The Powerful Influence of Colonization in India: History and Architecture
Table of Contents
Throughout history, India has been a coveted piece of land for those seeking global domination. The country’s geographical location was advantageous for trade purposes. Additionally, India was resourceful in terms of manpower, minerals, and spices. So in light of the industrial revolution, European nations viewed the Indian subcontinent as a significant territory to fuel their dream of global supremacy. Consequently, many European countries made an attempt to imperialize India through colonization.
European Colonies in India
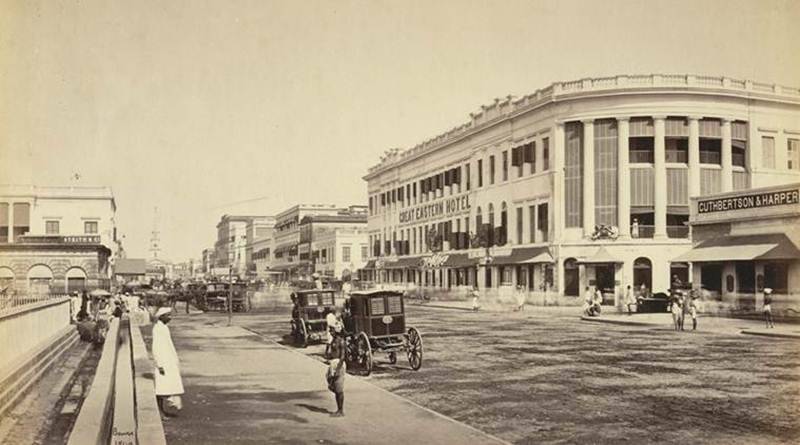

During the “age of discovery” from the 15th to 17th century, seafaring Europeans explored and colonized many Asian and African countries. Speaking of India, the Portuguese sailor Vasco da Gama was the first to reach Calicut (now Kozhikode) in 1498 which was a formidable port on the eastern coast. Following Portugal were the countries of the Netherlands, France, and Great Britain who battled with each other to claim their rule on Indian soil.
Portuguese India (1498-1961)
The Portuguese established a trading post in Goa in 1510, which was later turned into a colony. They also colonized other parts of India, including Daman, Diu, and Dadra and Nagar Haveli, which they ruled until 1961.
Dutch India (1605-1825)
The Dutch East India Company built trading posts in various parts of India, including Pulicat, Nagapattinam, Surat, and Chinsural. Dutch colonization of India came to an end due to British conquests of Dutch colonies.
French India (1668-1954)
The French East India Company established trading posts in India, including Pondicherry, Chandernagore, Yanam, Mahe, and Karikal, from 1668 onwards. French rule in India ended in 1954 when the territories were integrated into the Indian Union.
British India (1612-1947)
The British East India Company established its first factory in India at Surat in 1612. They established several presidencies, including Madras, Calcutta, and Bombay. In 1858, after the Indian Rebellion of 1857, the British Crown took direct control of India, which lasted until Indian independence in 1947.
Read more: What are Passive Design Strategies & Their Significance in Architecture - 2026
The Non-Architectural Impact of Colonization in India
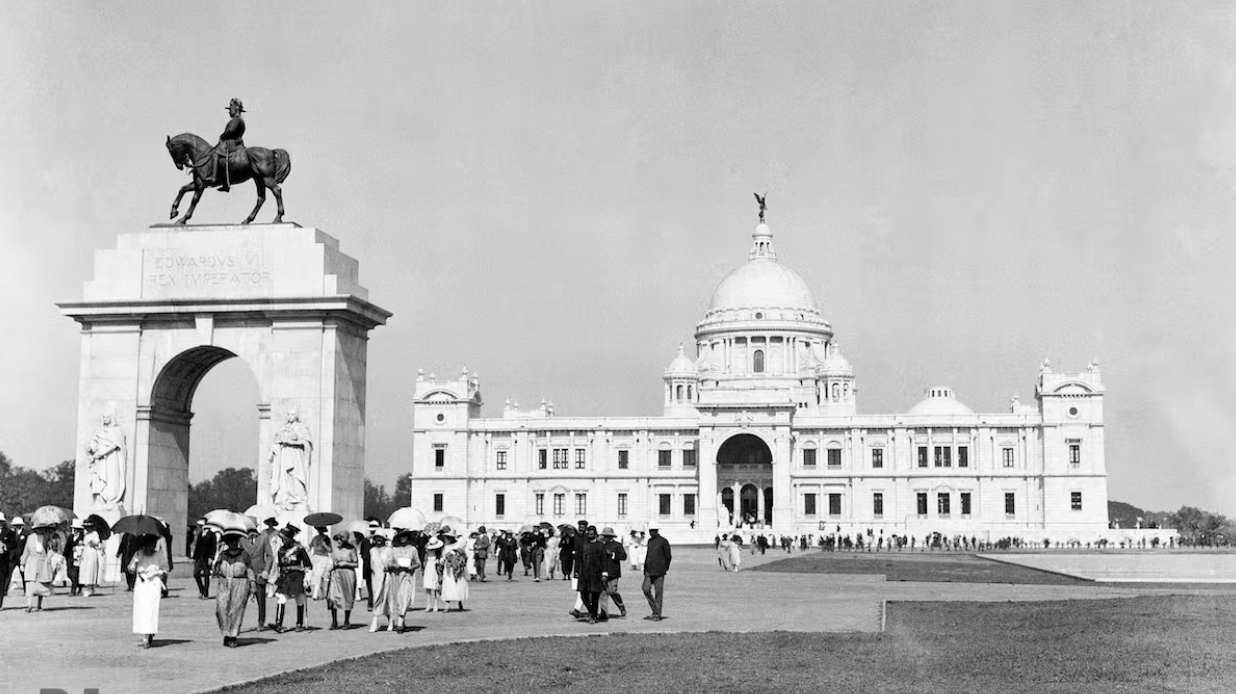

For better or worse, European colonization impacted the economic, socio-cultural, and political fabric of India. To begin with, colonization had a profound impact on India's economy due to the introduction of advanced machine-driven methods of production, transportation, and trade. This led to elimination of local businesses in the economy, as Indian artisans and craftsmen were unable to compete with the cheap goods imported from Europe.
Colonization of India also had significant social and cultural impacts on India as the Europeans brought with them new ideas about religion, education, and social organization. They also introduced modern forms of education, which emphasized Western knowledge and values that helped to create a new Indian elite that was familiar with European culture and ways of thinking.
Further, colonization had a profound impact on India's political system. The Europeans introduced new forms of administration and governance which centralized power in the hands of a colonial elite and disempowered local communities.
How Colonization Redefined the Architectural Landscape of India?
Prominent global architecture movements and styles, such as the Europeans, introduced new building styles, techniques, and materials that blended European and Indian elements, creating a unique architectural hybrid. They also introduced new forms of urban planning, which led to the construction of grand boulevards, public parks, and civic buildings that transformed the skylines of Indian cities. The grid-like planning paved the way for structured city planning.
The British, in particular, introduced railways, which connected different regions of India and facilitated the movement of people and goods. The telegraph was introduced as a new form of communication that helped to connect India with the rest of the world and facilitate the exchange of information.
Moreover, in terms of architectural styles, British colonial rule saw the rise of Indo-Saracenic architecture that fused Mughal, Rajput, and Gothic styles. Evident in landmarks like Mumbai’s Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus and Chennai’s Madras High Court.
Read more: The Ultimate Guide to Prominent Global Architectural Movements and Styles
The Contribution of Portuguese
1. Portuguese Architecture in India
The Portuguese brought with them their own architectural styles and techniques, which were influenced by the Manueline and Mannerist styles of architecture prevalent in Portugal at that time. Portuguese architecture in India, classic example of colonial buildings in India, was characterized by ornate facades, typically decorated with intricate carvings, moldings, and sculptures. Arches and columns were commonly used, giving the buildings a grand and imposing appearance. Balconies and verandahs were also popular features, providing shade and ventilation in the tropical climate of India.
The Portuguese also introduced new materials and building techniques to India. They were the first to use plaster and lime mortar to construct buildings, which allowed them to create intricate decorative elements such as cornices, moldings, and pilasters. They also introduced azulejos, (also known as glazed tiles) and terracotta, which were used to create colorful patterns and motifs on building facades.
Example of Portuguese Architecture in India
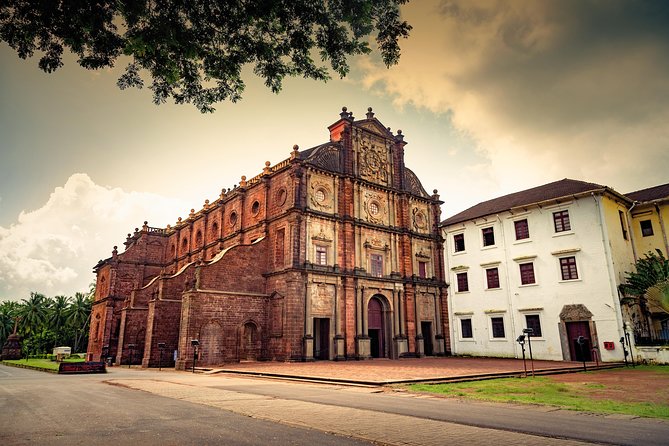

An excellent example of Portuguese colonial architecture in India is the Basilica of Bom Jesus in Old Goa. The basilica, a UNESCO World Heritage site, was built in the early 17th century and is home to the mortal remains of St. Francis Xavier. The building's facade is decorated with a mix of Renaissance and Baroque styles, with intricate carvings and sculptures. The use of limestone gives the building a distinctive white appearance, and the facade features a combination of arches and columns. The interior of the basilica is also decorated with paintings and frescoes, which add to its grandeur.
The Contribution of Dutch
1. Dutch Architecture in India
Colonial Dutch architecture in India is characterized by its functional and utilitarian style, with a focus on practicality rather than ornamentation. The buildings were typically made of brick and plaster, with simple and clean lines. The roofs were often steeply pitched and made of red tiles, which are a common feature in Dutch architecture. The use of gables, or triangular-shaped peaks at the top of the buildings, was also a distinctive feature of Dutch colonial architecture.
Dutch colonial buildings in India also incorporate local materials, such as teak wood, which was used for doors, windows, and furniture. The buildings were designed to withstand the hot and humid climate, with thick walls and high ceilings that provide natural ventilation. Verandahs and porches were common features, providing shade and a place to relax outdoors.
2. Example of Dutch Architecture in India
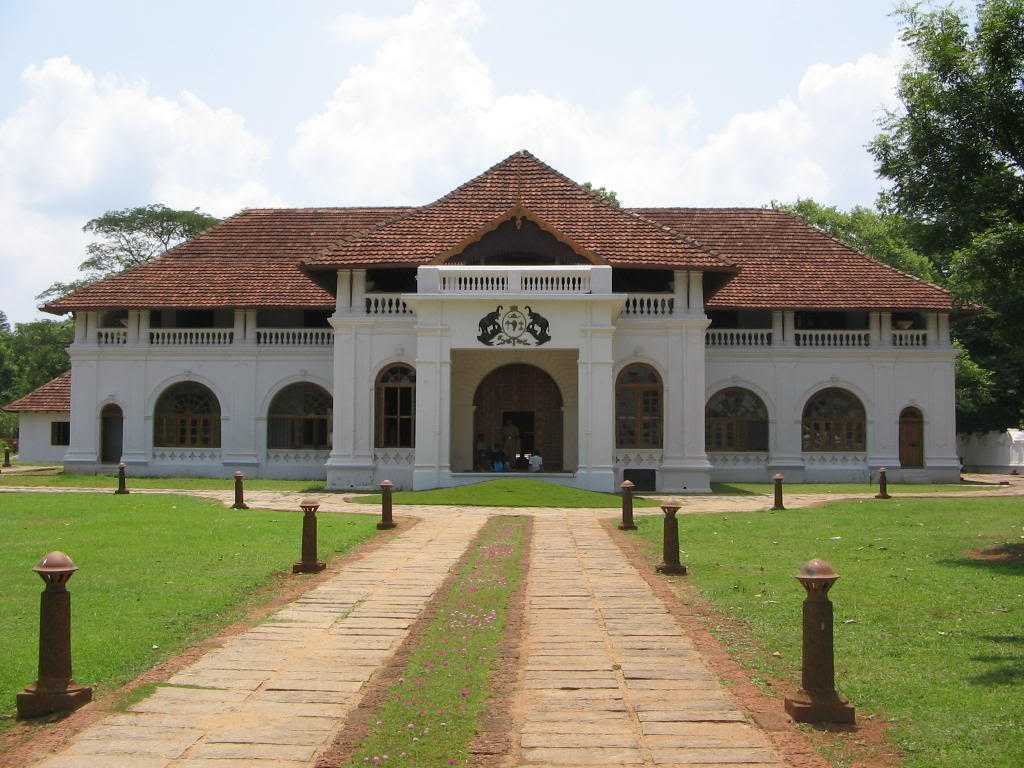

The Dutch Palace, also known as Mattancherry Palace in Kochi, Kerala, is an excellent example of Dutch architecture in India. The palace was built in the mid-16th century and is known for its unique blend of Dutch and traditional Kerala architectural styles. The palace's exterior is simple, with a white-washed facade and red-tiled roof, featuring a typical Dutch-style gable. The interior of the palace is decorated with intricate murals that depict scenes from the Ramayana and other Hindu legends. The palace is also home to a collection of weapons, utensils, and other artifacts that give visitors a glimpse into the region's history and culture.
Read more: What are Passive Design Strategies & Their Significance in Architecture - 2026
The Contribution of French
1. French Architecture in India
French architecture in India is known for its elegance, symmetry and attention to detail. The style is a fusion of French design elements and Indian motifs, resulting in a unique and distinctive aesthetic. One of the most notable features of French colonial architecture in India is the use of local materials such as limestone and granite, which were used to build impressive public buildings such as churches, municipal buildings and mansions.
Structures built by the French in India were designed to withstand the hot and humid climate of India and feature high ceilings, deep verandahs, and louvered windows that allow for natural ventilation. These buildings were also characterized by ornate and decorative elements, such as intricate carvings, detailed facades, and wrought iron balconies. These elements were often combined with local design elements such as chakras (projecting eaves) and jharokhas (balconies with overhanging eaves).
2. Example of French Architecture in India
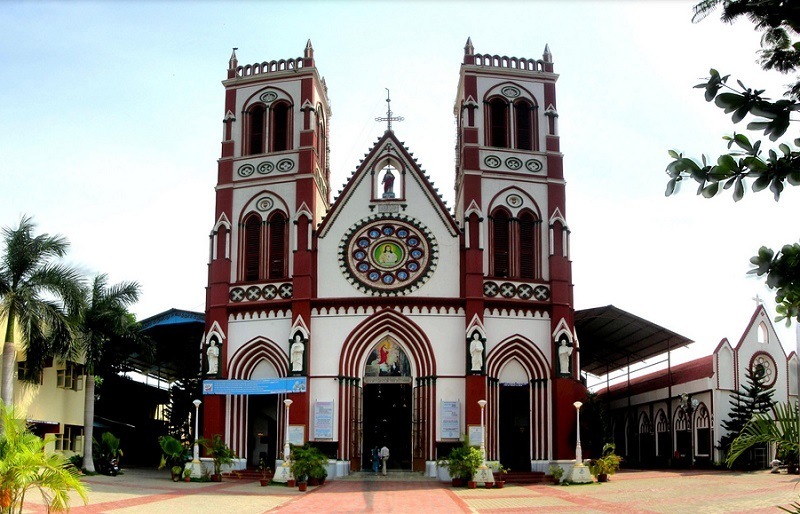

An iconic example of French colonial architecture in India is the Basilica of the Sacred Heart of Jesus, located in Pondicherry. The basilica is an impressive structure that blends Gothic and neo-Romanesque styles with Indian elements. Built in the early 20th century, the basilica features a distinctive white facade with two octagonal towers, along with a large central dome. The interior is equally impressive, with soaring ceilings, stained glass windows, and intricate carvings and paintings that adorn the walls and ceilings. A striking feature of the basilica is its ornate and decorative elements, which reflect a unique blend of French and Indian styles.
The Contribution of British
1. British Architecture in India
British architecture in India was heavily influenced by the neoclassical style, which featured symmetrical designs, columns, pediments, and domes. Many buildings were constructed using local materials like red sandstone and brick, which helped to keep the buildings cool in the hot Indian climate. Buildings designed by the British in India incorporated extensive gardens and landscaping, which were used to create a sense of tranquility and to provide relief from the heat.
They also incorporated Indian elements into their designs, resulting in a unique blend of British and Indian architectural styles. One of the most distinctive features of British architecture in India is the use of large verandahs or covered porches, which served as a social space for entertaining guests. British architects placed a great deal of emphasis on symmetry and proportion in their designs, resulting in buildings that are visually balanced and harmonious.
2. Example of British Architecture in India
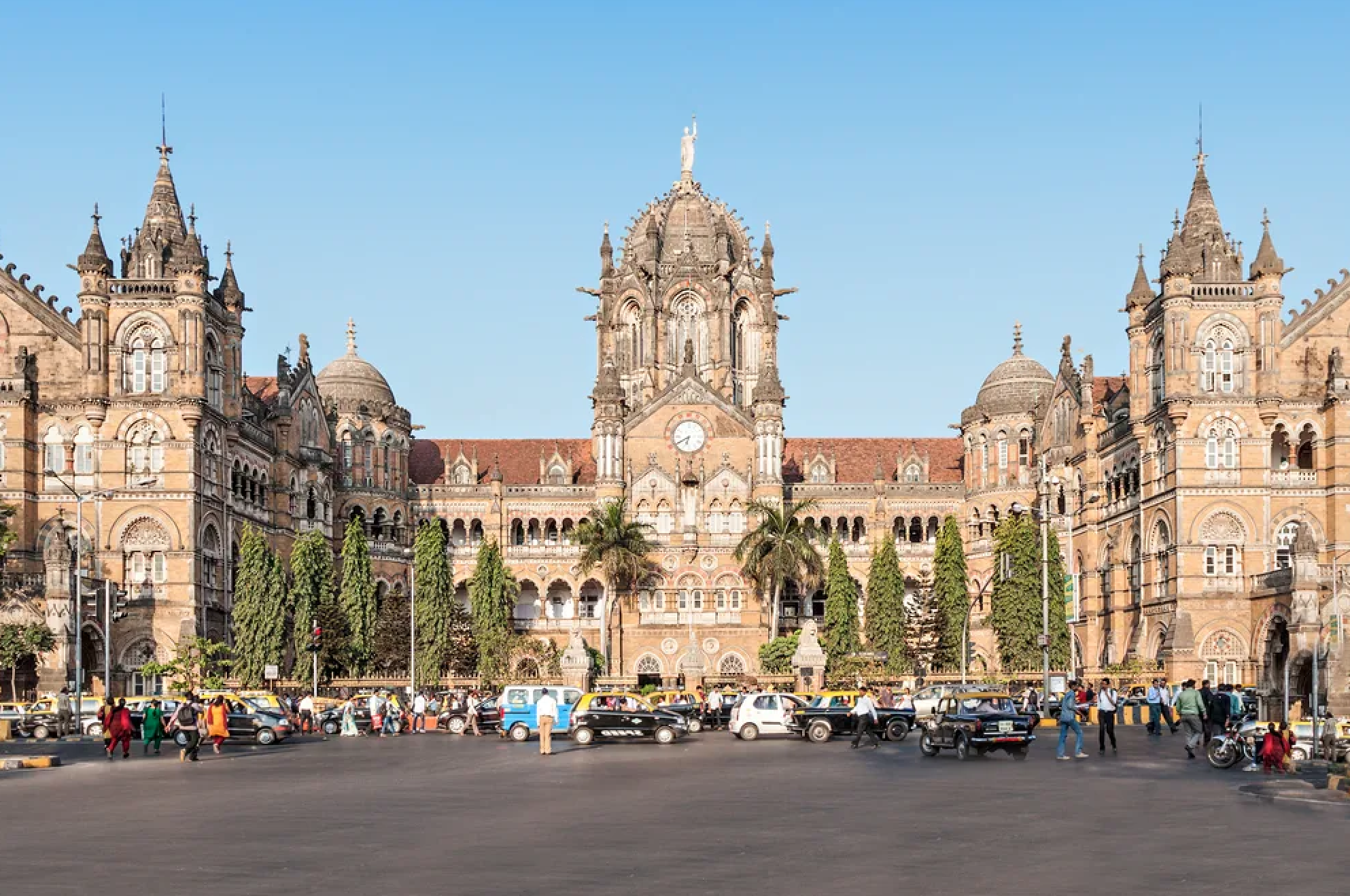

Victoria Terminus (now known as Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus), in Mumbai, Maharashtra is the most formidable example of colonial British architecture in India. Built in 1887, the building was originally constructed to serve as the headquarters of the Great Indian Peninsular Railway. The building was designed in the Victorian Gothic Revival style featuring intricate carvings, pointed arches, and stained glass windows. The building's most prominent feature is its large central dome, which is made of iron and weighs over 3,000 tons. The building interior is equally impressive, with a vaulted ceiling, a grand staircase, and a series of ornate carvings and sculptures.
In Conclusion
Despite the detrimental impact of colonization on India, it has facilitated the country and its people with a deeper appreciation and understanding of global art and architecture. Colonial architecture in India serves as a testament to the country’s diverse history and its relationship with the West. Young architects can seek inspiration from colonial architectural styles and apply flexibility, versatility, and forward-thinking in their designs to create structures that stand the test of time.
Do you want to design architectural marvels like the ones mentioned in this blog? If yes, explore Mater Computational Design Course offered by Novatr. Learn computational theory, master advanced tools, and discover industry workflows to visualize and construct landmark structures with ease.
Explore the course today!

 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!


.png)

-1.png)




