designs that may not have been explored through traditional methods.
- Offsite Manufacturing and Modular Construction: BIM plays an important role in aiding offsite manufacturing and modular construction practices. The detailed digital models allow precise fabrication of building components in controlled factory environments, which results in faster construction turn around time, reduced waste, and better quality control.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR are revolutionising how AEC professionals visualise and interact with BIM models. AR allows users to overlay digital information onto the real world, enabling on-site workers to view 3D models in context, access real-time data, and perform tasks with greater accuracy. VR provides immersive experiences, allowing stakeholders to virtually walk through a building design before it's even built, facilitating better understanding and communication.
- BIM for Infrastructure: While BIM has been widely adopted in the building sector, its application in infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, and tunnels is rapidly growing. BIM for Infrastructure offers similar benefits in terms of improved design coordination, cost control, and lifecycle management for these complex projects.
What’s Next for Architects, Civil Engineers, and MEP Engineers
These evolving BIM industry trends have significant implications for the roles and responsibilities of architects, civil engineers, and MEP engineers. Here’s how:

For Architects
The future of architecture will be intrinsically tied to BIM. Architects will need to go beyond designs that are simply visually appealing to explore alternative solutions via generative design tools, leverage BIM to conduct performance assessments (energy performance, daylighting), and collaborate with other disciplines within the BIM model to assist in a seamless workflow.
Architects will also need to get involved in defining what information is required from a BIM model, in addition to assuring quality and usability throughout the project life cycle. They will need to be proficient in using BIM software, paired with knowledge of data and management of data within a software tool set.
For Civil Engineers
BIM for infrastructure is changing the way civil engineers design and manage transportation networks, water systems, and other major projects. They will need to be proficient at creating and using 3D models for project tasks such as site analysis, earthwork calculations, bridge design, and utility coordination.
Moreover, they will need to understand how to incorporate various forms of geospatial data and other pertinent information into the BIM environment. As time progresses, being able to assess the performance of infrastructure assets with BIM data and contribute to the development of digital twins will become essential.
For MEP Engineers
BIM provides MEP engineers with never-before-seen before opportunities for coordination and collaboration. Working within a single model allows them to design advanced mechanical, electrical and plumbing systems with increased accuracy and efficiency, minimizing conflicts and maximizing performance.
Future MEP engineers will need to be proficient in using BIM software to route duct work and piping, lay out equipment and complete energy analysis. They will also need to understand how their designs fit into the architectural and structural models and how to utilize BIM data for the commissioning and lifecycle management of systems.
Conclusion
The evidence is clear: BIM is not going away; it is the very basis of a new era for the AEC industry. As more professionals and firms adopt BIM and as new BIM industry trends such as digital twins, generative design, and AR/VR become available, it marks a change in the way we design, build, and manage our built environment.
The future of the AEC industry will be intelligent, collaborative, and data-driven, and BIM is the key to unlocking the future. Professionals that take time to upskill in BIM and keep themselves apprised of trends in the developing BIM industry trends will put themselves in a position to excel in the new future of the AEC industry and create our world in more efficient, more sustainable, and more innovative ways. You need to get on board the BIM revolution now.
So, suppose this is something of interest to you, and you want to learn more about how BIM industry trends are changing the AEC landscape. In that case, you may want to learn about industry workflows and cutting-edge tools for more efficient construction processes with Novatr's BIM Professional Course for Civil Engineers, BIM for Architects, and BIM for MEP Engineers. Through a real-world industry project, you can gain knowledge of high-performance computational BIM and building analysis. Take advantage of opportunities for upskilling, professional certification, and limitless career options.
Take the next step in your career today! Explore Novatr’s Resource Page for the latest industry insights and updates.
Was this content helpful to you

TABLE OF CONTENTS




.png)
.png)
.png)